Study shows long-term effects of radiation in pediatric cancer patients
TBI before age 3 ups rate of endocrine, metabolic and other complications
2012-08-22
(Press-News.org) For many pediatric cancer patients, total body irradiation (TBI) is a necessary part of treatment during bone marrow transplant– it's a key component of long term survival. But lengthened survival creates the ability to notice long term effects of radiation as these youngest cancer patients age. A University of Colorado Cancer Center study recently published in the journal Pediatric Blood & Cancer details these late effects of radiation.
"These kids basically lie on a table and truly do get radiation from head to toe. There is a little blocking of the lungs, but nothing of, for example, the brain or the kidneys," says Jean Mulcahy-Levy, MD, research fellow at the CU Cancer Center and the paper's first author.
Of 15 patients who received TBI before age 3, many developed endocrine and metabolic problems including testicular malfunction (78 percent), restrictive pulmonary disease due to high levels of blood triglycerides (74 percent), and cataracts (78 percent). Likewise, 90 percent of patients showed abnormally low levels of growth hormone, and 71 percent were considerably under height. Additional late effects of TBI included kidney, liver, skeletal and cardiac malfunction – and three of four patients whose IQ had been tested before TBI showed cognitive decline.
"Fifteen doesn't seem like a large number, but because we have such a good pediatric bone marrow transplant program here at Children's Hospital Colorado and radiation therapy program at the CU Cancer Center, we were able to get a large enough cohort of patients to see these overall effects," Mulcahy-Levy says.
The study supports the recommendations of the Children's Oncology Group for long term follow up care for children receiving TBI (survivorshipguidelines.org). Specifically, Mulcahy-Levy hopes that increasing awareness of likely effects will help patients and their doctors screen for, detect, and correct likely effects of TBI.
"It's not so much that you want to stop TBI, which is frequently a necessary part of treatment, but this study shows it's important know about these problems in order to address them appropriately and proactively," Mulcahy-Levy says.
INFORMATION: END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2012-08-22
RIVERSIDE, Calif. — Transcription is a cellular process by which genetic information from DNA is copied to messenger RNA for protein production. But anticancer drugs and environmental chemicals can sometimes interrupt this flow of genetic information by causing modifications in DNA.
Chemists at the University of California, Riverside have now developed a test in the lab to examine how such DNA modifications lead to aberrant transcription and ultimately a disruption in protein synthesis.
The chemists report that the method, called "competitive transcription and adduct ...
2012-08-22
The Atlantic Ocean is kicking into high gear with low pressure areas that have a chance at becoming tropical depressions, storms and hurricanes. Satellite imagery from NASA's Terra and Aqua satellites have provided visible, infrared and microwave data on four low pressure areas. In addition, NASA's GOES Project has been producing imagery of all systems using NOAA's GOES-13 satellite to see post-Tropical Storm Gordon, Tropical Depression 9, and Systems 95L and 96L.
Tropical Storm Gordon is no longer a tropical storm and is fizzling out east of the Azores. Tropical Depression ...
2012-08-22
PASADENA, Calif.—The frontal lobes are the largest part of the human brain, and thought to be the part that expanded most during human evolution. Damage to the frontal lobes—which are located just behind and above the eyes—can result in profound impairments in higher-level reasoning and decision making. To find out more about what different parts of the frontal lobes do, neuroscientists at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) recently teamed up with researchers at the world's largest registry of brain-lesion patients. By mapping the brain lesions of these patients, ...
2012-08-22
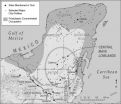
TEMPE, Ariz. — A new analysis of complex interactions between humans and the environment preceding the 9th century collapse and abandonment of the Central Maya Lowlands in the Yucatán Peninsula points to a series of events — some natural, like climate change; some human-made, including large-scale landscape alterations and shifts in trade routes — that have lessons for contemporary decision-makers and sustainability scientists.
In their revised model of the collapse of the ancient Maya, social scientists B.L. "Billie" Turner and Jeremy "Jerry" A. Sabloff provide an up-to-date, ...
2012-08-22
Though the seconds may tick by on the clock at a regular pace, our experience of the 'fourth dimension' is anything but uniform. When we're waiting in line or sitting in a boring meeting, time seems to slow down to a trickle. And when we get caught up in something completely engrossing – a gripping thriller, for example – we may lose sense of time altogether.
But what about the idea that time flies when we're having fun? New research from psychological science suggests that the familiar adage may really be true, with a caveat: time flies when we're have goal-motivated ...
2012-08-22
Researchers have developed a self-charging power cell that directly converts mechanical energy to chemical energy, storing the power until it is released as electrical current. By eliminating the need to convert mechanical energy to electrical energy for charging a battery, the new hybrid generator-storage cell utilizes mechanical energy more efficiently than systems using separate generators and batteries.
At the heart of the self-charging power cell is a piezoelectric membrane that drives lithium ions from one side of the cell to the other when the membrane is deformed ...
2012-08-22
There's double trouble in the northwestern Pacific Ocean in the form of Typhoon Tembin and Tropical Storm Bolaven. NASA's Terra and Aqua satellites teamed up to provide a look at both storms in one view.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument flies onboard NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites and the MODIS instrument on each captured a storm when both satellites flew over them on August 21 after midnight (Eastern Daylight Time). The two MODIS images which featured Bolaven and Tembin over the Philippine Sea were combined by NASA's MODIS Rapid ...
2012-08-22
A University of Rochester Medical Center study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, challenges treatment guidelines for early stage follicular lymphoma, concluding that six different therapies can bring a remission, particularly if the patient is carefully examined and staged at diagnosis.
The research underlines the fact that when cancer strikes, modern patients and their oncologists across the United States are taking many diverse treatment paths when there is scant data to support one method over another. This study suggests that the old standard approach ...
2012-08-22
Chimpanzees from African sanctuaries carry drug-resistant, human-associated strains of the bacteria Staphlyococcus aureus, a pathogen that the infected chimpanzees could spread to endangered wild ape populations if they were reintroduced to their natural habitat, a new study shows.
The study by veterinarians, microbiologists and ecologists was the first to apply the same modern sequencing technology of bacterial genomes used in hospitals to track the transmission of staph from humans to African wildlife. The results were published Aug. 21 by the American Journal of Primatology.
Drug-resistant ...
2012-08-22
RIVERSIDE, Calif. (www.ucr.edu) — Research by Nosang Myung, a professor at the University of California, Riverside, Bourns College of Engineering, has enabled a Riverside company to develop an "electronic nose" prototype that can detect small quantities of harmful airborne substances.
Nano Engineered Applications, Inc., an Innovation Economy Corporation company, has completed the prototype which is based on intellectual property exclusively licensed from the University of California. The device has potential applications in agriculture (detecting pesticide levels), industrial ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study shows long-term effects of radiation in pediatric cancer patients
TBI before age 3 ups rate of endocrine, metabolic and other complications