(Press-News.org) An intensifying Tropical storm called Kai-Tak (locally known as Helen) is causing more rain in the Philippines as it passes over northern Luzon. The Philippines have had a very wet month with the capital of Manila experiencing massive flooding earlier this month. NASA's TRMM satellite identified where the heavy rain was falling.
Kai-tak has caused another day of warnings in the Philippines. On August 14, Public storm warning signal #1 is in effect for these provinces in Luzon: La Union, Nueva Ecija, Pangasinan, Rest of Aurora, and Tarlac.
In addition, Public storm warning signal #2 has been posted for these Luzon provinces: the Abra and Batanes Group of Islands, Apayao, Benguet; Cagayan (including Calayan and Babuyan Group of Island), Ifugao, Ilocos South and North, Isabela, Kalinga, Mt. Province, Northern Aurora, Nueva Vizcaya, and Quirino.
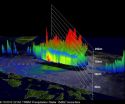
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite flew over Kai-tak on August 13, 2012 at 2216 UTC 4:16 p.m. EDT). TRMM's Microwave Imager (TMI) and Precipitation Radar (PR) data showed that the tropical storm was dropping extreme amounts of rainfall. TRMM PR revealed that the most intense rainfall of over 100mm/hr. (~3.9 inches) was east of the Philippines over the open waters of the Pacific Ocean. Some light to moderate rainfall from Kai-tak was shown falling on the island of Luzon.
TRMM's Precipitation Radar (PR) data were used in a 3-D image to show the vertical scale of the numerous powerful storms near Kai-tak's center. Some convective storms were reaching heights of about 15km (~9.3 miles).
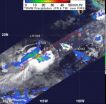
Tropical storm Kai-tak had maximum sustained winds near 50 knots (57.5 mph/92.6 kmh). It was located about 220 nautical miles (253 miles/407 km) northeast of Manila, Philippines, near 17.4 North latitude and 123.1 East longitude. Kai-tak was moving to the southwest at 10 knots (11.5 mph/18.5 kmh) and is expected to turn to the west-northwest.
Satellite data from August 14 has shown that Kai-tak's low-level center has become more organized. The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies onboard NASA's Aqua satellite showed cooler cloud top temperatures (a sign of more uplift and strength in the storm).
Kai-tak is taking a track across northern Luzon and is expected to move south of Taiwan before making landfall in China.
INFORMATION:
NASA sees more rain for the Philippines from Tropical Storm Kai-Tak
2012-08-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA's TRMM Satellite sees a small area of heavy rain left in Tropical Storm Hector
2012-08-15
Tropical Storm Hector is battling wind shear over the open waters of the Eastern Pacific Ocean, and NASA satellite data shows that has been affecting its organization and rainfall rates.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite known as TRMM is managed by both NASA and the Japanese Space Agency. From its orbit in space, TRMM's instruments can estimate rainfall from tropical cyclones.
The TRMM satellite captured rainfall rates from Tropical Storm Hector on August 14, 2012 1:28 a.m. EDT. TRMM data showed that Hector had a small area of moderate to heavy rainfall ...
NASA seeing sprites
2012-08-15
VIDEO:
Filmed at 10,000 frames per second by Japan's NHK television, movies like this of electromagnetic bursts called "sprites " will help scientists better understand how weather high in the atmosphere relates...
Click here for more information.
High above the clouds during thunderstorms, some 50 miles above Earth a different kind of lightning dances. Bursts of red and blue light, known as "sprites," flash for a scant one thousandth of a second. They are often ...
Meditation reduces loneliness
2012-08-15
Many elderly people spend their last years alone. Spouses pass and children scatter. But being lonely is much more than a silent house and a lack of companionship. Over time, loneliness not only takes a toll on the psyche but can have a serious physical impact as well.
Feeling lonely has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, Alzheimer's disease, depression and even premature death. Developing effective treatments to reduce loneliness in older adults is essential, but previous treatment efforts have had limited success.
What to do? Researchers at UCLA ...
Need an expert? Try the crowd
2012-08-15
In 1714, the British government held a contest. They offered a large cash prize to anyone who could solve the vexing "longitude problem" — how to determine a ship's east/west position on the open ocean — since none of their naval experts had been able to do so.
Lots of people gave it a try. One of them, a self-educated carpenter named John Harrison, invented the marine chronometer — a rugged and highly precise clock — that did the trick. For the first time, sailors could accurately determine their location at sea.
A centuries-old problem was solved. And, arguably, crowdsourcing ...
An artificial retina with the capacity to restore normal vision
2012-08-15
Two researchers at Weill Cornell Medical College have deciphered a mouse's retina's neural code and coupled this information to a novel prosthetic device to restore sight to blind mice. The researchers say they have also cracked the code for a monkey retina — which is essentially identical to that of a human —and hope to quickly design and test a device that blind humans can use.
The breakthrough, reported in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), signals a remarkable advance in longstanding efforts to restore vision. Current prosthetics provide blind ...
Deep inside the body, tiny mechanical microscope
2012-08-15
Tiny space age probes — those that can see inside single living cells — are increasingly being used to diagnose illness in hard-to-reach areas of the body.
NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital/Weill Cornell Medical Center's Dr. Michel Kahaleh often threads a tiny microscope into the narrow bile ducts that connect the liver to the small intestine to hunt for cancer. He also uses the device to minutely explore the pancreatic duct as one of a few doctors in the country to use such technology in this way.
But because these devices are comparatively new, Dr. Kahaleh, chief of ...
Study finds that yo-yo dieting does not thwart weight loss efforts or alter metabolism long term
2012-08-15
SEATTLE – Yo-yo dieting – the repetitive loss and regain of body weight, also called weight cycling – is prevalent in the Western world, affecting an estimated 10 percent to 40 percent of the population. The degree to which weight cycling may impact metabolism or thwart a person's ability to lose weight in the long run has been unclear – until now.
A new study by researchers at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, published online in the journal Metabolism, for the first time has shown that a history of yo-yo dieting does not negatively affect metabolism or the ability ...
'Strawberry' birthmarks grow rapidly when babies just weeks old, Mayo Clinic finds
2012-08-15
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Strawberry-shaped birthmarks called infantile hemangiomas (http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/hemangioma/DS00848) grow rapidly in infants much earlier than previously thought, Mayo Clinic and University of California, San Francisco, researchers found. Their study, published online in the journal Pediatrics (http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/), suggests that babies with complication-causing hemangiomas should be immediately referred to dermatologists for further evaluation.
MULTIMEDIA ALERT: For multimedia resources and video of Dr. Tollefson, ...
SF State researchers probe asymmetric warfare between earwigs
2012-08-15
SAN FRANCISCO -- Symmetrical looks are highly prized in the animal kingdom, but according to a new report by San Francisco State University biologists on an insect called the maritime earwig, asymmetry might come with its own perks.
Animals—including humans—seem to use symmetry as a shortcut for evaluating potential mates. Symmetrical features usually indicate normal development, while asymmetry could point to an underlying developmental defect that would render a mate less fit.
"The evolutionary theory that underpins symmetry in mate choice is very straightforward," ...
Can genes be early warning indicators of environmental risks?
2012-08-15
Though no systemic studies have been performed, it is generally believed that genes are the most sensitive toxicological endpoints for pollutants, and are thus desirable early warning indicators of environmental risks. A recent study, however, unexpectedly found that the sensitivity of the gene expression effect for cadmium was significantly lower than the individual level chronic toxicity indicators (such as the no observed effect concentration, NOEC). Therefore, the gene expression effect may not be the most sensitive toxicological endpoint. Dr Yan Zhenguang, Prof. Liu ...