(Press-News.org) A new study shows that the compound Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ) reduces oxidative damage, a key finding that hints at its potential to slow the progression of Huntington disease. The discovery, which appears in the inaugural issue of the Journal of Huntington's Disease, also points to a new biomarker that could be used to screen experimental treatments for this and other neurological disorders.
"This study supports the hypothesis that CoQ exerts antioxidant effects in patients with Huntington's disease and therefore is a treatment that warrants further study," says University of Rochester Medical Center neurologist Kevin M. Biglan, M.D., M.P.H., lead author of the study. "As importantly, it has provided us with a new method to evaluate the efficacy of potential new treatments."
Huntington's disease (HD) is a genetic, progressive neurodegenerative disorder that impacts movement, behavior, cognition, and generally results in death within 20 years of the disease's onset. While the precise causes and mechanism of the disease are not completely understood, scientists believe that one of the important triggers of the disease is a genetic "stutter" which produces abnormal protein deposits in brain cells. It is believed that these deposits – through a chain of molecular events – inhibit the cell's ability to meet its energy demands resulting in oxidative stress and, ultimately, cellular death.
Scientists had previously identified the correlation between a specific fragment of genetic code, called 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine (80HdG) and the presence of oxidative stress in brain cells. 80HdG can be detected in a person's blood, meaning that it could serve as a convenient and accessible biomarker for the disease. Researchers have also been evaluating the compound Coenzyme Q10 as a possible treatment for HD because of its ability to support the function of mitochondria – the tiny power plants the provide cells with energy – and counter oxidative stress.
The study's authors evaluated a series of blood samples of 20 individuals with HD who had previously undergone treatment with CoQ in clinical trial titled Pre-2Care. While these studies showed that CoQ alleviated some symptoms of the disease, it was not known what impact – if any – the treatment had at the molecular level in the brain. Upon analysis, the authors found that 80HdG levels dropped by 20 percent in individuals who had been treated with CoQ.
CoQ is currently being evaluated in a Phase 3 clinical trial, which is the largest therapeutic clinical study to date for HD. The trial – called 2Care – is being run by the Huntington Study Group, an international networks or investigators.
"Identifying treatments that slow the progression or delay the onset of Huntington's disease is a major focus of the medical community," said Biglan. "This study demonstrates that 80HdG could be an ideal marker to identify the presence oxidative injury and whether or not treatment is having an impact."
###Additional co-authors include Karl Kieburtz, M.D., M.P.H. and Ryan Evans M.D. with URMC, Ray Dorsey, M.D. with Johns Hopkins University, Steven Hersch, M.D., Ph.D. with Massachusetts General Hospital, and Ira Shoulson, M.D. with Georgetown University. The study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. Funding for the original Pre-2Care study was provided by the CHDI Foundation.
Study indicates promise in Huntington's treatment
2012-06-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Experts recommend men at risk for osteoporosis undergo bone density testing
2012-06-19
Chevy Chase, MD—Osteoporosis in men causes significant morbidity and mortality. Today, the Endocrine Society released clinical practice guidelines (CPG) for management of this condition in men. "Osteoporosis in Men: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline," is published in the June 2012 issue of the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism (JCEM), a publication of The Endocrine Society.
Osteoporosis is a silent disorder characterized by reduced bone strength predisposing to increased fracture risk. Approximately 20 percent of Americans with osteoporosis ...
New studies hint at possible approaches to protect those at risk for Huntington's disease
2012-06-19
Amsterdam, NL, 19 June 2012 – In Huntington's disease, abnormally long strands of glutamine in the huntingtin (Htt) protein, called polyglutamines, cause subtle changes in cellular functions that lead to neurodegeneration and death. Studies have shown that the activation of the heat shock response, a cellular reaction to stress, doesn't work properly in Huntington's disease. In their research to understand the effects of mutant Htt on the master regulator of the heat shock response, HSF1, researchers have discovered that the targets most affected by stress are not the ...
Reflected infrared light unveils never-before-seen details of Renaissance paintings
2012-06-19
WASHINGTON, June 18—When restoring damaged and faded works of art, artists often employ lasers and other sophisticated imaging techniques to study intricate details, analyze pigments, and search for subtle defects not visible to the naked eye. To refine what can be seen during the restoration process even further, a team of Italian researchers has developed a new imaging tool that can capture features not otherwise detectable with the naked eye or current imaging techniques.
The system, known as Thermal Quasi-Reflectography (TQR), is able to create revealing images using ...
Carbon is key for getting algae to pump out more oil
2012-06-19
UPTON, N.Y. — Overturning two long-held misconceptions about oil production in algae, scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory show that ramping up the microbes' overall metabolism by feeding them more carbon increases oil production as the organisms continue to grow. The findings — published online in the journal Plant and Cell Physiology on May 28, 2012 — may point to new ways to turn photosynthetic green algae into tiny "green factories" for producing raw materials for alternative fuels.
"We are interested in algae because they grow ...
Pediatric regime of chemotherapy proves more effective for young adults
2012-06-19
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), usually found in pediatric patients, is far more rare and deadly in adolescent and adult patients. According to the National Marrow Donor Program, child ALL patients have a higher than 80 percent remission rate, while the recovery rate for adults stands at only 40 percent.
In current practice, pediatric and young adult ALL patients undergo different treatment regimes. Children aged 0-15 years are typically given more aggressive chemotherapy, while young adults, defined as people between 16 and 39 years of age, are treated with a round ...
Key part of plants' rapid response system revealed
2012-06-19
Science has known about plant hormones since Charles Darwin experimented with plant shoots and showed that the shoots bend toward the light as long as their tips, which are secreting a growth hormone, aren't cut off.
But it is only recently that scientists have begun to put a molecular face on the biochemical systems that modulate the levels of plant hormones to defend the plant from herbivore or pathogen attack or to allow it to adjust to changes in temperature, precipitation or soil nutrients.
Now, a cross-Atlantic collaboration between scientists at Washington University ...
Peaches, plums, nectarines give obesity, diabetes slim chance
2012-06-19
COLLEGE STATION – Peaches, plums and nectarines have bioactive compounds that can potentially fight-off obesity-related diabetes and cardiovascular disease, according to new studies by Texas AgriLife Research.
The study, which will be presented at the American Chemical Society in Philadelphia next August, showed that the compounds in stone fruits could be a weapon against "metabolic syndrome," in which obesity and inflammation lead to serious health issues, according to Dr. Luis Cisneros-Zevallos, AgriLife Research food scientist.
"In recent years obesity ...
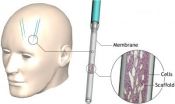
Device implanted in brain has therapeutic potential for Huntington's disease
2012-06-19
Amsterdam, NL, June 18, 2012 – Studies suggest that neurotrophic factors, which play a role in the development and survival of neurons, have significant therapeutic and restorative potential for neurologic diseases such as Huntington's disease. However, clinical applications are limited because these proteins cannot easily cross the blood brain barrier, have a short half-life, and cause serious side effects. Now, a group of scientists has successfully treated neurological symptoms in laboratory rats by implanting a device to deliver a genetically engineered neurotrophic ...
Link between vitamin C and twins can increase seed production in crops
2012-06-19
RIVERSIDE, Calif. — Biochemists at the University of California, Riverside report a new role for vitamin C in plants: promoting the production of twins and even triplets in plant seeds.
Daniel R. Gallie, a professor of biochemistry, and Zhong Chen, an associate research biochemist in the Department of Biochemistry, found that increasing the level of dehydroascorbate reductase (DHAR), a naturally occurring enzyme that recycles vitamin C in plants and animals, increases the level of the vitamin and results in the production of twin and triplet seedlings in a single seed.
The ...
Research breakthrough: High brain integration underlies winning performances
2012-06-19
Scientists trying to understand why some people excel — whether as world-class athletes, virtuoso musicians, or top CEOs — have discovered that these outstanding performers have unique brain characteristics that make them different from other people.
A study published in May in the journal Cognitive Processing found that 20 top-level managers scored higher on three measures — the Brain Integration Scale, Gibbs's Socio-moral Reasoning questionnaire, and an inventory of peak experiences — compared to 20 low-level managers that served as matched controls. This is the fourth ...