(Press-News.org) INDIANAPOLIS -- Researchers at the Indiana University Melvin and Bren Simon Cancer Center have published the first report using imaging to show that changes in brain tissue can occur in breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy.
The cognitive effects of chemotherapy, often referred to as "chemobrain," have been known for years. However, the IU research is the first to use brain imaging to study women with breast cancer before and after treatment, showing that chemotherapy can affect gray matter. The researchers reported their findings in the October 2010 edition of Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.
"This is the first prospective study," said Andrew Saykin, Psy.D., director of the Indiana University Center for Neuroimaging and a researcher at the IU Simon Cancer Center. "These analyses, led by Brenna McDonald, suggest an anatomic basis for the cognitive complaints and performance changes seen in patients. Memory and executive functions like multi-tasking and processing speed are the most typically affected functions and these are handled by the brain regions where we detected gray matter changes."
Dr. Saykin, who is Raymond C. Beeler Professor of Radiology at the IU School of Medicine,
and colleagues studied structural MRI scans of the brain obtained on breast cancer patients and healthy controls. The scans were taken after surgery, but before radiation or chemotherapy, to give the researchers a baseline. Scans were then repeated one month and one year after chemotherapy was completed.
The researchers found gray matter changes were most prominent in the areas of the brain that are consistent with cognitive dysfunction during and shortly after chemotherapy. Gray matter density in most women improved a year after chemotherapy ended.
For many patients, Dr. Saykin said, the effects are subtle. However, they can be more pronounced for others. Although relatively rare, some patients -- often middle-aged women -- are so affected that they are never able to return to work. More commonly, women will still be able to work and multi-task, but it may be more difficult to do so.
The study focused on 17 breast cancer patients treated with chemotherapy after surgery, 12 women with breast cancer who did not undergo chemotherapy after surgery, and 18 women without breast cancer.
"We hope there will be more prospective studies to follow so that the cause of these changes in cancer patients can be better understood," Dr. Saykin said.
Dr. Saykin and his colleagues started their research at Dartmouth Medical School before finishing the data analyses at IU. A new, independent sample is now being studied at the IU Simon Cancer Center to replicate and further investigate this problem affecting many cancer patients.
INFORMATION:
Other researchers included lead author Brenna McDonald, Psy.D., M.B.A., assistant professor, Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences, IU School of Medicine; Susan Conroy, M.D., Ph.D. student; Tim Ahles, Ph.D., professor of psychiatry, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, N.Y.; and John West, M.S., an imaging researcher at the IU Center for Neuroimaging.
The study was supported by a grant from the Office of Cancer Survivorship of the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health and the Indiana Economic Development Corp.
IU researchers: Chemotherapy alters brain tissue in breast cancer patients
2010-09-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Alcohol consumers are becoming the norm, UT Southwestern analysis finds
2010-09-30
DALLAS – Sept. 29, 2010 – More people are drinking than 20 years ago, according to a UT Southwestern Medical Center analysis of national alcohol consumption patterns. Gathered from more than 85,000 respondents, the data suggests that a variety of factors, including social, economic and ethnic influences and pressures, are involved in the increase.
"The reasons for the uptick vary and may involve complex sociodemographic changes in the population, but the findings are clear: More people are consuming alcohol now than in the early 1990s," said Dr. Raul Caetano, dean of ...
Milky Way sidelined in galactic tug-of-war
2010-09-30
The Magellanic Stream is an arc of hydrogen gas spanning more than 100 degrees of the sky as it trails behind the Milky Way's neighbor galaxies, the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds. Our home galaxy, the Milky Way, has long been thought to be the dominant gravitational force in forming the Stream by pulling gas from the Clouds. A new computer simulation by Gurtina Besla (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics) and her colleagues now shows, however, that the Magellanic Stream resulted from a past close encounter between these dwarf galaxies rather than effects of the ...
Hepatitis C virus faces new weapon from Florida State scientists
2010-09-30
In recent human trials for a promising new class of drug designed to target the hepatitis C virus (HCV) without shutting down the immune system, some of the HCV strains being treated exhibited signs of drug resistance.
In response, an interdisciplinary team of Florida State University biologists, chemists and biomedical researchers devised a novel genetic screening method that can identify the drug-resistant HCV strains and the molecular-level mechanisms that make them that way –– helping drug developers to tailor specific therapies to circumvent them.
The potentially ...
Surgery offers long-term survival for early stage prostate cancer patients
2010-09-30
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- In the largest, most modern, single-institution study of its kind, Mayo Clinic urologists mined a long-term data registry for survival rates of patients who underwent radical prostatectomy (http://www.mayoclinic.org/radical-prostatectomy/) for localized prostate cancer. The findings are being presented at the North Central Section of the American Urological Association's 84th Annual Meeting in Chicago.
A radical prostatectomy is an operation to remove the prostate gland and some of the tissue around it. In this study, Mayo Clinic researchers discovered ...
Correction: Abatacept found ineffective in treatment of non-life threatening lupus
2010-09-30
Results from a 12-month multi-center clinical trial did not show therapeutic benefit of abatacept over placebo in patients with non-life threatening systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Abatacept failed to prevent new disease flares in SLE patients tapered from corticosteroids in an analysis where mild, moderate and severe disease flares were evaluated together. Full details of the phase IIb clinical trial are published in the October issue of Arthritis & Rheumatism, a journal of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
The ACR estimates that 161,000 to 322,000 adults ...
NASA uses 3 satellites to see strengthening Tropical Storm Nicole
2010-09-30
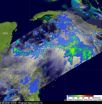
NASA is providing data from three satellites to give forecasters valuable information on newly strengthened Tropical Storm Nicole. Nicole was Tropical Depression 16 until 11 a.m. EDT, Sept. 29 and NASA data helped confirm her new designation. Satellite data from NASA showed frigid thunderstorm cloud top temperatures, heavy rainfall, and extensive cloud cover as Nicole strengthened.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument uses infrared technology to take a tropical cyclone's temperature. AIRS sits on NASA's Aqua satellite and captured an image of those cloud ...
Penn biologists say species accumulate on Earth at slower rates than in the past
2010-09-30
PHILADELPHIA –- Computational biologists at the University of Pennsylvania say that species are still accumulating on Earth but at a slower rate than in the past.
In the study, published in the journal PLoS Biology, Penn researchers developed a novel computational approach to infer the dynamics of species diversification using the family trees of present-day species. Using nine patterns of diversification as alternative models, they examined 289 phylogenies, or evolutionary trees, representing amphibians, arthropods, birds, mammals, mollusks and flowering plants.
The ...
Resource restoration planning process begins for BP/Deepwater Horizon oil spill
2010-09-30
The Department of the Interior, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the co-trustees for natural resources affected by the BP/Deepwater Horizon oil spill announced today they have started the injury assessment and restoration planning phase of the Natural Resource Damage Assessment, a legal process to determine the type and amount of restoration needed to compensate the public for harm to natural resources and their human uses as a result of the spill.
This is the second phase of the NRDA process. Much of the initial "preassessment" phase has already ...
California's leadership in tobacco control results in lower lung cancer rate
2010-09-30
A study led by researchers at the University of California, San Diego shows that California's 40 year-long tobacco control program has resulted in lung cancer rates that are nearly 25 percent lower than other states.
"The consistency in the trends from cigarette sales and population surveys was reassuring" said John P. Pierce, PhD, Sam M. Walton Professor of Cancer Research in the Department of Family and Preventive Medicine at UCSD School of Medicine and director of the Population Sciences Division at Moores UCSD Cancer Center. "What is really important is that the widening ...
Less than half of essential workers willing to report to work during a serious pandemic
2010-09-30
September 28, 2010 – Although first responders willingly put themselves in harm's way during disasters, new research indicates that they may not be as willing— if the disaster is a potentially lethal pandemic.
In a recent study, researchers at Columbia University's Mailman School of Public Health found that more than 50% of the first responders and other essential workers they surveyed might be absent from work during a serious pandemic, even if they were healthy.
The study, reported online in the October issue of the Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, ...