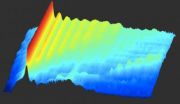
(Press-News.org) Two NASA satellites have captured data on the activity of Typhoon Haikui as it nears the China coast. NASA's Terra satellite provided a visible look at the storm, while NASA's Aqua satellite investigated it in infrared light. Both showed some strong thunderstorms within that were likely packing heavy rainfall.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Typhoon Haikui on August 5. The AIRS instrument captured an infrared image of the cloud temperatures that showed the strongest storms and heaviest rainfall in all quadrants of the storm except the northern area. The strongest storms had cloud top temperatures near or exceeding -63 Fahrenheit (-52 Celsius). In an image captured on August 5 at 0441 UTC (12:41 a.m. EDT), those strong storms were seen over Okinawa, Japan. On August 6, 2012 at 0220 UTC NASA's Terra satellite captured a visible image of Haikui. It showed the western edge of the storm brushing mainland China.
On August 6 at 0900 UTC (5 a.m. EDT), the center of Haikui was northeast of Ishigakijima, Okinawa, Japan. Ishigakijima is the Okinawa Prefecture's third largest island and is Japan's southernmost city island. Haikui is also about 220 nautical miles (253 miles/407 km) northeast of Taipei, Taiwan. The storm is moving to the west-southwest at 5 knots (5.7 mph/9.2 kmh). Its maximum sustained winds were near 65 knots (75 mph/120 kmh).
Haikui is expected to make landfall south of Shanghai early on August 8.
INFORMATION:
High-resolution MODIS image available at: http://lance-modis.eosdis.nasa.gov/cgi-bin/imagery/single.cgi?image=Haikui.A2012219.0220.2km.jpg.
NASA sees Typhoon Haikui approaching China in visible and infrared light
2012-08-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Disney Research technique improves rendering of smoke, dust and participating media
2012-08-07
ZURICH – Computer graphic artists often struggle to render smoke and dust in a way that makes a scene look realistic, but researchers at Disney Research, Zürich, Karlsruhe Technical Institute in Germany, and the University of Montreal in Canada have developed a new and efficient way to simulate how light is absorbed and scattered in such scenes.
"Our technique could be used to simulate anything from vast cloudscapes, to everyday 'solid' objects such as a glass of orange juice, a piece of fruit or virtually any organic substance," said Dr. Wojciech Jarosz of Disney Research ...
The scientific side of steroid use and abuse
2012-08-07
Leslie Henderson is concerned about steroid abuse, not necessarily by sports luminaries like Barry Bonds and Mark McGwire, but rather by adolescents.
"There is this disconnect among young people that somehow your emotions, your thought processes—things that have to do with your brain—are separate and different from what steroids may be doing to your body—your muscles, your heart, or your liver, or anything like that," says Henderson, a professor of physiology and neurobiology, and of biochemistry at the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth. She is also the senior associate ...
Risk of stroke from cardiac catheterizations
2012-08-07
MAYWOOD, Il. -- When a patient undergoes a cardiac catheterization procedure such as a balloon angioplasty, there's a slight risk of a stroke or other neurological complication.
While the risk is extremely small, neurologists nevertheless may expect to see catheterization-induced complications because so many procedures are performed, Loyola neurologists write in the journal MedLink Neurology.
Cardiac catheterizations include diagnostic angiograms, balloon angioplasties and stent placements. More than 1.4 million procedures are successfully performed each year. Cardiac ...
Mothers, children underestimate obesity in China
2012-08-07
Childhood obesity is on the rise in China, and children and parents there tend to underestimate body weight, according to Penn State health policy researchers.
"Because many overweight Chinese children underestimate their weight, they are less likely to do anything to improve their diet or exercise patterns," said Nengliang Yao, graduate student in health policy and administration. "If they don't make changes, they are likely to be obese and have a lot of health problems in the future -- as we often see in the United States already."
Children between the ages of 6 and ...
New study examines injuries to US workers with disabilities
2012-08-07
A new study conducted by researchers at the Center for Injury Research and Policy of The Research Institute at Nationwide Children's Hospital and The Ohio State University compared medically attended noncccupational and occupational injuries among U.S. workers with and without disabilities.
The study, appearing online in the American Journal of Public Health, found that workers with disabilities are significantly more likely to experience both nonoccupational and occupational injuries than those without disabilities. Rates of nonoccupational and occupational injuries ...
Racial differences in diabetes diagnostic thresholds
2012-08-07
BOSTON – Healthcare providers should take into account differences among racial groups when using hemoglobin A1C levels to diagnose and monitor diabetes, new research from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center suggests.
In a study published Aug. 7 in the Annals of Internal Medicine, researchers analyzed National Health and Nutrition Survey data from 2005 to 2008 to examine the association between hemoglobin A1C levels in black and white adults and the risk for retinopathy, an eye complication of diabetes that is detectable early in the disease and can ultimately lead to ...
Extreme plasma theories put to the test
2012-08-07
The first controlled studies of extremely hot, dense matter have overthrown the widely accepted 50-year old model used to explain how ions influence each other's behavior in a dense plasma. The results should benefit a wide range of fields, from research aimed at tapping nuclear fusion as an energy source to understanding the inner workings of stars.
The study also demonstrates the unique capabilities of the Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) X-ray laser at the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory. While researchers have created extremely ...
Brain signal IDs responders to fast-acting antidepressant
2012-08-07
Scientists have discovered a biological marker that may help to identify which depressed patients will respond to an experimental, rapid-acting antidepressant. The brain signal, detectable by noninvasive imaging, also holds clues to the agent's underlying mechanism, which are vital for drug development, say National Institutes of Health researchers.
The signal is among the latest of several such markers, including factors detectable in blood, genetic markers, and a sleep-specific brain wave, recently uncovered by the NIH team and grantee collaborators. They illuminate ...
Scientists define new limits of microbial life in undersea volcanoes
2012-08-07
By some estimates, a third of Earth's organisms live in our planet's rocks and sediments, yet their lives are almost a complete mystery.
This week, the work of microbiologist James Holden of the University of Massachusetts-Amherst and colleagues shines a light into this dark world.
In the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), they report the first detailed data on methane-exhaling microbes that live deep in the cracks of hot undersea volcanoes.
"Evidence has built that there's an incredible amount of biomass in the Earth's subsurface, in ...
WSU researcher sees how forests thrive after fires and volcanoes
2012-08-07
PULLMAN, Wash.—Forests hammered by windstorms, avalanches and wildfires may appear blighted, but a Washington State University researcher says such disturbances can be key to maximizing an area's biological diversity.
In fact, says Mark Swanson, land managers can alter their practices to enhance such diversity, creating areas with a wide variety of species, including rare and endangered plants and animals.
"The 1980 eruption of Mt. St. Helens, for example, has created very diverse post-eruption conditions, and has some of the highest plant and animal diversity in the ...