(Press-News.org) Researchers at Warwick Medical School have discovered a way of identifying which women are most at risk of postnatal depression (PND) by checking for specific genetic variants. The findings could lead to the development of a simple, accurate blood test which checks for the likelihood of developing the condition.
Presenting the research to the International Congress of Endocrinology/European Congress of Endocrinology, Professor Dimitris Grammatopoulos, Professor of Molecular Medicine at the University of Warwick, said that approximately one in seven women who give birth suffer from PND, which normally starts around two weeks after childbirth.
He explained: "Current screening policies rely on the opportunistic finding of PND cases using tools such as the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Score (EPDS), but such tests cannot identify women at risk, ahead of them developing the condition."
The researchers assessed a group of 200 pregnant women for PND using the EPDS, once during their first visit to the ante-natal clinic, and again two to eight weeks after they had given birth. They found that the women who developed PND were more likely to have specific genetic variants of the bcl1 and rs242939 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)[2] of the glucocorticoid receptor and the corticotrophin-releasing hormone receptor-1 genes, respectively.
These receptors control the activity of the hypothalamo-pituitary adrenal (HPA) axis - an endocrine system that is activated in response to stress. The hypothalamus is part of the brain that monitors many aspects of the state of the body's systems and is closely linked with the pituitary gland, which releases a number of hormones into the blood stream that control vital body functions.
The finding appears to show that postnatal depression is a specific subgroup of depression with a distinct genetic element which means that some women are genetically more reactive to the environmental factors which trigger depression.
"Although we knew already that there was an association of the HPA axis with depression, ours is the first study to show a link between specific elements of this pathway and the particular case of PND," said Professor Grammatopoulos.
"We now intend to conduct further research on other genetic variants of the HPA axis in a larger, multi-centre study involving women from Coventry, Birmingham, and London.
"We think that we have made an important step forward in characterising the prospective risks and are therefore paving the way for timely, appropriate medical treatment for women who are likely to develop PND."
PND is a serious condition, the researchers say, and quite different from the 'baby blues', which is milder and shorter-lived. Symptoms include sadness, changes in eating and sleeping patterns, crying episodes, reduced libido, anxiety and irritability.
Effects on children can be significant; for example, depressed mothers are less likely to be affectionate towards and to play with their children and they may use less 'baby talk' which is designed to engage the child's attention. This may lead to learning and emotional difficulties for the children in later life.
Although it may seem evident that PND is caused by some kind of hormonal upheaval but the role of the HPA axis in this form of depression has not been proved until now.
"We believe that we have made a discovery with important clinical and social implications. If we can identify women likely to suffer from PND in advance so that they can be treated appropriately and at an early stage, we will have improved the lives not just of the parents, but also of their children," Professor Grammatopoulos concluded.
INFORMATION:
Background information:
The Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale is a 10-item self-reported questionnaire developed to identify women with PND. Items of the scale correspond to various symptoms of clinical depression, and overall assessment is done by the total score of the sum of the ten items.
The research was funded by the Departments of Pathology and Obstetrics, University Hospital Coventry and Warwickshire departmental funds, Warwick Medical School and by the Robert Gaddie Memorial Fund.
The joint 15th International Congress of Endocrinology/14th European Congress of Endocrinology, Europe's biggest scientific meeting on hormones, took place in Florence, Italy on 5-9 May 2012. For the full programme, see www.ice-ece2012.com .
For further information, please contact her Kate Cox, Communications Manager, Warwick Medical School on +44 (0)2476 574255/150483, m: +44(0)7920 531221 or kate.cox@warwick.ac.uk.
END
Genes play a greater role in forming character traits - such as self-control, decision making or sociability - than was previously thought, new research suggests.
A study of more than 800 sets of twins found that genetics were more influential in shaping key traits than a person's home environment and surroundings.
Psychologists at the University of Edinburgh who carried out the study, say that genetically influenced characteristics could well be the key to how successful a person is in life.
The study of twins in the US – most aged 50 and over– used a series of ...
Across the United States, approximately 747,408 individuals are listed on sex offender registries. Contrary to popular belief, they are an incredibly heterogeneous group; they come from all walks of life, represent varied demographics and have criminal histories that range from a single relatively minor infraction to a laundry list of antisocial behavior.
Despite their diversity, sex offenders are treated much the same: they are listed on registries for all the public to see, they are prohibited from holding certain jobs or living in particular areas, they are often ...
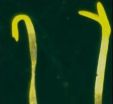
"The plants developed in the dark as if they were in light," says the Director of the studies Tilman Lamparter, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT). The seeds and seedlings of thale cress were fed with a synthetic substance named "15Ea-phycocyanobilin". In the plant cell, this substance replaces the natural, photoactive component of the photoreceptor, the "phytochromobilin". Incorporation of 15Ea-PCB activates the photoreceptor and the plant is made believe it is exposed to light. In spite of the darkness, model plants germinate and grow similar to a control group exposed ...
In Illinois, a judgment creditor can obtain a court order to put in place a wage deduction from your earnings. This is commonly referred to as garnishment. This wage deduction takes a percentage of your wages, before you ever see them, and transfers them to your creditor.
Wage Garnishment
This wage deduction, or garnishment, can only be done where there is a valid judgment debt. In Illinois, the creditor then files an action in court to deduct the lesser of either 15 percent of your gross wages for a week or the amount by which disposable weekly earnings exceed 45 ...
While experiments in the 1970s using electrical brain stimulation identified areas of the brain responsible for starting locomotion, the precise neuron-by-neuron pathway has not been described in any vertebrate – until now.
To find this pathway, Dr Edgar Buhl and colleagues in Bristol's School of Biological Sciences studied a small, simple vertebrate: the Xenopus frog tadpole.
They found that the pathway to initiate swimming consists of just four types of neurons. By touching skin on the head of the tadpole and applying cellular neurophysiology and anatomy techniques, ...
Jerusalem, May 16, 2012 – A method developed at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem for training blind persons to "see" through the use of a sensory substitution device (SSD) has enabled those using the system to actually "read" an eye chart with letter sizes smaller than those used in determining the international standard for blindness.
The eight congenitally blind participants in the Hebrew University test group passed the conventional eye-exam of the Snellen acuity test, technically surpassing the world-agreed criterion of the World Health Organization (WHO) for ...
Chapter 11 bankruptcy is designed to offer relief to business corporations and partnerships that have become overwhelmed by debt. In some cases, Chapter 11 bankruptcy can also be helpful to high-income individuals who do not qualify for relief under Chapter 7 or Chapter 13.
Chapter 11 was developed more than 30 years ago as a way for filers to reorganize their financial affairs and pay creditors back over time. Recently, though, a number of prominent bankruptcy lawyers have begun to voice concerns that the current Chapter 11 system may not be well-suited to the realities ...
In a study about to be published in EPJ E¹, French physicists from the Curie Institute in Paris have demonstrated that the behaviour of a thin layer of cells in contact with an unfavourable substrate is akin to that of thin fluid or elastic films. Understanding the mechanism by which a thin layer of cells splits into disjointed patches, thus breaking the layer's structural integrity, bears great significance because the human tissue, or epithelium, covering organs can only fulfil its role if there are no holes or gaps between the cells.
Thanks to the analogy between the ...
In what the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) refers to as a "clerical error," the notice of proposed rules concerning sleep apnea of truck drivers was released and withdrawn on the same day in April.
The request for public comments details some of the factors the FMCSA may consider for a final rulemaking on the issue of drivers who suffer from obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a respiratory dysfunction where breathing temporarily stops, interfering with the exchange of oxygen in the lungs. The Mayo ...
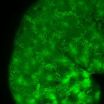
Microscopes provide valuable insights in the structure and dynamics of cells, in particular when the latter remain in their natural environment. However, this is very difficult especially for higher organisms. Researchers of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT), the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research, Mainz, and the American National Institutes of Health (NIH) have now developed a new method to visualize cell structures of an eighth of a micrometer in size in living fish larvae. It is published in the Nature Methods magazine (DOI:10.1038/nmeth.2025). "The zebrafish ...