(Press-News.org) Dr Julian Hiscox and Dr John Barr of the University's Faculty of Biological Sciences are working with the Health Protection Agency Porton (HPA) to build a bank of molecular signatures that will help identify the severity of virus infection from characteristic changes seen in cells. Currently the team is barcoding different strains of influenza virus and human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV) - a virus associated with the onset of asthma in young children.
"Diseases such as flu infect and hijack our cells, turning them into virus producing factories," says Dr Hiscox. "The infection causes the balance of proteins in a cell to change - some proteins are overproduced and others suppressed. Which proteins are affected and by how much varies depending on the type of virus, allowing us to identify a unique barcode of disease for each."
The research, published today (14 May) in Proteomics, investigates changes in lung cells infected with swine flu from the 2009 outbreak compared with seasonal flu. The team used a labelling technique called SILAC to measure and compare thousands of different proteins in a sample.
This technique was used alongside mass spectrometry to identify the proteins most affected by viral infection and used these as molecular signatures to provide the 'barcode' of disease. The paper reports how several processes in the cell were affected by the virus, with most changes seen in proteins involved in cell replication.
"Swine flu affects the lungs in a similar way to seasonal flu and this was reflected in the barcodes we found for each," explains Dr Barr. "Using this test might have been a way to identify how lethal the 2009 swine flu pandemic was going to be, lessening worldwide panic.
"Our next step is to test more lethal strains of flu, such as bird flu, to see how the barcodes differ. Flu virus frequently mutates, resulting in new strains which may be life-threatening and become pandemic. If we can test new strains using our method, we can determine their potential impact on health by comparing their barcode of disease to those of viruses already studied."
The group from Leeds has already barcoded two types of HRSV which can cause severe respiratory disease in young children. Co-author Professor Miles Carroll of HPA Porton says: "We have focused our work on common respiratory viruses, such as flu and HRSV, but this method could be applied to a wide variety of viruses, including tropical diseases that are prone to sudden outbreaks and can be lethal."
###The research was funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) and the Medical Research Council (MRC).
Virus 'barcodes' offer rapid detection of mutated strains
2012-05-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New type of retinal prosthesis could better restore sight to blind, Stanford study says
2012-05-14
STANFORD, Calif. — Using tiny solar-panel-like cells surgically placed underneath the retina, scientists at the Stanford University School of Medicine have devised a system that may someday restore sight to people who have lost vision because of certain types of degenerative eye diseases.
This device — a new type of retinal prosthesis — involves a specially designed pair of goggles, which are equipped with a miniature camera and a pocket PC that is designed to process the visual data stream. The resulting images would be displayed on a liquid crystal microdisplay embedded ...
Berkeley Lab scientists generate electricity from viruses
2012-05-14
Imagine charging your phone as you walk, thanks to a paper-thin generator embedded in the sole of your shoe. This futuristic scenario is now a little closer to reality. Scientists from the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have developed a way to generate power using harmless viruses that convert mechanical energy into electricity.
The scientists tested their approach by creating a generator that produces enough current to operate a small liquid-crystal display. It works by tapping a finger on a postage stamp-sized electrode ...
Wasted milk is a real drain on our resources, study shows
2012-05-14
Milk poured down Britain's kitchen sinks each year creates a carbon footprint equivalent to thousands of car exhaust emissions, research shows.
Scientists say the 360,000 tonnes of milk wasted in the UK each year creates greenhouse gas emissions equivalent to 100,000 tonnes of CO2. The study by the University of Edinburgh says this is the same as is emitted by about 20,000 cars annually.
The research identifies ways that consumers could also help curb greenhouse gas emissions – by reducing the amount of food they buy, serve and waste. They also suggest the food industry ...
Reducing post-traumatic stress after ICU
2012-05-14
Women are more likely to suffer post-traumatic stress than men after leaving an intensive care unit (ICU), finds a new study published in BioMed Central's open access journal Critical Care. However, psychological and physical 'follow-up' can reduce both this and post-ICU depression.
Patients in the ICU often suffer post-traumatic stress, anxiety, or depression due, not only to the illness or trauma that put them there, but to the very nature of the ICU and life-saving treatment. As a result, follow-up schemes have been put in to place to help alleviate these psychological ...
BGI reports the completed sequence of foxtail millet genome
2012-05-14
May 13, 2012, Shenzhen, China – BGI, the world's largest genomics organization, in cooperation with Zhangjiakou Academy of Agricultural Science, has completed the genome sequence and analysis of foxtail millet (Setaria italica), the second-most widely planted species of millet. This study provides an invaluable resource for the study and genetic improvement of foxtail millet and millet crops at a genome-wide level. Results of the latest study were published online today in Nature Biotechnology.
Foxtail millet is an important cereal crop providing food and feed in semi-arid ...
Researchers map path to quantum electronic devices
2012-05-14
DURHAM, N.C. – A team of Duke University engineers has created a master "ingredient list" describing the properties of more than 2,000 compounds that might be combined to create the next generation of quantum electronics devices.
The goal is topological insulators (TI), man-made crystals that are able to conduct electrical current on their surfaces, while acting as insulators throughout the interior of the crystal. Discovering TIs has become of great interest to scientists, but because of the lack of a rational blueprint for creating them, researchers have had to rely ...
Americans support national clean-energy standard
2012-05-14
The average U.S. citizen is willing to pay 13 percent more for electricity in support of a national clean-energy standard (NCES), according to Yale and Harvard researchers in Nature Climate Change.
Americans, on average, are willing to pay $162 per year in higher electricity bills to support a national standard requiring that 80 percent of the energy be "clean," or not derived from fossil fuels. Support was lower for a national standard among nonwhites, older individuals and Republicans.
In addition, the results suggest that the Obama Administration's proposal for ...
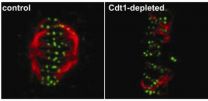
DNA replication protein also has a role in mitosis, cancer
2012-05-14
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – The foundation of biological inheritance is DNA replication – a tightly coordinated process in which DNA is simultaneously copied at hundreds of thousands of different sites across the genome. If that copying mechanism doesn't work as it should, the result could be cells with missing or extra genetic material, a hallmark of the genomic instability seen in most birth defects and cancers.
University of North Carolina School of Medicine scientists have discovered that a protein known as Cdt1, which is required for DNA replication, also plays an important ...
Time, place and how wood is used are factors in carbon emissions from deforestation
2012-05-14
A new study from the University of California, Davis, provides a deeper understanding of the complex global impacts of deforestation on greenhouse gas emissions.
The study, published May 13 in the advance online edition of the journal Nature Climate Change, reports that the volume of greenhouse gas released when a forest is cleared depends on how the trees will be used and in which part of the world the trees are grown.
When trees are felled to create solid wood products, such as lumber for housing, that wood retains much of its carbon for decades, the researchers ...
New study discovers powerful function of single protein that controls neurotransmission
2012-05-14
NEW YORK (May 13, 2012) -- Scientists at Weill Cornell Medical College have discovered that the single protein -- alpha 2 delta -- exerts a spigot-like function, controlling the volume of neurotransmitters and other chemicals that flow between the synapses of brain neurons. The study, published online in Nature, shows how brain cells talk to each other through these signals, relaying thoughts, feelings and action, and this powerful molecule plays a crucial role in regulating effective communication.
In the study, the investigators also suggest how the widely used pain ...