(Press-News.org) New York, NY and Oxford, UK, August 1, 2012 – The body has a built-in system known as autophagy, or 'self-eating,' that controls how cells live or die. Deregulation of autophagy is linked to the development of human diseases, including neural degeneration and cancer.
In a study published online this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, scientists at the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research in Oxford discovered a critical molecular switch that regulates autophagy. They also studied the links between autophagy and a cellular process called senescence that stops cell growth permanently.
The researchers identified ASPP2, a tumor suppressor, as a molecular switch that can dictate the ability of a common cancer gene, known as the RAS oncogene, to either stop or promote senescence.
As Yihua Wang and researchers in Xin Lu's group at the Ludwig Institute investigated the life cycle of fibroblast cells – the most common connective tissue cells in animals – they found that reduced levels of the ASPP2 protein increase RAS oncogene-induced autophagic activity. This in turn prevented cells from entering senescence. Without ASPP2, the cells continued to proliferate unchecked, thereby promoting tumor growth.
ASPP2 is known to play a role in suppressing tumor development. Mice that have a deficiency or malfunction in this protein have a predisposition to developing tumors. And low ASPP2 levels in patients are linked to poor prognoses in cancers, such as large B-cell lymphomas. Reduced ASPP2 expression has also been observed in highly metastatic breast tumors. But until now, researchers did not understand why.
"We found that in the presence of the common cancer-causing RAS oncogene, ASPP2 interacted with a protein complex that is responsible for deciding cell fate via autophagy," said Yihua Wang, PhD, Ludwig researcher in Oxford.
"What this means is that the cell's emergency stop button is disabled when ASPP2 expression is reduced or lost, allowing it to proliferate unchecked as with cancer," added Wang.
"The balance between the RAS oncogene and ASPP2 activity is crucial to determining whether or not tumor growth is promoted. Our next step will be to identify ways to alter ASPP2 activity at that critical switch point. This could be an effective way to treat cancers with reduced ASPP2 expression and mutated RAS, such as breast and colon cancers," concluded Wang.
"Some of the recently developed anti-cancer drugs are potent inducers of autophagy. The new findings may also offer an explanation as to why patient response to these drugs can vary dramatically. There are factors at play within the body that can dictate authophagic activity and impact clinical outcomes," said Xin Lu, PhD, director of Ludwig's Oxford Branch. "While further study is needed, these findings may in the longer term help doctors to identify patients who are more likely to respond well to autophagic inhibition," added Lu.
###About The Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research
LICR is an international non-profit organization committed to improving the understanding and control of cancer through integrated laboratory and clinical discovery. Leveraging its worldwide network of investigators and the ability to sponsor and conduct its own clinical trials, the Institute is actively engaged in translating its discoveries into applications for patient benefit. Since its establishment in 1971, the Institute has expended more than $1.5 billion on cancer research.
Molecular switch identified that controls key cellular process
2012-08-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Test flight over Peru ruins could revolutionize archaeological mapping
2012-08-02
Archaeological sites that currently take years to map will be completed in minutes if tests underway in Peru of a new system being developed at Vanderbilt University go well.
The Aurora Flight Sciences unmanned aerial vehicle will be integrated into a larger system that combines the flying device that can fit into a backpack with a software system that can discern an optimal flight pattern and transform the resulting data into three-dimensional maps. The project is an interdisciplinary collaboration between Vanderbilt archaeologist Steven Wernke and engineering professor ...
In pilot study, a peptide controls blood sugar in people with congenital hyperinsulinism
2012-08-02
A pilot study in adolescents and adults has found that an investigational drug shows promise as the first potential medical treatment for children with the severest type of congenital hyperinsulinism, a rare but potentially devastating disease in which gene mutations cause insulin levels to become dangerously high.
"There is currently no effective medicine for children with the most common and most severe form of hyperinsulinism," said study leader Diva D. De Leon, M.D., a pediatric endocrinologist at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia. "Our new research shows that ...
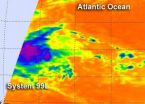
NASA satellite sees strength in developing Atlantic tropical low
2012-08-02
NASA's Aqua satellite spotted some very cold, high, thunderstorms around the center of a tropical low pressure area in the Atlantic Ocean today, indicating that the system is getting stronger and more organized.
The low pressure area, designated as "System 99L" was located about 850 miles east of the southern Windward Islands, near 10.7 North latitude and 46.9 West longitude. It was moving west between 15 and 20 mph.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over System 99L on August 1 at 0405 UTC (12:05 a.m. EDT) and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an ...
Caffeine may ease Parkinson's symptoms
2012-08-02
Montreal, August 1, 2012 – Caffeine, which is widely consumed around the world in coffee, tea and soft drinks, may help control movement in people suffering from Parkinson's. This is the finding of a study conducted at the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre (RI MUHC) that was recently published in Neurology®, the official journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study opens the door to new treatment options for Parkinson's disease that affects approximately 100 000 Canadians.
"This is one of the first studies to show the benefits of caffeine ...
Researchers discover female spiders produce mating plugs to prevent unwanted sex from males
2012-08-02
Scientists at the Smithsonian and their colleagues have discovered a new mechanism of animal mating plug production. In the giant wood spider Nephila pilipes, a highly sexually dimorphic and polygamous species, many small males compete with one other for access to a few huge females. During copulation these males are known to sever their own genitals in an attempt to plug the female, thereby gaining paternity advantage by preventing other males from mating with her.
Until recently however, nothing has been known about the origin and function of additional and very solid ...
NASA sees twin typhoons headed for double China landfall
2012-08-02
NASA's Terra satellite captured two tropical cyclones on visible imagery today, August 1 as they head for landfall. Typhoon Saola is approaching Taiwan and Typhoon Damrey approaching southern Japan, are both headed for landfall in China. Saola is forecast to landfall south of Shanghai on August 3, while Damrey is forecast to make landfall north of Shanghai on August 2.
NASA satellites have been tracking the twin tropical troublemakers, providing forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center with visible, infrared and microwave imagery. The Moderate Resolution Imaging ...
Wrecks and effects
2012-08-02
A study by a University of Iowa economist finds that many car race fans do, indeed, watch NASCAR races because they want to see car wrecks, but more of them have been tuning in to see who actually wins the race since the circuit adopted its Chase for the Cup championship series in 2004.
John Solow, a professor of economics in the Tippie College of Business, and co-author Peter Von Allmen of Skidmore College, looked at 135 NASCAR races between 2001 and 2009. They used a formula that measured the impact on each race's television ratings by incorporating a dozen statistics, ...
Writing graphics software gets much easier
2012-08-02
Image-processing software is a hot commodity: Just look at Instagram, a company built around image processing that Facebook is trying to buy for a billion dollars. Image processing is also going mobile, as more and more people are sending cellphone photos directly to the Web, without transferring them to a computer first.
At the same time, digital-photo files are getting so big that, without a lot of clever software engineering, processing them would take a painfully long time on a desktop computer, let alone a cellphone. Unfortunately, the tricks that engineers use to ...
Google it?: Internet searches often provide inaccurate information about infant sleep safety
2012-08-02
Cincinnati, OH, August 2, 2012 – In 2010, 59% of the U.S. population used internet searches for health information, and parents searching for information regarding their children were among the top users. In 2011, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) published recommendations for infant sleep safety to reduce the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), suffocation, strangulation, and other accidental sleep-related deaths. However, according to a study scheduled for publication in The Journal of Pediatrics, Google internet searches related to infant sleep safety ...
HCOs find risks & opportunities in quest for reduced costs & improved quality
2012-08-02
Rochester, MN, August 2, 2012 – Many health care systems across the US have declined to participate in the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services' (CMMS) Accountable Care Organization (ACO) program, developed under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA), to improve efficiency and quality of health care delivery. In a groundbreaking collection of commentaries in the current issue of Mayo Clinic Proceedings, representatives of six leading health care organizations write about the challenges of reducing health care costs while improving health care quality. ...