(Press-News.org) This press release is available in German.
Finding new particles usually requires high energies – that is why huge accelerators have been built, which can accelerate particles to almost the speed of light. But there are other creative ways of finding new particles: At the Vienna University of Technology, scientists presented a method to prove the existence of hypothetical "axions". These axions could accumulate around a black hole and extract energy from it. This process could emit gravity waves, which could then be measured.
Axions are hypothetical particles with a very low mass. According to Einstein, mass is directly related to energy, and therefore very little energy is required to produce axions. "The existence of axions is not proven, but it is considered to be quite likely", says Daniel Grumiller. Together with Gabriela Mocanu he calculated at the Vienna University of Technology (Institute for Theoretical Physics), how axions could be detected.
Astronomically Large Particles
In quantum physics, every particle is described as a wave. The wavelength corresponds to the particle's energy. Heavy particles have small wavelengths, but the low-energy axions can have wavelengths of many kilometers. The results of Grumiller and Mocanu, based on works by Asmina Arvanitaki and Sergei Dubovsky (USA/Russia), show that axions can circle a black hole, similar to electrons circling the nucleus of an atom. Instead of the electromagnetic force, which ties the electrons and the nucleus together, it is the gravitational force which acts between the axions and the black hole.
The Boson-Cloud
However, there is a very important difference between electrons in an atom and axions around a black hole: Electrons are fermions – which means that two of them can never be in the same state. Axions on the other hand are bosons, many of them can occupy the same quantum state at the same time. They can create a "boson-cloud" surrounding the black hole. This cloud continuously sucks energy from the black hole and the number of axions in the cloud increases.
Sudden Collapse
Such a cloud is not necessarily stable. "Just like a loose pile of sand, which can suddenly slide, triggered by one single additional grain of sand, this boson cloud can suddenly collapse", says Daniel Grumiller. The exciting thing about such a collapse is that this "bose-nova" could be measured. This event would make space and time vibrate and emit gravity waves. Detectors for gravity waves have already been developed, in 2016 they are expected to reach an accuracy at which gravity waves should be unambiguously detected. The new calculations in Vienna show that these gravity waves can not only provide us with new insights about astronomy, they can also tell us more about new kinds of particles.
INFORMATION:
Black holes as particle detectors
Previously undiscovered particles could be detected as they accumulate around black holes say scientists at the Vienna University of Technology
2012-06-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New cerebellar ataxia gene identified in dogs
2012-06-19
Researchers at the University of Helsinki and the Folkhälsan Research Center, Finland, have identified the genetic cause of early-onset progressive cerebellar degeneration the Finnish Hound dog breed. The study, led by Professor Hannes Lohi, revealed a new disease mechanism in cerebellar degeneration. A mutation was identified in the SEL1L gene, which has no previous link to inherited cerebellar ataxias.
This gene find is the first in canine early-onset cerebellar degeneration, and has enabled the development of a genetic test to help eradicate the disease from the breed. ...
Family first – caring within UK Bangladeshi and Pakistani communities
2012-06-19
Over the next 20 years the proportion of older people living within the Bangladeshi and Pakistani communities in the UK will increase significantly. Most expect that their immediate family, particularly female family members, will provide the majority of care for them in their old age, according to new research funded by the Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC).
The research by Professor Christina Victor of Brunel University, found very few, at best five to ten per cent of the older people within these communities who were interviewed received any form of formal ...
Digital revolution bypassing UK education
2012-06-19
Teaching and learning in the 21st century needs to be 'turbo-charged' by educational technology rather than using technologies designed for other purposes, according to a new report developed by the Technology-Enhanced Learning Research Programme (TEL) - a five-year research programme funded jointly by the Economic and Social Research Council and the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council.
The report System Upgrade: Realising the vision for UK Education is the work of academics, industry and practitioners from across the UK. They warn that to prosper in the ...
Study shows no evidence medical marijuana increases teen drug use
2012-06-19
DENVER (June 18, 2012) – While marijuana use by teens has been increasing since 2005, an analysis of data from 1993 through 2009 by economists at three universities has found no evidence to link the legalization of medical marijuana to increased use of the drug among high school students.
"There is anecdotal evidence that medical marijuana is finding its way into the hands of teenagers, but there's no statistical evidence that legalization increases the probability of use," said Daniel I. Rees, a professor of economics at the University of Colorado Denver.
Rees co-authored ...
Petland Novi Strongly Supports Senior Centers Having Pets
2012-06-19
For aging adults, leaving the homestead and going to a retirement center or assisted living facility is a difficult decision. But for many, it is even harder when they are unable to bring their beloved pets with them. However, it seems that is not always the case nowadays. A FOX News article has revealed that more retirement communities are allowing seniors to take their pets with them. Petland Novi, a pet store, wants more retirement centers to embrace this idea because of the benefits it brings to seniors.
Regency Grand, a California-based facility, provides meals, ...
GTRI researchers develop prototype automated pavement crack detection and sealing system
2012-06-19
VIDEO:
Researchers from the Georgia Tech Research Institute developed an prototype automated pavement crack detection and sealing system.
Click here for more information.
Sealing cracks in roadways ensures a road's structural integrity and extends the time between major repaving projects, but conventional manual crack sealing operations expose workers to dangerous traffic and cover a limited amount of roadway each day.
To address these challenges, the Georgia Tech Research ...
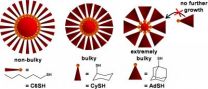
Study improves understanding of surface molecules in controlling size of gold nanoparticles
2012-06-19
North Carolina State University researchers have shown that the "bulkiness" of molecules commonly used in the creation of gold nanoparticles actually dictates the size of the nanoparticles – with larger so-called ligands resulting in smaller nanoparticles. The research team also found that each type of ligand produces nanoparticles in a particular array of discrete sizes.
"This work advances our understanding of nanoparticle formation, and gives us a new tool for controlling the size and characteristics of gold nanoparticles," says Dr. Joseph Tracy, an assistant professor ...
Children, brain development and the criminal law
2012-06-19
The legal system needs to take greater account of new discoveries in neuroscience that show how a difficult childhood can affect the development of a young person's brain which can increase the risk adolescent crimes, according to researchers. The research will be presented as part of an Economic and Social Research Council seminar series in conjunction with the Parliamentary Office of Science and Technology.
Neuroscientists have recently shown that early adversity – such as a very chaotic and frightening home life – can result in a young child becoming hyper vigilant ...
Yankee fans keep enemy Red Sox closer, NYU study shows
2012-06-19
Fans of the New York Yankees incorrectly perceive Fenway Park, home of the archrival Boston Red Sox, to be closer to New York City than is Camden Yards, home of the Baltimore Orioles, a study by New York University psychologists has found. Their research, which appears in the Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, shows how social categorization, collective identification, and identity threat work in concert to shape our representations of the physical world.
"Sun Tzu, the Chinese military general, philosopher, and author of what is arguably the most famous book ...
Helping superconductors turn up the heat
2012-06-19
VIDEO:
University of Miami physics professor Josef Ashkenazi discusses supercooling with liquid nitrogen and superconductors.
Click here for more information.
CORAL GABLES, FL (June 18, 2012)--Researchers from the University of Miami (UM) are unveiling a novel theory for high-temperature superconductivity. The team hopes the new finding gives insight into the process, and brings the scientific community closer to achieving superconductivity at higher temperatures than currently ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Black holes as particle detectorsPreviously undiscovered particles could be detected as they accumulate around black holes say scientists at the Vienna University of Technology