(Press-News.org) North Carolina State University researchers have shown that the "bulkiness" of molecules commonly used in the creation of gold nanoparticles actually dictates the size of the nanoparticles – with larger so-called ligands resulting in smaller nanoparticles. The research team also found that each type of ligand produces nanoparticles in a particular array of discrete sizes.
"This work advances our understanding of nanoparticle formation, and gives us a new tool for controlling the size and characteristics of gold nanoparticles," says Dr. Joseph Tracy, an assistant professor of materials science and engineering at NC State and co-author of a paper describing the research. Gold nanoparticles are used in industrial chemical processes, as well as medical and electronics applications.
When creating gold nanoparticles, scientists often use organic molecules called ligands to facilitate the process. The ligands effectively bring gold atoms together in a solution to create the nanoparticles. In the process, ligands essentially line up side by side and surround the nanoparticles in all three dimensions.
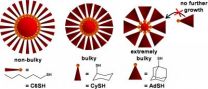
The researchers wanted to see whether the bulkiness of the ligands affected nanoparticle size, and opted to assess three types of thiol ligands – a family of ligands commonly used to synthesize gold nanoparticles. Specifically, the molecules bound to the gold nanoparticles are linear hexanethiolate (-SC6), cyclohexanethiolate (-SCy) and 1-adamantanethiolate (-SAd). Each of these ligands has a bulkier configuration than the last.
For example, picture each ligand as a slice of pie, with a gold atom attached to the pointed end. -SC6 looks like a very narrow slice of pie. -SCy is slightly larger, and -SAd is the largest of the three – with the "crust" end of the pie wedge far wider than the pointed end.
The researchers found that the bulkiness of the ligands determined the size of the nanoparticles. Because fewer -SAd and -SCy ligands can line up next to each other in three dimensions, fewer gold atoms are brought together in the core. Therefore, the nanoparticles are smaller. -SC6, the least bulky of the thiolates, can create the largest nanoparticles.
"While we've shown that this is an effective means of controlling size in gold nanoparticles, we think it may have implications for other materials as well," says Peter Krommenhoek, a Ph.D. student at NC State and lead author of the paper. "That's something we're exploring."
But the researchers made another interesting finding as well.
When particularly small nanoparticles form, they tend to form at very specific sizes, called discrete sizes. For instance, some types of nanoparticles may consist of 25 or 28 atoms – but never 26 or 27 atoms.
In this study, the researchers found that the bulkiness of the ligands also changed the discrete sizes of the nanoparticles. "This is interesting, in part, because each discrete size represents a different number of gold atoms and ligands," Tracy says, "which could influence the nanoparticle's chemical behavior. That question has yet to be addressed."
INFORMATION:
The paper, "Bulky Adamantanethiolate and Cyclohexanethiolate Ligands Favor Smaller Gold Nanoparticles with Altered Discrete Sizes," is published online in ACS Nano. The paper was co-authored by Dr. Junwei Wang, a former postdoctoral research associate at NC State; Dr. Nathaniel Hentz, of the Golden LEAF Biomanufacturing Training and Education Center at NC State; Krystian Kozek, a former undergraduate at NC State; Dr. Aaron Johnston-Peck, a postdoctoral researcher at Brookhaven National Laboratory; and Dr. Gregory Kalyuzhny of San Diego State University.
The research was supported by the National Science Foundation and the U.S. Department of Education.
Study improves understanding of surface molecules in controlling size of gold nanoparticles
2012-06-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Children, brain development and the criminal law
2012-06-19
The legal system needs to take greater account of new discoveries in neuroscience that show how a difficult childhood can affect the development of a young person's brain which can increase the risk adolescent crimes, according to researchers. The research will be presented as part of an Economic and Social Research Council seminar series in conjunction with the Parliamentary Office of Science and Technology.
Neuroscientists have recently shown that early adversity – such as a very chaotic and frightening home life – can result in a young child becoming hyper vigilant ...
Yankee fans keep enemy Red Sox closer, NYU study shows
2012-06-19
Fans of the New York Yankees incorrectly perceive Fenway Park, home of the archrival Boston Red Sox, to be closer to New York City than is Camden Yards, home of the Baltimore Orioles, a study by New York University psychologists has found. Their research, which appears in the Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, shows how social categorization, collective identification, and identity threat work in concert to shape our representations of the physical world.
"Sun Tzu, the Chinese military general, philosopher, and author of what is arguably the most famous book ...
Helping superconductors turn up the heat
2012-06-19
VIDEO:
University of Miami physics professor Josef Ashkenazi discusses supercooling with liquid nitrogen and superconductors.
Click here for more information.
CORAL GABLES, FL (June 18, 2012)--Researchers from the University of Miami (UM) are unveiling a novel theory for high-temperature superconductivity. The team hopes the new finding gives insight into the process, and brings the scientific community closer to achieving superconductivity at higher temperatures than currently ...
BaBar data hint at cracks in the Standard Model
2012-06-19
Menlo Park, Calif. — Recently analyzed data from the BaBar experiment may suggest possible flaws in the Standard Model of particle physics, the reigning description of how the universe works on subatomic scales. The data from BaBar, a high-energy physics experiment based at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, show that a particular type of particle decay called "B to D-star-tau-nu" happens more often than the Standard Model says it should.
In this type of decay, a particle called the B-bar meson decays into a D meson, an antineutrino ...
Science of parenting, the link between sexism and racism, death and the supernatural, and more
2012-06-19
Story leads this month from new articles on parenting by the norm, the link between sexism and racism, death and the supernatural, how brands shape identity and more...
Parenting by the social norm
For parents, it is not only important to pass on to their children values that they personally endorse but also to teach values that they think are the societal norms, according to a new study. Particularly among immigrant parents, conforming to values that they perceive as norms is important. "Intersubjective Model of Value Transmission: Parents Using Perceived Norms as ...
Presidential candidates should address childhood obesity and bullying, poll says
2012-06-19
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – During this presidential election season, there will be plenty of debate between the candidates on the issues. But when it comes to childhood health concerns, a new poll shows many adults agree on the top priorities they want to see the candidates address: childhood obesity and bullying.
The University of Michigan C.S. Mott Children's Hospital National Poll on Children's Health recently asked adults to name the top child health concerns that the presidential candidates should address.
In a survey of more than 2,100 adults, participants selected the ...
Study indicates promise in Huntington's treatment
2012-06-19
A new study shows that the compound Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ) reduces oxidative damage, a key finding that hints at its potential to slow the progression of Huntington disease. The discovery, which appears in the inaugural issue of the Journal of Huntington's Disease, also points to a new biomarker that could be used to screen experimental treatments for this and other neurological disorders.
"This study supports the hypothesis that CoQ exerts antioxidant effects in patients with Huntington's disease and therefore is a treatment that warrants further study," says University ...
Experts recommend men at risk for osteoporosis undergo bone density testing
2012-06-19
Chevy Chase, MD—Osteoporosis in men causes significant morbidity and mortality. Today, the Endocrine Society released clinical practice guidelines (CPG) for management of this condition in men. "Osteoporosis in Men: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline," is published in the June 2012 issue of the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism (JCEM), a publication of The Endocrine Society.
Osteoporosis is a silent disorder characterized by reduced bone strength predisposing to increased fracture risk. Approximately 20 percent of Americans with osteoporosis ...
New studies hint at possible approaches to protect those at risk for Huntington's disease
2012-06-19
Amsterdam, NL, 19 June 2012 – In Huntington's disease, abnormally long strands of glutamine in the huntingtin (Htt) protein, called polyglutamines, cause subtle changes in cellular functions that lead to neurodegeneration and death. Studies have shown that the activation of the heat shock response, a cellular reaction to stress, doesn't work properly in Huntington's disease. In their research to understand the effects of mutant Htt on the master regulator of the heat shock response, HSF1, researchers have discovered that the targets most affected by stress are not the ...
Reflected infrared light unveils never-before-seen details of Renaissance paintings
2012-06-19
WASHINGTON, June 18—When restoring damaged and faded works of art, artists often employ lasers and other sophisticated imaging techniques to study intricate details, analyze pigments, and search for subtle defects not visible to the naked eye. To refine what can be seen during the restoration process even further, a team of Italian researchers has developed a new imaging tool that can capture features not otherwise detectable with the naked eye or current imaging techniques.
The system, known as Thermal Quasi-Reflectography (TQR), is able to create revealing images using ...