(Press-News.org) Irvine, Calif., July 30, 2012 – UC Irvine scientists have discovered intriguing differences in the brains and mental processes of an extraordinary group of people who can effortlessly recall every moment of their lives since about age 10.
The phenomenon of highly superior autobiographical memory – first documented in 2006 by UCI neurobiologist James McGaugh and colleagues in a woman identified as "AJ" – has been profiled on CBS's "60 Minutes" and in hundreds of other media outlets. But a new paper in the peer-reviewed journal Neurobiology of Learning & Memory's July issue offers the first scientific findings about nearly a dozen people with this uncanny ability.
All had variations in nine structures of their brains compared to those of control subjects, including more robust white matter linking the middle and front parts. Most of the differences were in areas known to be linked to autobiographical memory, "so we're getting a descriptive, coherent story of what's going on," said lead author Aurora LePort, a doctoral candidate at UCI's Center for the Neurobiology of Learning & Memory.
Surprisingly, the people with stellar autobiographical memory did not score higher on routine laboratory memory tests or when asked to use rote memory aids. Yet when it came to public or private events that occurred after age 10½, "they were remarkably better at recalling the details of their lives," said McGaugh, senior author on the new work.
"These are not memory experts across the board. They're 180 degrees different from the usual memory champions who can memorize pi to a large degree or other long strings of numbers," LePort noted. "It makes the project that much more interesting; it really shows we are homing in on a specific form of memory."
She said interviewing the subjects was "baffling. You give them a date, and their response is immediate. The day of the week just comes out of their minds; they don't even think about it. They can do this for so many dates, and they're 99 percent accurate. It never gets old."
The study also found statistically significant evidence of obsessive-compulsive tendencies among the group, but the authors do not yet know if or how this aids recollection. Many of the individuals have large, minutely catalogued collections of some sort, such as magazines, videos, shoes, stamps or postcards.
UCI researchers and staff have assessed more than 500 people who thought they might possess highly superior autobiographical memory and have confirmed 33 to date, including the 11 in the paper. Another 37 are strong candidates who will be further tested.
"The next step is that we want to understand the mechanisms behind the memory," LePort said. "Is it just the brain and the way its different structures are communicating? Maybe it's genetic; maybe it's molecular."
McGaugh added: "We're Sherlock Holmeses here. We're searching for clues in a very new area of research."
INFORMATION:
Fellow authors are Aaron Mattfeld, Heather Dickinson-Anson, James Fallon, Craig Stark, Frithjof Kruggel and Larry Cahill. Funding was provided by the National Institutes of Health, the Gerard Family Trust and Unither Neurosciences Inc.
About the University of California, Irvine: Founded in 1965, UCI is a top-ranked university dedicated to research, scholarship and community service. Led by Chancellor Michael Drake since 2005, UCI is among the most dynamic campuses in the University of California system, with nearly 28,000 undergraduate and graduate students, 1,100 faculty and 9,000 staff. Orange County's second-largest employer, UCI contributes an annual economic impact of $4 billion. For more UCI news, visit www.today.uci.edu.
News Radio: UCI maintains on campus an ISDN line for conducting interviews with its faculty and experts. Use of this line is available for a fee to radio news programs/stations that wish to interview UCI faculty and experts. Use of the ISDN line is subject to availability and approval by the university.
UCI maintains an online directory of faculty available as experts to the media. To access, visit www.today.uci.edu/experts.
For UCI breaking news, visit www.zotwire.uci.edu.
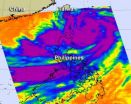
Typhoon Saola looks like a monster tropical cyclone in infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite today, July 30. Although Saola's center is over 300 nautical miles (368 miles/592 km) south-southeast of Taiwan, it stretches over the north and central Philippines and has triggered a number of warnings throughout the country.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument on NASA's Terra satellite captured an image of Typhoon Saola approaching Taiwan on July 30 at 0215 UTC (July 29 at 10:15 p.m. EDT). The image showed a ragged eye in the storm's center ...
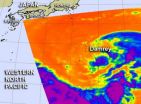
Tropical Storm Damrey appears to be a compact tropical storm on NASA satellite imagery as it heads west. It is expected to pass north of Iwo To, Japan and later south of Kyushu, one of Japan's large islands.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Damrey on July 30 at 03:21 UTC (July 29 at 11:21 p.m. EDT) and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an infrared image of the storm. It showed that strong, high, cold cloud tops of thunderstorms were in a tight circle around the center of circulation. There were bands of thunderstorms mostly north ...
Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center researchers have identified how one of the genes most commonly mutated in lung cancer may promote such tumors.
The investigators found that the protein encoded by this gene, called EPHA3, normally inhibits tumor formation, and that loss or mutation of the gene – as often happens in lung cancer – diminishes this tumor-suppressive effect, potentially sparking the formation of lung cancer. The findings, published July 24 in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, could offer direction for personalizing cancer treatments and development ...
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — Sandia National Laboratories' wind energy researchers are re-evaluating vertical axis wind turbines (VAWTs) to help solve some of the problems of generating energy from offshore breezes.
Though VAWTs have been around since the earliest days of wind energy research at Sandia and elsewhere, VAWT architecture could transform offshore wind technology.
The economics of offshore windpower are different from land-based turbines, due to installation and operational challenges. VAWTs offer three big advantages that could reduce the cost of wind energy: a ...
Montreal, July 30, 2012 – Rows of chip bags in a vending machine, endless bottles of shampoo on pharmacy shelves, long lines of books arranged in the bestsellers section at the bookstore. From supermarket shelves to barroom beer selection, long lines of horizontally arranged products are the norm when it comes to the shopping experience.
But how does where a product is placed on the storeroom shelf influence which option a consumer will ultimately choose? It turns out that the shopper's eye has a very central focus.
"Consumers are more likely to purchase products ...
Scientists at the University of Liverpool have discovered that variations in the long-term reversal rate of the Earth's magnetic field may be caused by changes in heat flow from the Earth's core into the base of the overlying mantle.
The Earth is made up of a solid inner core, surrounded by a liquid outer core, in turn covered by a thicker or more viscous mantle, and ultimately by the solid crust beneath our feet. The magnetic field is generated by the motions of the liquid iron alloy in the outer core, approximately 3,000 km beneath the Earth's crust. These motions ...
WASHINGTON, DC, July 25, 2012 — Policies that reward abstinence from terrorism are more successful in reducing such acts of violence than tactics that aim to punish terrorists, suggests a new study in the August issue of the American Sociological Review.
Titled, "Moving Beyond Deterrence: The Effectiveness of Raising the Expected Utility of Abstaining from Terrorism in Israel," the study looked specifically at the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and found that between 1987 and 2004, Israeli policies and actions that encouraged and rewarded refrain from terrorist acts were ...
A new strain of influenza virus found in harbor seals could represent a threat to wildlife and human health, according to the authors of a study appearing July 31 in mBio®, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology. It is crucial to monitor viruses like this one, which originated in birds and adapted to infect mammals, the authors say, so that scientists can better predict the emergence of new strains of influenza and prevent pandemics in the future.
"There is a concern that we have a new mammalian-transmissible virus to which humans haven't ...
Alexandria, VA – One man's trash is quickly becoming society's new treasure. In the August issue of EARTH Magazine, we explore how materials that were once considered garbage are now being recognized for their true potential as valuable energy resources capable of solving multiple problems at once. If successful, these "waste-to-energy" options could serve as a silver bullet – displacing fossil fuels, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and decreasing the amount of trash that winds up in already teeming landfills.
Although several of these options have existed for many ...
To protect a dangerous and endangered animal -- be it a tiger in Nepal or a wolf in Michigan - you really do have to ask people "how do you FEEL about your predatory neighbor?"
Effective conservation calls for not only figuring out what protected species need – like habitat and food sources. It also requires an understanding of what it takes for their human neighbors to tolerate them. A Michigan State University doctoral student studying tigers in Nepal found that those feelings can provide critical information on how best to protect species.
"People have complex psychological ...