(Press-News.org)
VIDEO:
This video shows the annual cycle of global and Asian fatal landslides (for the full dataset described in the research paper).
They have been divided into the 52 weeks...
Click here for more information.
Landslides kill ten times more people across the world than was previously thought, according to research by Durham University, UK.
A new database of hazards shows that 32,300 people died in landslides between 2004 and 2010. Previous estimates ranged from 3,000 to 7,000 fatalities.
The database, which provides the first detailed analysis of fatal landslides across the world, maps hotspots including China, Central and South America, and India.
The researchers say that the new database, the Durham Fatal Landslide Database (DFLD), can help policymakers to prioritise areas for action to manage hazards and to lessen the risks to human populations living in hotspot regions.
The findings are published in the journal Geology.
Lead researcher, Professor David Petley, a Geographer at the International Landslide Centre, and Co-Director of The Institute of Hazard, Risk and Resilience, Durham University, said: "The environmental effects of landslides are often devastating for nearby human populations.
"We need to recognise the extent of the problem and take steps to manage what is a major environmental risk to people across the world. Our database will enable us to do this by identifying areas most at risk and could help to save thousands of lives."
The DFLD includes only fatal landslides and is compiled using a number of search tools and analysis of government statistics, aid agency reports, and research papers.
It is still likely that the database underestimates the number of landslides and deaths. The database excludes data from landslides caused by earthquakes due to the high level of uncertainty associated with these events. Following an earthquake, where there is a fatal landslide, the deaths are attributed to the earthquake trigger itself, rather than the landslide.
The researchers say that weather patterns, deforestation, melting permafrost in high mountainous areas, and high and increasing human population densities are important factors in the cause, distribution, number, extent and effects of landslides.
More fatal landslide events are recorded in May to October and the dominant global trigger is rain from the monsoon. Tropical cyclones also generate extreme rainfall events that trigger landslides in Asia, and hurricanes have the same effect on regions in the Caribbean and Central America.
In some areas with a history of fatal landslides, such as Hong Kong, programmes to mitigate the risks of landslides have been successful.
Professor David Petley said: "Areas with a combination of high relief, intense rainfall, and a high population density are most likely to experience high numbers of fatal landslides. Landslides are a global hazard requiring a major change in perception and policy.
"There are things that we can do to manage and mitigate landslide risks such as controlling land use, proactive forest management, and guiding development away from vulnerable areas."
Global landslide hotspots:
Southern edge of the Himalayan Arc
South west coast of India
Sri Lanka
Southern and eastern coasts of China
Central China, notably the mountains around the Sichuan Basin
Western edge of the Philippine Sea plate (Japan, Taiwan and the Philippines)
Central Caribbean islands including Haiti
Indonesia, especially in Java
Along the mountainous chain from Mexico, Central America, to Chile, South America, but especially in Colombia
INFORMATION:
Landslide fatalities are greater than previously thought
2012-08-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New report presents research program for solar and space physics over the next decade
2012-08-16
WASHINGTON — A new report from the National Research Council presents a prioritized program of basic and applied research for 2013-2022 that will advance scientific understanding of the sun, sun-Earth connections and the origins of "space weather," and the sun's interactions with other bodies in the solar system. This second decadal survey in solar and space physics -- the product of a 18-month effort by more than 85 solar and space physicists and space system engineers -- lays out four scientific goals for the next 10 years along with guiding principles and recommended ...
Phoenix cluster sets record pace at forming stars
2012-08-16
VIDEO:
This animation shows how large numbers of stars form in the Phoenix Cluster. It begins by showing several galaxies in the cluster and hot gas (in red). This hot gas...
Click here for more information.
Astronomers have found an extraordinary galaxy cluster, one of the largest objects in the universe, that is breaking several important cosmic records. Observations of the Phoenix cluster with NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory, the National Science Foundation's South ...
Researchers reveal behaviors of the tiniest water droplets
2012-08-16
A new study by researchers at the University of California, San Diego, and Emory University has uncovered fundamental details about the hexamer structures that make up the tiniest droplets of water, the key component of life – and one that scientists still don't fully understand.
The research, recently published in The Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS), provides a new interpretation for experimental measurements as well as a vital test for future studies of our most precious resource. Moreover, understanding the properties of water at the molecular level ...
Record-breaking galaxy cluster discovered
2012-08-16
A massive galaxy cluster nearly six billion light years from Earth has been discovered with an astounding and unexpected burst of star formation – more prodigious than any galaxy cluster yet observed, an international team of astronomers and NASA announced today.
In a wide-ranging discussion on the eve of the announcement, two of the leading astronomers on the project talked about the record-breaking galaxy cluster, called Phoenix, and how its surprising properties are prompting astronomers to re-think how galaxy clusters – among the largest structures in the universe ...
Good vibrations
2012-08-16
A long-time staple of science fiction is the tractor beam, a technology in which light is used to move massive objects – recall the tractor beam in the movie Star Wars that captured the Millennium Falcon and pulled it into the Death Star. While tractor beams of this sort remain science fiction, beams of light today are being used to mechanically manipulate atoms or tiny glass beads, with rapid progress being made to control increasingly larger objects. Those who see major roles for optomechanical systems in a host of future technologies will take heart in the latest results ...
Team uncovers link between hormone levels and risk for metabolic disease
2012-08-16
JUPITER, FL, August 15, 2012 – Working with a national team of researchers, a scientist from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute has shown for the first time a link between low levels of a specific hormone and increased risk of metabolic disease in humans.
The study, published online ahead of print in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, focuses on the hormone adropin, which was previously identified by Scripps Research Associate Professor Andrew Butler's laboratory during an investigation of obese and insulin-resistant mice. Adropin is ...
Giant galaxy cluster sets record pace for star creation
2012-08-16
Astronomers have found an extraordinary galaxy cluster — one of the largest objects in the universe — that is breaking several important cosmic records. The discovery of this cluster, known as the Phoenix Cluster, made with the National Science Foundation's South Pole Telescope, may force astronomers to rethink how these colossal structures, and the galaxies that inhabit them, evolve.
Follow-up observations made in ultraviolet, optical and infrared wavelengths show that stars are forming in this object at the highest rate ever seen in the middle of a galaxy cluster. The ...
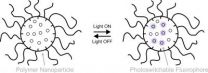
Designing tiny molecules that glow in water to shed light on biological processes
2012-08-16
CORAL GABLES, FL (August, 15, 2012)--University of Miami scientists have developed a way to switch fluorescent molecules on and off within aqueous environments, by strategically trapping the molecules inside water-soluble particles and controlling them with ultraviolet light. The new system can be used to develop better fluorescent probes for biomedical research.
Previous studies have used water-soluble particles to bring organic molecules into water. What is novel about this system is the use of a photoswitching mechanism in combination with these particles.
The findings ...
NSF's South Pole Telescope discovers a galaxy cluster creating stars at a record pace
2012-08-16
A National Science Foundation-funded radio telescope in Antarctica has found an extraordinary galaxy cluster that may force astronomers to rethink how galaxy clusters and the galaxies that inhabit them evolve.
The galaxy cluster was discovered some 5.7 billion light years from Earth by the 10-meter wide South Pole Telescope (SPT) located at NSF's Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station in Antarctica, which is funded by NSF's Office of Polar Programs.
NSF manages the U.S. Antarctic Program, through which it coordinates all U.S research and required logistical support on the ...
Lunar reconnaissance orbiter spectrometer detects helium in moon's atmosphere
2012-08-16
Scientists using the Lyman Alpha Mapping Project (LAMP) spectrometer aboard NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) have made the first spectroscopic observations of the noble gas helium in the tenuous atmosphere surrounding the Moon.
These remote-sensing observations complement in situ measurements taken in 1972 by the Lunar Atmosphere Composition Experiment (LACE) deployed by Apollo 17.
Although designed to map the lunar surface, the LAMP team expanded its science investigation to examine the far ultraviolet emissions visible in the tenuous atmosphere above the ...