(Press-News.org) NASA scientist Tom Hanisco is helping to fill a big gap in scientists' understanding of how much urban pollution -- and more precisely formaldehyde -- ultimately winds up in Earth's upper atmosphere where it can wreak havoc on Earth's protective ozone layer.
He and his team at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., have developed an automated, lightweight, laser-induced fluorescence device that measures the levels of this difficult-to-measure organic compound in the lower troposphere and then again at much higher altitudes. The primary objective is determining how much pollution a storm can transport through convection and then using those insights to improve chemistry-climate models. "It's a major problem in modeling knowing how to treat transport and clouds," Hanisco explained.
In the spring, he flew the In-Situ Airborne Formaldehyde Instrument for the first time on a NASA DC-8 research aircraft, a former passenger airplane that can fly up to 43,000 feet.
Size and Sensitivity
"People like this instrument because it's small, sensitive, and easy to maintain," said Hanisco. The instrument weighs only 60 pounds, and therefore is easily installed inside other research aircraft, including NASA's ER-2, Global Hawk, and WB57, which fly at much higher altitudes. In addition, it's automated and doesn't require anyone onboard to operate it, Hanisco said.
Prior to its development, only one other airborne instrument could measure formaldehyde. That instrument, however, weighed 600 pounds, required an onboard operator, and used a less-sensitive measurement technique -- absorption spectroscopy -- to gather data.
"I've been doing laser-induced fluorescence on other molecules for a while," Hanisco said, explaining why he sought and received Goddard Internal Research and Development funds to apply the measurement technique to a formaldehyde-sensitive instrument. "Formaldehyde isn't measured well at high altitudes. There was a real need for improvement."
With laser-induced fluorescence (LIF), a laser first illuminates the species of interest and "then you watch it fluoresce. It is a single photon-counting instrument," Hanisco said. Consequently, it's faster and more sensitive -- even at concentrations in the parts per trillion, he said.
The DC-8 campaign in Kansas, sponsored by the National Center for Atmospheric Research's Deep Convective Clouds and Chemistry Project, bore out the wisdom of his pursuit, proving that his instrument offered a factor-of-10 improvement in size, sensitivity, and complexity. During that campaign, a DC-8 flew as low as 500 feet above the ground and sampled air entering a storm. It then spiraled up to 30,000 to 40,000 feet and measured the air coming out at the top of the storm.
'Big Step Forward'
The instrument found that 30 to 40 percent of the formaldehyde produced in the "boundary" layer -- the lowest part of the troposphere closest to Earth's surface -- was transported to the upper troposphere during storms. "That number is a rough guideline, but we didn't have it before. Every storm is different, but knowing how much air gets through is a big step forward."
Hanisco attributes the instrument's success to its greatly simplified design and a new fiber-laser system that is smaller and less expensive than those used in other LIF-type instruments. He also attributes its success to a new air-sampling system, which features a glass- and Teflon-coated tube that draws in and directs air into the instrument's detection cell. Though the polymer-coated sampling system allows air to flow quickly, its surface prevents particles from sticking -- particularly useful because they could corrupt results. "We had to work hard to ensure that the sampling system was every bit as good as the detection," Hanisco said.
Hanisco anticipates many other flight opportunities in the future. "There was a real need for this instrument. There aren't a lot of instruments out there doing this."
INFORMATION:
NASA's new way to track formaldehyde
2012-08-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Thinking abstractly may help to boost self-control
2012-08-10
Many of the long term goals people strive for — like losing weight — require us to use self-control and forgo immediate gratification. And yet, denying our immediate desires in order to reap future benefits is often very hard to do.
In a new article in the August issue of Current Directions in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science, researchers Kentaro Fujita and Jessica Carnevale of The Ohio State University propose that the way people subjectively understand, or construe, events can influence self-control.
Research from psychological ...
'Treating the whole person with autism' sets direction for parent-clinician collaboration
2012-08-10
NEW YORK, N.Y. (August 9, 2012) – Over 400 attendees from across the U.S. and around the world participated in the first national conference for families and professionals, "Treating the Whole Person with Autism: Comprehensive Care for Children and Adolescents with ASD."
Autism Speaks, the world's leading autism science and advocacy organization, organized and hosted the conference in collaboration with educational partners at Nationwide Children's Hospital (NCH), The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), and the Health ...
Gecko feet hold clues to creating bandages that stick when wet
2012-08-10
VIDEO:
Researchers Alyssa Stark and Tim Sullivan test the adhesion of a geckos feet in water. Their findings may help improve the adhesion of bandages, sutures and similar items in moist...
Click here for more information.
Akron, Ohio, August 9, 2012 — Scientists already know that the tiny hairs on geckos' toe pads enable them to cling, like Velcro, to vertical surfaces. Now, University of Akron researchers are unfolding clues to the reptiles' gripping power in wet conditions ...
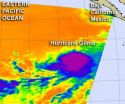
The cold power of Hurricane Gilma revealed by NASA satellite
2012-08-10
High, cold cloud tops with bitter cold temperatures are indicators that there's a lot of strength in the uplift of air within a tropical cyclone. NASA's Aqua satellite passed by Hurricane Gilma and saw a concentrated area of very cold cloud tops.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Hurricane Gilma on August 9 at 5:53 a.m. EDT. The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an infrared image of the cloud temperatures that showed the strongest storms and heaviest rainfall were wrapped around the storm's center. Cloud top temperatures in that area were as cold ...
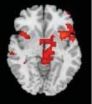
Brain hubs boil when hoarders face pitching their own stuff
2012-08-10
In patients with hoarding disorder, parts of a decision-making brain circuit under-activated when dealing with others' possessions, but over-activated when deciding whether to keep or discard their own things, a National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)-funded study has found. NIMH is part of the National Institutes of Health.
Brain scans revealed the abnormal activation in areas of the anterior cingulate cortex and insula known to process error monitoring, weighing the value of things, assessing risks, unpleasant feelings, and emotional decisions.
NIMH grantee David ...
UCLA scientist discovers plate tectonics on Mars
2012-08-10
For years, many scientists had thought that plate tectonics existed nowhere in our solar system but on Earth. Now, a UCLA scientist has discovered that the geological phenomenon, which involves the movement of huge crustal plates beneath a planet's surface, also exists on Mars.
"Mars is at a primitive stage of plate tectonics. It gives us a glimpse of how the early Earth may have looked and may help us understand how plate tectonics began on Earth," said An Yin, a UCLA professor of Earth and space sciences and the sole author of the new research.
Yin made the discovery ...
Blood test for Alzheimer's gaining ground
2012-08-10
The possibility of an inexpensive, convenient test for Alzheimer's disease has been on the horizon for several years, but previous research leads have been hard to duplicate.
In a study to be published in the August 28 issue of the journal Neurology, scientists have taken a step toward developing a blood test for Alzheimer's, finding a group of markers that hold up in statistical analyses in three independent groups of patients.
"Reliability and failure to replicate initial results have been the biggest challenge in this field," says lead author William Hu, MD, PhD, ...
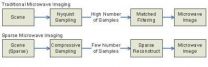
Sparse microwave imaging: A new concept in microwave imaging technology
2012-08-10
Sparse microwave imaging is a novel concept in microwave imaging that is intended to deal with the problems of increasing microwave imaging system complexity caused by the requirements of the system applications. Under the support of the 973 program "Study of theory, system and methodology of sparse microwave imaging", Chinese scientists have conducted considerable research into most aspects of sparse microwave imaging, including its fundamental theories, system design, performance evaluation and applications. Their work, consisting of a series of papers, was published ...
North American freshwater fishes race to extinction
2012-08-10
North American freshwater fishes are going extinct at an alarming rate compared with other species, according to an article in the September issue of BioScience. The rate of extinctions increased noticeably after 1950, although it has leveled off in the past decade. The number of extinct species has grown by 25 percent since 1989.
The article, by Noel M. Burkhead of the US Geological Survey, examines North American freshwater fish extinctions from the end of the 19th Century to 2010, when there were 1213 species in the continent, or about 9 percent of the Earth's freshwater ...
Rustin Records Sign To Blue Pie's White Label Music Program
2012-08-10
Blue Pie are excited to announce that California-based independent label Rustin Records has signed to our White Label Music Program. The program provides labels with back end infrastructure and management systems.
Rustin Records was established by Sam Rustin in August of 2008 and is currently being run by both himself and Earl Pampaian. Sam also acts as producer and sound engineer when recording his label's exciting roster of artists, including Mizz Playah Proof, M.O.B., Shorty, and Vital Impulse.
Rustin Records primarily focuses on Hip Hop, but is open to other ...