(Press-News.org) If you have ever looked over the edge of a cliff and felt dizzy, you understand the challenges faced by people who suffer from symptoms of vestibular dysfunction such as vertigo and dizziness. There are over 70 million of them in North America. For people with vestibular loss, performing basic daily living activities that we take for granted (e.g. dressing, eating, getting in and out of bed, getting around inside as well as outside the home) becomes difficult since even small head movements are accompanied by dizziness and the risk of falling.
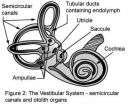
We've known for a while that a sensory system in the inner ear (the vestibular system) is responsible for helping us keep our balance by giving us a stable visual field as we move around. And while researchers have already developed a basic understanding of how the brain constructs our perceptions of ourselves in motion, until now no one has understood the crucial step by which the neurons in the brain select the information needed to keep us in balance.
The way that the brain takes in and decodes information sent by neurons in the inner ear is complex. The peripheral vestibular sensory neurons in the inner ear take in the time varying acceleration and velocity stimuli caused by our movement in the outside world (such as those experienced while riding in a car that moves from a stationary position to 50 km per hour). These neurons transmit detailed information about these stimuli to the brain (i.e. information that allows one to reconstruct how these stimuli vary over time) in the form of nerve impulses.
Scientists had previously believed that the brain decoded this information linearly and therefore actually attempted to reconstruct the time course of velocity and acceleration stimuli. But by combining electrophysiological and computational approaches, Kathleen Cullen and Maurice Chacron, two professors in McGill University's Department of Physiology, have been able to show for the first time that the neurons in the vestibular nuclei in the brain instead decode incoming information nonlinearly as they respond preferentially to unexpected, sudden changes in stimuli.
It is known that representations of the outside world change at each stage in this sensory pathway. For example, in the visual system neurons located closer to the periphery of the sensory system (e.g. ganglion cells in the retina) tend to respond to a wide range of sensory stimuli (a "dense" code), whereas central neurons (e.g. in the primary visual cortex at the back of the head tend to respond much more selectively (a "sparse" code). Chacron and Cullen have discovered that the selective transmission of vestibular information they were able to document for the first time occurs as early as the first synapse in the brain. "We were able to show that the brain has developed this very sophisticated computational strategy to represent sudden changes in movement in order to generate quick accurate responses and maintain balance," explained Prof. Cullen. "I keep describing it as elegant, because that's really how it strikes me."
This kind of selectivity in response is important for everyday life, since it enhances the brain's perception of sudden changes in body posture. So that if you step off an unseen curb, within milliseconds, your brain has both received the essential information and performed the sophisticated computation needed to help you readjust your position. This discovery is expected to apply to other sensory systems and eventually to the development of better treatments for patients who suffer from vertigo, dizziness, and disorientation during their daily activities. It should also lead to treatments that will help alleviate the symptoms that accompany motion and/or space sickness produced in more challenging environments.
INFORMATION:
The research was conducted by Corentin Massot a Postdoctoral fellow in the Department of Physiology, and Adam Schneider a Ph.D. Student in the Department of Physics.
The research was funded by: The Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) and the Fonds de recherche du Québec - Nature et technologies (FQRNT)
Decoding the secrets of balance
New understanding of how the brain processes information from inner ear offers hope for sufferers of vertigo
2012-07-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Big horns trump smooth pickup lines every time
2012-07-27
EAST LANSING, Mich. — Elk and rhinoceros beetles aren't diabetic, but to grow big horns and attract mates it appears that the males are insulin-dependent.
Ian Dworkin, Michigan State University zoologist, was part of a team that for the first time ever showed why horns – from elk to rhinoceros beetles – and other decorative, mate-attracting structures are sensitive to changes in nutrition. As reported in the current issue of Science, the key ingredient for this growth is insulin, Dworkin said.
"Clearly elk antlers, peacock tail feathers and beetle horns are very different, ...
Rivers flowing into the sea offer vast potential as electricity source
2012-07-27
WASHINGTON, July 25, 2012 — The latest episode in the American Chemical Society's (ACS') award-winning Global Challenges/Chemistry Solutions podcast series describes a process that could pave the way for a new genre of electric power-generating stations. These stations could supply electricity for more than a half billion people by tapping just one-tenth of the global potential of a little-known energy source that exists where rivers flow into the ocean.
Based on a report by Menachem Elimelech, Ph.D., and Ngai Yin Yip in the ACS journal Environmental Science & Technology, ...
New research confirms efficacy of transcranial magnetic stimulation for depression
2012-07-27
PROVIDENCE, R.I. – In one of the first studies to look at transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) in real-world clinical practice settings, researchers at Butler Hospital, along with colleagues across the U.S., confirmed that TMS is an effective treatment for patients with depression who are unable to find symptom relief through antidepressant medications. The study findings are published online in the June 11, 2012 edition of Depression and Anxiety in the Wiley Online Library.
Previous analysis of the efficacy of TMS has been provided through more than 30 published ...
Photovoltaics from any semiconductor
2012-07-27
A technology that would enable low-cost, high efficiency solar cells to be made from virtually any semiconductor material has been developed by researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and the University of California (UC) Berkeley. This technology opens the door to the use of plentiful, relatively inexpensive semiconductors, such as the promising metal oxides, sulfides and phosphides, that have been considered unsuitable for solar cells because it is so difficult to taylor their properties by chemical means.
"It's ...
MRSA cases in academic hospitals double in 5 years: study
2012-07-27
CHICAGO (July 26, 2012) -- Infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) doubled at academic medical centers in the U.S. between 2003 and 2008, according to a report published in the August issue of Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, the journal of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America.
Researchers from the University of Chicago Medicine and the University HealthSystem Consortium (UHC) estimate hospitalizations increased from about 21 out of every 1,000 patients hospitalized in 2003 to about 42 out of every 1,000 in 2008, ...
NASA X-ray concept inspired from a roll of Scotch® tape
2012-07-27
The inspiration behind NASA scientist Maxim Markevitch's quest to build a highly specialized X-ray mirror using a never-before-tried technique comes from an unusual source: a roll of Scotch® tape.
Markevitch and a team of X-ray optics experts at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., have begun investigating the feasibility of fashioning a low-cost mirror from plastic tape and tightly rolling it like the sticky adhesive commonly found in most homes and offices.
"I remember looking at a roll of Scotch tape and thinking, 'was it possible to use the same ...
Maric Industries MarVac Achieves Title of UL Recognized Supplier
2012-07-27
Maric Industries'MarVac division is proud to inform you that we are now a UL Recognized supplier of wire and cable assemblies. This means that you can be confident that MarVac is building exactly to the customers specifications spelled out on their print. It also means we are using the exact components called out on the print or BOM and no deviation will be made.
Visit
http://maricindustries.com/press-release/
Maric Industries Signifies Quality
Maric Industries solutions serve broadband operators, telecommunication system contractors and many other markets. ...
Boeing Performance Excellence Award Issued to Pasternack
2012-07-27
Pasternack Enterprises, Inc., a leading ISO 9001:2008 manufacturer and International supplier of custom and standard RF, microwave and fiber optic products, today announced that it has received the 2011 Boeing Performance Excellence Award.
The Boeing Company issues the award annually to recognize suppliers who have achieved superior performance. Pasternack maintained a Silver composite performance rating for each month of the 12-month performance period, from Oct. 1, 2010, to Sept. 30, 2011. This year, Boeing recognized 407 suppliers who achieved a Silver level Boeing ...
Heliski Operator's 'Ultimate Gear Giveaway'
2012-07-27
Canadian heliski operator Last Frontier Heliskiing has joined with leading outdoor brands Oakley and Marmot to create its summer 2012 'Ultimate Gear Giveaway' offering $600 of the latest ski gear in a Facebook contest which runs till July, 30, 2012.
Skiing and snowboarding in the most testing conditions since 1996, Last Frontier Heliskiing know riders value equipment that helps them take their sport to new heights.
"Our Ultimate Gear Giveaway is a great way to connect with people that are passionate about spending time in the elements", Steve Rosset - Media ...
Westfield Southgate to Host 3rd Annual Suncoast Jobs Career Fair on September 18, 2012
2012-07-27
Westfield Southgate is proud to announce that it has partnered with Suncoast Jobs to host the 3rd Annual Suncoast Jobs Career Fair on September 18, 2012, from 8:00am-1:00pm at Westfield Southgate (in the dining court).
Hundreds of job seekers will have the opportunity to connect with over 50 local employers face to face. The employers will represent a wide variety of industries such as healthcare, technology, finance, sales, and retail.
"This event has been extremely successful the past two years, and we are very excited to partner with Suncoast Jobs and connect ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How sleep disruption impairs social memory: Oxytocin circuits reveal mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities
Natural compound from pomegranate leaves disrupts disease-causing amyloid
A depression treatment that once took eight weeks may work just as well in one
New study calls for personalized, tiered approach to postpartum care
The hidden breath of cities: Why we need to look closer at public fountains
Rewetting peatlands could unlock more effective carbon removal using biochar
Microplastics discovered in prostate tumors
ACES marks 150 years of the Morrow Plots, our nation's oldest research field
Physicists open door to future, hyper-efficient ‘orbitronic’ devices
$80 million supports research into exceptional longevity
Why the planet doesn’t dry out together: scientists solve a global climate puzzle
Global greening: The Earth’s green wave is shifting
You don't need to be very altruistic to stop an epidemic
Signs on Stone Age objects: Precursor to written language dates back 40,000 years
MIT study reveals climatic fingerprints of wildfires and volcanic eruptions
A shift from the sandlot to the travel team for youth sports
Hair-width LEDs could replace lasers
The hidden infections that refuse to go away: how household practices can stop deadly diseases
Ochsner MD Anderson uses groundbreaking TIL therapy to treat advanced melanoma in adults
A heatshield for ‘never-wet’ surfaces: Rice engineering team repels even near-boiling water with low-cost, scalable coating
Skills from being a birder may change—and benefit—your brain
Waterloo researchers turning plastic waste into vinegar
Measuring the expansion of the universe with cosmic fireworks
How horses whinny: Whistling while singing
US newborn hepatitis B virus vaccination rates
When influencers raise a glass, young viewers want to join them
Exposure to alcohol-related social media content and desire to drink among young adults
Access to dialysis facilities in socioeconomically advantaged and disadvantaged communities
Dietary patterns and indicators of cognitive function
New study shows dry powder inhalers can improve patient outcomes and lower environmental impact
[Press-News.org] Decoding the secrets of balanceNew understanding of how the brain processes information from inner ear offers hope for sufferers of vertigo