(Press-News.org) A pilot study in adolescents and adults has found that an investigational drug shows promise as the first potential medical treatment for children with the severest type of congenital hyperinsulinism, a rare but potentially devastating disease in which gene mutations cause insulin levels to become dangerously high.
"There is currently no effective medicine for children with the most common and most severe form of hyperinsulinism," said study leader Diva D. De Leon, M.D., a pediatric endocrinologist at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia. "Our new research shows that this investigational drug, a peptide called exendin-(9-39), controls blood sugar levels in people, a very promising result."
The study appeared today online ahead of print in the journal Diabetes.
In congenital hyperinsulinism (HI), mutations disrupt the insulin-secreting beta cells in the pancreas. Uncontrolled, excessive insulin levels thus sharply reduce blood glucose levels, a condition called hypoglycemia. If untreated, hypoglycemia may cause irreversible brain damage or death in children. Congenital HI occurs in an estimated one in 50,000 U.S. children, with a higher incidence among Ashkenazic Jews and certain other groups.
The standard treatment for some forms of congenital HI is diazoxide, a drug that controls insulin secretion by opening potassium channels in beta cells. However, this drug does not work in the most common types of HI, in which mutations prevent these potassium channels from forming.
When abnormal beta cells occur only in a discrete portion of the pancreas, precise surgery on the tiny organ can remove the lesion and cure HI. The Congenital Hyperinsulinism Center at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia is a world leader in diagnosing such lesions and performing the curative surgery on newborns.
However, in roughly half of congenital HI cases, abnormal cells are diffused through the pancreas, and surgeons must remove nearly the entire pancreas. This leaves the majority of patients at high risk of developing diabetes.
The current study, which builds on previous research by De Leon and colleagues in animals, uses exendin-(9-39), which blocks the action of a hormone receptor, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), in beta cells. The GLP-1 receptor is currently the target of drugs that treat diabetes, using the opposite effect from that investigated in this HI study.
The current pilot study included nine subjects, aged 15 to 47 years old, who had hyperinsulinism caused by mutations in potassium channels. None were being treated for HI at the time of the study, but all were at risk of hypoglycemia during periods of fasting.
In all nine subjects, the drug controlled blood glucose levels during fasting. Exendin also controlled insulin secretion in cell studies of beta cells taken from newborns with HI. The current research did not focus on the biological mechanisms that occurred, but De Leon said the results are encouraging enough to progress to a clinical study in children with HI over the next year.
INFORMATION:
Financial support for this study came from the National Institutes of Health (grant 1R03DK07835), the Lester and Liesel Baker Foundation, and the Clifford and Katherine Goldsmith Foundation. De Leon's co-authors, all from Children's Hospital, were Charles A. Stanley, M.D., Andrew C. Calabria, M.D., Changhong Li, M.D., and Paul R. Gallagher In addition to their positions at Children's Hospital, De Leon, Stanley and Li also are in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
"The GLP-1 Receptor Antagonist Exendin-(9-39) Elevates Blood Fasting Glucose Levels in Congenital Hyperinsulinism due to Inactivating Mutations in the ATP-sensitive Potassium Channel," Diabetes, published online Aug.1, 2012, to appear in print, October 2012. doi: 10.2337/db12-0166.
About The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia: The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia was founded in 1855 as the nation's first pediatric hospital. Through its long-standing commitment to providing exceptional patient care, training new generations of pediatric healthcare professionals and pioneering major research initiatives, Children's Hospital has fostered many discoveries that have benefited children worldwide. Its pediatric research program is among the largest in the country, ranking third in National Institutes of Health funding. In addition, its unique family-centered care and public service programs have brought the 516-bed hospital recognition as a leading advocate for children and adolescents. For more information, visit http://www.chop.edu.
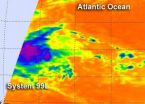
NASA's Aqua satellite spotted some very cold, high, thunderstorms around the center of a tropical low pressure area in the Atlantic Ocean today, indicating that the system is getting stronger and more organized.
The low pressure area, designated as "System 99L" was located about 850 miles east of the southern Windward Islands, near 10.7 North latitude and 46.9 West longitude. It was moving west between 15 and 20 mph.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over System 99L on August 1 at 0405 UTC (12:05 a.m. EDT) and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an ...
Montreal, August 1, 2012 – Caffeine, which is widely consumed around the world in coffee, tea and soft drinks, may help control movement in people suffering from Parkinson's. This is the finding of a study conducted at the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre (RI MUHC) that was recently published in Neurology®, the official journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study opens the door to new treatment options for Parkinson's disease that affects approximately 100 000 Canadians.
"This is one of the first studies to show the benefits of caffeine ...
Scientists at the Smithsonian and their colleagues have discovered a new mechanism of animal mating plug production. In the giant wood spider Nephila pilipes, a highly sexually dimorphic and polygamous species, many small males compete with one other for access to a few huge females. During copulation these males are known to sever their own genitals in an attempt to plug the female, thereby gaining paternity advantage by preventing other males from mating with her.
Until recently however, nothing has been known about the origin and function of additional and very solid ...
NASA's Terra satellite captured two tropical cyclones on visible imagery today, August 1 as they head for landfall. Typhoon Saola is approaching Taiwan and Typhoon Damrey approaching southern Japan, are both headed for landfall in China. Saola is forecast to landfall south of Shanghai on August 3, while Damrey is forecast to make landfall north of Shanghai on August 2.
NASA satellites have been tracking the twin tropical troublemakers, providing forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center with visible, infrared and microwave imagery. The Moderate Resolution Imaging ...
A study by a University of Iowa economist finds that many car race fans do, indeed, watch NASCAR races because they want to see car wrecks, but more of them have been tuning in to see who actually wins the race since the circuit adopted its Chase for the Cup championship series in 2004.
John Solow, a professor of economics in the Tippie College of Business, and co-author Peter Von Allmen of Skidmore College, looked at 135 NASCAR races between 2001 and 2009. They used a formula that measured the impact on each race's television ratings by incorporating a dozen statistics, ...
Image-processing software is a hot commodity: Just look at Instagram, a company built around image processing that Facebook is trying to buy for a billion dollars. Image processing is also going mobile, as more and more people are sending cellphone photos directly to the Web, without transferring them to a computer first.
At the same time, digital-photo files are getting so big that, without a lot of clever software engineering, processing them would take a painfully long time on a desktop computer, let alone a cellphone. Unfortunately, the tricks that engineers use to ...
Cincinnati, OH, August 2, 2012 – In 2010, 59% of the U.S. population used internet searches for health information, and parents searching for information regarding their children were among the top users. In 2011, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) published recommendations for infant sleep safety to reduce the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), suffocation, strangulation, and other accidental sleep-related deaths. However, according to a study scheduled for publication in The Journal of Pediatrics, Google internet searches related to infant sleep safety ...
Rochester, MN, August 2, 2012 – Many health care systems across the US have declined to participate in the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services' (CMMS) Accountable Care Organization (ACO) program, developed under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA), to improve efficiency and quality of health care delivery. In a groundbreaking collection of commentaries in the current issue of Mayo Clinic Proceedings, representatives of six leading health care organizations write about the challenges of reducing health care costs while improving health care quality. ...
Proteins do not need to be surrounded by water to carry out their vital biological functions, according to scientists from the Institut de Biologie Structurale (IBS) in Grenoble, the University of Bristol, the Australian National University, the Institut Laue Langevin and the Jülich Centre for Neutron Science.
In a new paper, published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, the team used a state-of-the-art neutron scattering technique to demonstrate that when myoglobin, an oxygen-binding protein found in the muscle tissue of vertebrates, is enclosed in a sheath ...
A chemical sensing system developed by engineers at the University of Connecticut is believed to be the first of its kind capable of detecting vapors from buried landmines and other explosive devices with the naked eye rather than advanced scientific instrumentation.
The research was first reported in the May 11, 2012 online edition of Advanced Functional Materials.
The key to the system is a fluorescent nanofiberous film that can detect ultra-trace levels of explosive vapors and buried explosives when applied to an area where explosives are suspected. A chemical reaction ...