(Press-News.org) LOS ALAMOS, N.M., August 23, 2012 — Members of the Mars Science Laboratory Curiosity rover ChemCam team, including Los Alamos National Laboratory scientists, squeezed in a little extra target practice after zapping the first fist-sized rock that was placed in the laser's crosshairs last weekend.
Much to the delight of the scientific team, the laser instrument has fired nearly 500 shots so far that have produced strong, clear data about the composition of the Martian surface.
"The spectrum we have received back from Curiosity is as good as anything we looked at on Earth," said Los Alamos National Laboratory planetary scientist Roger Wiens, Principal Investigator of the ChemCam Team. "The entire MSL team was very excited about this and we popped a little champagne."
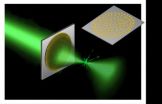
When ChemCam fires its extremely powerful laser pulse, it briefly focuses the energy of a million light bulbs onto an area the size of a pinhead. The laser blast vaporizes a small amount of its target up to seven meters (23 feet) away. The resultant flash of glowing plasma is viewed by the system's 4.3-inch aperture telescope, which sends the light down an optical fiber to a spectrometer located in the body of the rover. There, the colors of light from the flash are recorded and then sent to Earth, enabling scientists to determine the elemental composition of the vaporized material.
Scientists tested the system on Earth in a chamber that simulated the Martian atmosphere. Some of the initial spectral data from Mars look similar to some of the terrestrial standards at first glance. In the coming weeks, ChemCam researchers will pore over the data to look for tiny variations among the peaks and valleys within spectral data captured on Earth and on Mars. These comparisons will allow the team to fine tune and calibrate the instrument, ensuring that every spectral signature gathered by the rover is accurate.
Each element on the Periodic Table has a unique spectral signature. ChemCam scientists will be able to use these spectral fingerprints to decipher the composition of Martian geology, including information about whether Mars rocks ever existed in a watery environment or underwent changes due to interactions with biological organisms.
With regard to Coronation rock (the rock formerly known as N-165), ChemCam's inaugural target, "at first glance it appears consistent with a basaltic composition," Wiens said.
"What's more interesting, however, is whether the rock had dust on it or some other kind of surface coating," he said. "ChemCam saw peaks of hydrogen and magnesium during the first shots that we didn't see in subsequent firings. This could mean the rock surface was coated with dust or some other material."
With Coronation's analyses complete, the science team had a chance to pick new targets.
"After Coronation, we got to shoot at a group of ugly-looking rocks in the area named 'Goulburn,'" Wiens said. "That is one of the areas near the rover that was blasted by the thrusters of the landing vehicle, but these rocks were much farther away from the rover than Coronation, providing a bit more of a test for the ChemCam's laser."
The ChemCam system is one of 10 instruments mounted on the MSL mission's Curiosity rover—a six-wheeled mobile laboratory that will roam more than 12 miles of the planet's surface during the course of one Martian year (98 Earth weeks). The system is designed to capture as many as 14,000 observations throughout the mission.
"We are just jubilant," Wiens said. "This mission is absolutely amazing. Everything is working so well. The same applies to our instrument."
ChemCam's laser, telescope, and camera were provided by the French space agency, CNES, while the spectrometers, electronics, and software were built at Los Alamos National Laboratory, which leads the investigation. The spectrometers were developed with the aid of Ocean Optics, Incorporated, and Jet Propulsion Laboratory assisted with various aspects of development.
The Curiosity science team plans next to take the rover out for a short spin to test out other systems. As the mission progresses, researchers will study the Martian environment in the vicinity of Mount Sharp, a towering peak with a summit nearly three miles above the rover. Mount Sharp appears to contain layers of sedimentary history dating back several billion years. These layers are like pages of a book that could teach researchers much about the geological history of the planet, including whether the Martian environment ever was, or ever may be, suitable for life as we know it.
###
For more information about the mission, visit: http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/msl/
About Los Alamos National Laboratory (www.lanl.gov)
Los Alamos National Laboratory, a multidisciplinary research institution engaged in strategic science on behalf of national security, is operated by Los Alamos National Security, LLC, a team composed of Bechtel National, the University of California, The Babcock & Wilcox Company, and URS for the Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration.
Los Alamos enhances national security by ensuring the safety and reliability of the U.S. nuclear stockpile, developing technologies to reduce threats from weapons of mass destruction, and solving problems related to energy, environment, infrastructure, health, and global security concerns.
ChemCam laser first analyses yield beautiful results
Curiosity beams back strong, clear data from 'scour' area on Martian surface
2012-08-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Flat lens offers a perfect image
2012-08-24
Cambridge, Mass. – August 23, 2012 – Applied physicists at the Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have created an ultrathin, flat lens that focuses light without imparting the distortions of conventional lenses.
At a mere 60 nanometers thick, the flat lens is essentially two-dimensional, yet its focusing power approaches the ultimate physical limit set by the laws of diffraction.
Operating at telecom wavelengths (i.e., the range commonly used in fiber-optic communications), the new device is completely scalable, from near-infrared to terahertz ...
IBN develops superior fuel cell material
2012-08-24
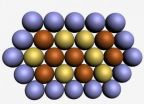
Singapore, August 24, 2012 – Using a mixture of gold, copper and platinum nanoparticles, IBN researchers have developed a more powerful and longer lasting fuel cell material. This breakthrough was published recently in leading journal, Energy and Environmental Science.
Fuel cells are a promising technology for use as a source of electricity to power electronic devices, vehicles, military aircraft and equipment. A fuel cell converts the chemical energy from hydrogen (fuel) into electricity through a chemical reaction with oxygen. A fuel cell can produce electricity continuously ...
Most mutations come from dad
2012-08-24
Humans inherit more than three times as many mutations from their fathers as from their mothers, and mutation rates increase with the father's age but not the mother's, researchers have found in the largest study of human genetic mutations to date.
The study, based on the DNA of around 85,000 Icelanders, also calculates the rate of human mutation at high resolution, providing estimates of when human ancestors diverged from nonhuman primates. It is one of two papers published this week by the journal Nature Genetics as well as one published at Nature that shed dramatic ...
Survival statistics show hard fight when malignant brain tumors appear at multiple sites
2012-08-24
LOS ANGELES (Embargoed until 10 a.m. EDT on Aug. 24, 2012) – When aggressive, malignant tumors appear in more than one location in the brain, patient survival tends to be significantly shorter than when the disease starts as a single tumor, even though patients in both groups undergo virtually identical treatments, according to research at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center's Maxine Dunitz Neurosurgical Research Institute.
"We've known that certain independent factors, such as age at diagnosis, amount of residual tumor after surgery, and the patient's functional status are useful ...
Bigger creatures live longer, travel farther for a reason
2012-08-24
DURHAM, N.C. -- A long-standing mystery in biology about the longer lifespans of bigger creatures may be explained by the application of a physical law called the Constructal Law (www.constructal.org).
What this law proposes is that anything that flows -- a river, bloodstream or highway network -- will evolve toward the same basic configuration out of a need to be more efficient. And, as it turns out, that same basic law applies to all bodies in motion, be they animals or tanker trucks, says Adrian Bejan, the J.A. Jones Professor of mechanical engineering at Duke and ...
New model gives hands-on help for learning the secrets of molecules
2012-08-24
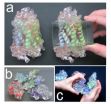
For biology researchers, the complex world of molecular proteins – where tens of thousands of atoms can comprise a single protein – may be getting clearer with the help of a new soft, transparent, and squishy silicone model they can hold in their hands. Its advantage over traditional computer and solid models is that it is mostly transparent and easy to manipulate, which will help researchers more intuitively understand protein structures, positions, and interactions. The models will enable researchers to quickly and collaboratively see, touch, and test ideas about molecular ...
Modeling metastasis
2012-08-24
Cancer metastasis, the escape and spread of primary tumor cells, is a common cause of cancer-related deaths. But metastasis remains poorly understood. Studies indicate that when a primary tumor breaks through a blood vessel wall, blood's "stickiness" tears off tumor cells the way a piece of tape tears wrapping paper. Until now, no one knew the physical forces involved in this process, the first step in metastasis. Using a statistical technique employed by animators, scientists created a new computer simulation that reveals how cancer cells enter the bloodstream. The researchers ...
The end of an era? Branding horses does not enable them to be identified
2012-08-24
There are many reasons why it is important to be able to identify farm animals, horses and small companion animals. Unique identification marks are essential for ensuring the correctness of breeding programmes, for preventing the spread of disease and for eliminating the possibility of deceit in competitions or when animals are sold. The traditional method of marking larger farm animals relies on branding with hot irons or on ear-tagging but this is deemed inappropriate for use on dogs and cats, which are identified by the implant of a microchip transponder. Until recently, ...
Astrocytes control the generation of new neurons from neural stem cells
2012-08-24
Astrocytes are cells that have many functions in the central nervous system, such as the control of neuronal synapses, blood flow, or the brain's response to neurotrauma or stroke.
Reduces brain tissue damage
Prof. Pekny's laboratory together with collaborators have earlier demonstrated that astrocytes reduce the brain tissue damage after stroke and that the integration of transplanted neural stem cells can be largely improved by modulating the activity of astrocytes.
Generation of new neurons
In their current study, the Sahlgrenska Academy researchers show how astrocytes ...
Researchers describe new molecular interactions behind the inhibition of TGF beta-signaling
2012-08-24
This press release is available in Spanish.
Researchers headed by Maria Macias an ICREA researcher at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) and Joan Massagué, a Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigator at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) in New York, have identified a new molecular mechanism that plays a crucial role in the control of the activation of certain genes associated with cancer.
Through detailed structural and biochemical studies, the researchers identified a key domain present in a family of proteins called Smads, whose ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
[Press-News.org] ChemCam laser first analyses yield beautiful resultsCuriosity beams back strong, clear data from 'scour' area on Martian surface