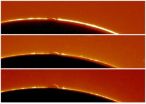
(Press-News.org) When Venus transits the sun on June 5th and 6th, an armada of spacecraft and ground-based telescopes will be on the lookout for something elusive and, until recently, unexpected: The Arc of Venus.
"I was flabbergasted when I first saw it during the 2004 transit," recalls astronomy professor Jay Pasachoff of Williams College. "A bright, glowing rim appeared around the edge of Venus soon after it began to move into the sun."
For a brief instant, the planet had turned into a "ring of fire."
Researchers now understand what happened. Backlit by the sun, Venus's atmosphere refracted sunlight passing through layers of air above the planet's cloudtops, creating an arc of light that was visible in backyard telescopes and spacecraft alike.
It turns out, researchers can learn a lot about Venus by observing the arc. Indeed, it touches on some of the deepest mysteries of the second planet.
"We do not understand why our sister planet's atmosphere evolved to be so different than Earth's," explains planetary scientist Thomas Widemann of the Observatoire de Paris.
Earth and Venus are similar distances from the sun, are made of the same basic materials, and are almost perfect twins in terms of size. Yet the two planets are wrapped in stunningly dissimilar blankets of air. Venus's atmosphere is almost 100 times more massive than Earth's and consists mainly of CO2, a greenhouse gas that raises the surface temperature to almost 900°F. Clouds of sulfuric acid tower 14 miles high and whip around the planet as fast as 220 mph. A human being transported to this hellish environment would be crushed, suffocate, desiccate, and possibly ignite.
For the most part, planetary scientists have no idea how Venus turned out this way.
"Our models and tools cannot fully explain Venus, which means we lack the tools for understanding our own planet," points out Widemann. "Caring about Venus is caring about ourselves."
One of the biggest mysteries of Venus is super-rotation. The whole atmosphere circles the planet in just four Earth days, much faster than the planet's spin period of 243 days. "The dynamics of super-rotation are still a puzzle despite a wealth of data from landmark missions such as NASA's Pioneer Venus, Russia's Venera and VEGA missions, NASA's Magellan and more recently ESA's Venus Express."
This is where the Arc of Venus comes in. The brightness of the arc reveals the temperature and density structure of Venus's middle atmosphere, or "mesosphere," where the sunlight is refracted. According to some models, the mesosphere is key to the physics of super-rotation. By analyzing the lightcurve of the arc, researchers can figure out the temperature and density of this critical layer from pole to pole.
When the arc appeared in 2004, the apparition took astronomers by surprise; as a result, their observations were not optimized to capture and analyze the fast-changing ring of light.
This time, however, they are ready. Together, Pasachoff and Widemann have organized a worldwide effort to monitor the phenomenon on June 5th, 2012. "We're going to observe the arc using 9 coronagraphs spaced around the world," says Pasachoff. "Observing sites include Haleakala, Big Bear, and Sacramento Peak. Japan's Hinode spacecraft and NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory will also be gathering data."
Pasachoff has some advice for amateur astronomers who wish to observe the arc. "The best times to look are ingress and egress--that is, when the disk of Venus is entering and exiting the sun. Ingress is between 22:09 and 22:27 UT on June 5th; egress occurs between 04:32 and 04:50 UT. Be sure your telescope is safely filtered. Both white light and H-alpha filters might possibly show the arc."
INFORMATION:
The mysterious arc of Venus
2012-06-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ill, older patients who rely on emergency room often live final days in hospital, study finds
2012-06-05
Half of adults over age 65 made at least one emergency department (ED) visit in the last month of life, in a study led by a physician at the San Francisco VA Medical Center (SFVAMC) and UCSF.
Three quarters of ED visits led to hospital admissions, and more than two-thirds of those admitted to the hospital died there.
In contrast, the 10 percent of study subjects who had enrolled in hospice care at least one month before death were much less likely to have made an ED visit or died in the hospital.
"For too many older Americans, the emergency department is a conduit ...
New in Lithosphere: Mars, Iraq, Canada, and the Spanish Pyrenees
2012-06-05
Boulder, Colo., USA – New Lithosphere science posted online 4 June 2012 includes a study of the Valles Marineris fault zone, Mars, and asks why such a trough system occurs there, when such structures on Earth are mainly associated with plate tectonics. Other papers discuss landslides in the Pyrenees; first evidence of a "missing" Cretaceous arc assemblage in the Iraqi segment of the Zagros orogenic belt; and new information on the age of the Okanagan Valley shear zone, Canada.
Abstracts are online at http://lithosphere.gsapubs.org/content/early/recent. Representatives ...
Orange County Sports Medicine Specialist Adds Online Forms
2012-06-05
California sports medicine specialist Dr. Ralph Venuto (http://www.drvenuto.com) recently added downloadable forms on his website, helping patients get the resources they need before their first office visit. The Medical History form, Patient Financial Agreement, Notice of Privacy Practices Receipt, and Patient Information Form for the practice are all now available online. Dr. Venuto believes that giving patients access to medical forms online is a step that helps his team become more efficient in patient care.
"Online medical forms have become a norm at the modern ...
Practical tool can 'take pulse' of blue-green algae status in lakes
2012-06-05
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Scientists have designed a screening tool that provides a fast, easy and relatively inexpensive way to predict levels of a specific toxin in lakes that are prone to blue-green algal blooms.
Blue-green algae is not your average pond scum - rather than consisting of plant-like organisms, blue-green algae actually are cyanobacteria, and some species are linked to the production and release of the toxin microcystin into the water. Human exposure to the toxin through drinking or recreational water contact can threaten public health by causing liver damage, ...
Post-stroke depression linked to functional brain impairment
2012-06-05
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Researchers studying stroke patients have found a strong association between impairments in a network of the brain involved in emotional regulation and the severity of post-stroke depression. Results of the study are published online in the journal Radiology.
"A third of patients surviving a stroke experience post-stroke depression (PSD)," said lead researcher Igor Sibon, M.D., Ph.D., professor of neurology at the University of Bordeaux in Bordeaux, France. "However, studies have failed to identify a link between lesions in the brain caused by ischemia ...
Webcast Gives Lawyers the Keys to Effective Uses of Social Media
2012-06-05
For attorneys, social media tools such as Facebook, Twitter and blogs are the new word-of-mouth advertising of the 21st century -- a powerful way for law firms to stand out online and engage with clients and prospects in a direct, immediate, and meaningful way.
A free one-hour webcast upcoming on Wednesday, June 13th, is designed for attorneys who want to learn more about social media, its relevance to attorneys, and why social media is the future of online client development for law firms.
Social Media: Fish Where the Fish Are, a FindLaw event co-hosted by Ohio ...
Higher taxes, smoke-free policies are reducing smoking in moms-to-be
2012-06-05
San Diego, CA, June 5, 2012 – It's estimated that almost 23% of women enter pregnancy as smokers and more than half continue to smoke during pregnancy, leading to excess healthcare costs at delivery and beyond. In one of the first studies to assess smoking bans and taxes on cigarettes, along with the level of tobacco control spending, researchers have found that state tobacco control policies can be effective in curbing smoking during pregnancy, and in preventing a return to smoking within four months on average, after delivery. The results were published online today ...
Philadelphia Personal Injury Attorney Dean Weitzman of MyPhillyLawyer Discusses SEPTA Crashes Resulting in Serious Injury to Philadelphia Residents
2012-06-05
During a recent segment on FOX 29, personal injury attorney Dean Weitzman of MyPhillyLawyer discussed how reckless bus drivers put countless lives in danger by ignoring traffic signals throughout Philadelphia. "Drivers need to understand and really appreciate that they have 50 souls in their hands every trip they take," commented Weitzman.
That number doesn't include other drivers and their passengers, pedestrians and cyclists who share the Philly roadways with SEPTA buses, SEPTA tandem buses, tour buses and trolley buses. SEPTA buses range from 40 to 60 feet ...
Sepsis outbreak at L.A. County dialysis center prompts public health investigation
2012-06-05
San Antonio, Texas, June 5, 2012 – Three patients with chronic kidney failure treated at a dialysis center in Los Angeles County, California contracted a bacterial infection in the blood (sepsis) caused by improper cleaning and disinfection of a reusable medical device called a dialyzer – an artificial kidney.
Described in a poster presented at the 39th Annual Educational Conference and International Meeting of the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology (APIC), the County of Los Angeles Department of Public Health, conducted an investigation ...
MRSA incidence reduced among elderly patients by 82 percent over nearly 3-year period
2012-06-05
San Antonio, Texas, June 5, 2012 – The introduction of daily bathing with disposable, germ-killing cloths resulted in a sustained, significant decrease in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) incidence at a Canadian geriatric facility, according to a poster presented at the 39th Annual Educational Conference and International Meeting of the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology (APIC).
Infection preventionists, working in the Acute Care Transition (ACT) unit at Baycrest, a geriatric healthcare system in Ontario, reduced the ...