(Press-News.org) University of California, Berkeley, Haas School of Business -- A just completed multi-year research project by the Fisher CIO Leadership Program at UC Berkeley's Haas School of Business has uncovered the most important, role specific career success factors of chief information officers.
The study was initiated by Max Hopper, the iconic author of American Airlines industry-changing SABRE system and conducted by the Fisher CIO Leadership Program. Hopper was concerned that so many companies were failing to achieve much if any benefit from their expensive IT organizations, often after spending large amounts of money with little to show for it. He formed a committee to identify the world's more successful CIOs – those few who had a major, enduring positive impact both on their companies as well as their industries.
A Fisher Program team interviewed in depth each of the fourteen prominent CIOs identified by the Hopper Committee. The companies represented included American Airlines, WalMart, Charles Schwab, FedEX, Marriott, Levi Strauss, FritoLay, Cisco and several others.
An event discussing the findings of this ground-breaking study will take place at UC-Berkeley's Haas School of Business on September 14th and will be attended by most of the CIOs who were interviewed as well as by CIOs and individuals in related professions.
###
For more information about this study or to attend the Sept. 14 event, please contact James M. Spitze, executive of the Fisher CIO Leadership Program and the study's lead author, at 510-409-2888 or jim_spitze@haas.berkeley.edu
To obtain a copy of the study, titled "The Renaissance CIO Project: the Invisible Factors of Extraordinary Success," as published in the Winter 2012 issue of the California Management Review (CMR), please visit the CMR website at http://www.ucpressjournals.com/journal.php?j=cmr or contact Jim Spitze.
Berkeley-Haas study identifies success factors of extraordinary CIOs
Future of CIO profession to be discussed at Sept. 14 event in Berkeley, Calif.
2012-07-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
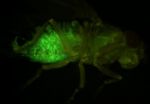
Fruit flies light the way for A*STAR scientists to pinpoint genetic changes that spell cancer
2012-07-30
By studying fruit flies, scientists at A*STAR's Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology (IMCB) have successfully devised a fast and cost-saving way to uncover genetic changes that have a higher potential to cause cancer. With this new approach, researchers will now be able to rapidly distinguish the range of genetic changes that are causally linked to cancer (i.e. "driver" mutations) versus those with limited impact on cancer progression. This research paves the way for doctors to design more targeted treatment against the different cancer types, based on the specific ...
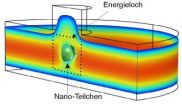
A giant step in a miniature world: UZH researcher measures the electrical charge of nano particles
2012-07-30
In order to observe the individual particles in a solution, Prof. Madhavi Krishnan and her co-workers «entice» each particle into an «electrostatic trap». It works like this: between two glass plates the size of a chip, the researchers create thousands of round energy holes. The trick is that these holes have just a weak electrostatic charge. The scientists than add a drop of the solution to the plates, whereupon each particle falls into an energy hole and remains trapped there. But the particles do not remain motionless in their trap. Instead, molecules in the solution ...
Archaeologists from Bonn discover in Mexico the tomb of a Maya prince
2012-07-30
Archaeologists from the Department of Anthropology of the Americas at the University of Bonn have been excavating for the past four years together with the Mexican National Institute of Anthropology and History in the Maya city of Uxul in Campeche, Mexico. The aim of the excavation project under the direction of Prof. Dr. Nikolai Grube and Dr. Kai Delvendahl is to investigate the process of centralization and collapse of hegemonic state structures in the Maya Lowlands using the example of a mid-sized classic Maya city (Uxul) and its ties to a supra-regional center (Calakmul). ...
Telling the tale of the wealth tail
2012-07-30
A mathematical physicist and her colleague, both from the Free University of Bozen-Bolzano, Italy, are about to publish a study in EPJ B¹ on a family of taxation and wealth redistribution models. The findings could lead to numerical simulations of potential wealth distribution scenarios playing out over the long term and could be used for policy decision making.
Maria Letizia Bertotti and Giovanni Modanese propose a mechanism of individual interaction of economic agents involved in wealth redistribution on a one-to-one level as a means of understanding their collective ...
Brain development is delayed in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder
2012-07-30
Philadelphia, PA, July 30, 2012 – Is attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) due to a delay in brain development or the result of complete deviation from typical development? In the current issue of Biological Psychiatry, Dr. Philip Shaw and colleagues present evidence for delay based on a study by the National Institutes of Health.
The cerebral cortex is the folded gray tissue that makes up the outermost portion of the brain, covering the brain's inner structures. This tissue has left and right hemispheres and is divided into lobes. Each lobe performs specific ...
Archeologists unearth extraordinary human sculpture in Turkey
2012-07-30
A beautiful and colossal human sculpture is one of the latest cultural treasures unearthed by an international team at the Tayinat Archaeological Project (TAP) excavation site in southeastern Turkey. A large semi-circular column base, ornately decorated on one side, was also discovered. Both pieces are from a monumental gate complex that provided access to the upper citadel of Kunulua, capital of the Neo-Hittite Kingdom of Patina (ca. 1000-738 BC).
"These newly discovered Tayinat sculptures are the product of a vibrant local Neo-Hittite sculptural tradition," said Professor ...
In Massachusetts, 'individual mandate' led to decreased hospital productivity
2012-07-30
Philadelphia, Pa. (July 30, 2012) - As the "individual mandate" of the Affordable Care Act moves forward, debate and speculation continue as to whether universal health insurance coverage will lead to significant cost savings for hospitals. The assumption is that providing appropriate primary care will improve the overall health of the population, resulting in less need for hospital services and less severe illness among hospitalized patients. Findings from a recent study published in Health Care Management Review challenge that assumption. Health Care Management Review ...
Long-distance distress signal from periphery of injured nerve cells begins with locally made protein
2012-07-30
PHILADELPHIA (July 30, 2012)— When the longest cells in the body are injured at their farthest reaches, coordinating the cells' repair is no easy task. This is in part because these peripheral nerve cells can be extremely long – up to one meter in adult humans – which is a lot of distance for a molecular distress signal to cover in order to reach the "command center" of the cell's nucleus.
Scientists have believed this process to be even more challenging because their textbook understanding for many years has been that the axons – the long extensions of nerve cells away ...
Obesity in type 2 diabetes: Recommendations from guidelines are largely consistent
2012-07-30
On 10th July 2012, the German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) published the results of a literature search for evidence-based guidelines for the treatment of obesity in type 2 diabetes. The aim of the report was to identify those recommendations from current guidelines of high methodological quality that may be relevant for a possible new obesity module in the disease management programme (DMP) for type 2 diabetes.
Diet, exercise and behavioural therapy generally advised
IQWiG found that the recommendations of the various guidelines for the ...
Health coaches could be key to successful weight loss, study suggests
2012-07-30
(PROVIDENCE, R.I.) – Coaches can help athletes score touchdowns and perfect their golf swing, but can they also influence weight loss? Researchers from The Miriam Hospital's Weight Control and Diabetes Research Center say health coaches could play an important role in the battle of the bulge, according to the findings of a pilot study published online in the journal Obesity.
In the first study of its kind, obese individuals participating in a low-intensity behavioral weight loss program who were supported by either a professional health coach or a peer coach lost clinically ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
[Press-News.org] Berkeley-Haas study identifies success factors of extraordinary CIOsFuture of CIO profession to be discussed at Sept. 14 event in Berkeley, Calif.