Production of chemicals without petroleum
Systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms allows efficient production of natural and non-natural chemicals from renewable non-food biomass
2012-05-21
(Press-News.org) In our everyday life, we use gasoline, diesel, plastics, rubbers, and numerous chemicals that are derived from fossil oil through petrochemical refinery processes. However, this is not sustainable due to the limited nature of fossil resources. Furthermore, our world is facing problems associated with climate change and other environmental problems due to the increasing use of fossil resources. One solution to address above problems is the use of renewable non-food biomass for the production of chemicals, fuels and materials through biorefineries. Microorganisms are used as biocatalysts for converting biomass to the products of interest. However, when microorganisms are isolated from nature, their efficiencies of producing our desired chemicals and materials are rather low. Metabolic engineering is thus performed to improve cellular characteristics to desired levels. Over the last decade, much advances have been made in systems biology that allows system-wide characterization of cellular networks, both qualitatively and quantitatively, followed by whole-cell level engineering based on these findings. Furthermore, rapid advances in synthetic biology allow design and synthesis of fine controlled metabolic and gene regulatory circuits. The strategies and methods of systems biology and synthetic biology are rapidly integrated with metabolic engineering, thus resulting in "systems metabolic engineering".
In the paper published online in Nature Chemical Biology on May 17, Professor Sang Yup Lee and his colleagues at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Daejeon, Korea present new general strategies of systems metabolic engineering for developing microorganisms for the production of natural and non-natural chemicals from renewable biomass. They first classified the chemicals to be produced into four categories based on whether they have thus far been identified to exist in nature (natural vs. nonnatural) and whether they can be produced by inherent pathways of microorganisms (inherent, noninherent, or created): natural-inherent, natural-noninherent, non-natural-noninherent, and non-natural-created ones. General strategies for systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms for the production of these chemicals using various tools and methods based on omics, genome-scale metabolic modeling and simulation, evolutionary engineering, synthetic biology are suggested with relevant examples. For the production of non-natural chemicals, strategies for the construction of synthetic metabolic pathways are also suggested. Having collected diverse tools and methods for systems metabolic engineering, authors also suggest how to use them and their possible limitations.
Professor Sang Yup Lee said "It is expected that increasing number of chemicals and materials will be produced through biorefineries. We are now equipped with new strategies for developing microbial strains that can produce our desired products at very high efficiencies, thus allowing cost competitiveness to those produced by petrochemical refineries."
Editor of Nature Chemical Biology, Dr. Catherine Goodman, said "It is exciting to see how quickly science is progressing in this field – ideas that used to be science fiction are taking shape in research labs and biorefineries. The article by Professor Lee and his colleagues not only highlights the most advanced techniques and strategies available, but offers critical advice to progress the field as a whole."
###
The works of Professor Lee have been supported by the Advanced Biomass Center and Intelligent Synthetic Biology Center of Global Frontier Program from the Korean Ministry of Education, Science and Technology through National Research Foundation.
Further Contacts:
Dr. Sang Yup Lee, Distinguished Professor and Dean, KAIST, Daejeon, Korea (leesy@kaist.ac.kr, +82-42-350-3930)
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2012-05-21
Athens, Ga. – Decades of research show people born into poverty are likely to continue to live that way as adults. But one University of Georgia researcher has found a way out—education.
Children reared in disadvantaged communities and poor families earn less money and experience more health problems as adults than do children raised without adversity, according to Kandauda Wickrama, a professor of human development and life science in the UGA College of Family and Consumer Sciences.
"Early adverse life experiences, such as community or family poverty, have a detrimental ...
2012-05-21
Montreal, May 18, 2012 – The surgical team at the Montreal Heart Institute (MHI) achieved a North American surgical milestone on May 1st with a sutureless aortic valve replacement through a thoracic incision just five centimetres long. The two patients in their seventies who underwent this innovative procedure, which was performed by cardiac surgeons Denis Bouchard and Michel Carrier, were doing well only one week after their operations.
A novel combination
"This innovative combination of implanting a Perceval™ S valve through a minimally invasive thoracotomy signals ...
2012-05-21
It was used to help Apollo astronauts navigate in space, and has since been applied to problems as diverse as economics and weather forecasting, but Harvard scientists are now using a powerful statistical tool to not only track sea level rise over time, but to determine where the water causing the rise is coming from.
As described in an April 23 paper in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), graduate students Eric Morrow and Carling Hay demonstrate the use of a statistical tool called a Kalman smoother to identify "sea level fingerprints" – tell-tale ...
2012-05-21
Vacuum tubes have been retro for decades. They almost completely disappeared from the electronics scene when consumers exchanged their old cathode ray tube monitors for flat screen TVs. Their replacement – the semiconductor – is generally the cheaper, lighter, more efficient, and easier to manufacture of the two technologies. But vacuum tubes are more robust in high-radiation environments such as outer space. And since electrons travel faster in a vacuum than through a semiconductor, vacuum tubes are an intrinsically better medium for electricity.
An international team ...
2012-05-21
Quantum physics promises faster and more powerful computers, but quantum versions of basic logic functions are still needed to bring this technology to fruition. Researchers from the University of Cambridge and Toshiba Research Europe Ltd. have taken one step toward this goal by creating an all-semiconductor quantum logic gate, a controlled-NOT (CNOT) gate. They achieved this breakthrough by coaxing nanodots to emit single photons of light on demand.
"The ability to produce a photon in a very precise state is of central importance," said Matthew Pooley of Cambridge ...
2012-05-21
Ed Randall's Fans for the Cure (www.fans4thecure.org) today launched its "Stadium of Champions" membership drive, designed to increase awareness of prostate cancer treatment, prevention and detection. The Stadium of Champions is the charity's VIP membership club. It offers advocates an easy opportunity to support the charity, while also enjoying unique benefits reserved exclusively for these Champions. Buy your tickets today before the stadium is sold out.
"Every prostate cancer survivor, loved ones who supported the men in their life fighting prostate ...
2012-05-21
Cell cultures need glucose for energy, but too much sugar can create a diabetic-like environment in which cell proteins undergo unwanted structural changes. Standard methods to monitor glucose levels require invasive and time-consuming handling of the cell culture. A team of engineers at the National University of Singapore and Singapore's Institute of Microelectronics is developing an alternative approach that takes advantage of new microfluidic techniques. In a continuous and controlled process, the researchers created small droplets of polymer that encapsulated pairs ...
2012-05-21
Urologic conditions like urinary tract infections, kidney stones, and prostate cancer are a major economic burden on Americans, resulting in health care costs of close to $40 billion annually, according to a newly released national report that charts the demographic and economic impact of urologic diseases in the U.S.
Urologic Diseases in America (UDA), last published in 2007, has been revised and updated for 2012 and includes a wealth of new, detailed information on the utilization of resources and the costs associated with urologic diseases among men, women and children. ...
2012-05-21
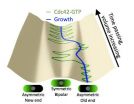
VIDEO:
This video shows active Cdc42 oscillating through yeast cells.
Click here for more information.
A collaboration between Lehigh University physicists and University of Miami biologists addresses an important fundamental question in basic cell biology: How do living cells figure out when and where to grow?
The teams of Assistant Professor Dimitrios Vavylonis and Associate Professor Fulvia Verde discovered that protein Cdc42 oscillates throughout yeast cells, precipitating ...
2012-05-21
Now reaching an unheard of total of 199 awards for TV commercial production, the world's first internet-based discount TV advertising agency, Cheap TV Spots, is proud to claim the Gold Remi, presented by the prestigious Worldfest competition of 2012.
Worldfest is the one of the longest running international film and TV festivals in North America, and Cheap-TV-Spots.com is the longest-operating producer of original, discount-priced TV commercials for the U.S. and international markets.
Cheap TV Spots offers two rare advantages for advertisers. One, the experienced ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Production of chemicals without petroleum
Systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms allows efficient production of natural and non-natural chemicals from renewable non-food biomass