(Press-News.org) The extent of the sea ice covering the Arctic Ocean has shrunk. According to scientists from NASA and the NASA-supported National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) in Boulder, Colo., the amount is the smallest size ever observed in the three decades since consistent satellite observations of the polar cap began.
The extent of Arctic sea ice on Aug. 26, as measured by the Special Sensor Microwave/Imager on the U.S. Defense Meteorological Satellite Program spacecraft and analyzed by NASA and NSIDC scientists, was 1.58 million square miles (4.10 million square kilometers), or 27,000 square miles (70,000 square kilometers) below the Sept. 18, 2007, daily extent of 1.61 million square miles (4.17 million square kilometers).
The sea ice cap naturally grows during the cold Arctic winters and shrinks when temperatures climb in the spring and summer. But over the last three decades, satellites have observed a 13 percent decline per decade in the minimum summertime extent of the sea ice. The thickness of the sea ice cover also continues to decline.
"The persistent loss of perennial ice cover -- ice that survives the melt season -- led to this year's record summertime retreat," said Joey Comiso, senior research scientist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. "Unlike 2007, temperatures were not unusually warm in the Arctic this summer."
The new record was reached before the end of the melt season in the Arctic, which usually takes place in mid- to late-September. Scientists expect to see an even larger loss of sea ice in the coming weeks.
"In 2007, it was actually much warmer," Comiso said. "We are losing the thick component of the ice cover. And if you lose the thick component of the ice cover, the ice in the summer becomes very vulnerable."
"By itself it's just a number, and occasionally records are going to get set," NSIDC research scientist Walt Meier said about the new record. "But in the context of what's happened in the last several years and throughout the satellite record, it's an indication that the Arctic sea ice cover is fundamentally changing."
INFORMATION:
For images, video and background on sea ice, go to:
http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/Gallery/ArcticSeaIceResources.html
For National Snow and Ice Data Center information on Arctic Sea Ice, go to:
http://nsidc.org/arcticseaicenews/
Arctic sea ice shrinks to new low in satellite era
2012-08-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
WSU researcher documents links between nutrients, genes and cancer spread
2012-08-28
PULLMAN, Wash.—More than 40 plant-based compounds can turn on genes that slow the spread of cancer, according to a first-of-its-kind study by a Washington State University researcher.
Gary Meadows, WSU professor and associate dean for graduate education and scholarship in the College of Pharmacy, says he is encouraged by his findings because the spread of cancer is most often what makes the disease fatal. Moreover, says Meadows, diet, nutrients and plant-based chemicals appear to be opening many avenues of attack.
"We're always looking for a magic bullet," he says. "Well, ...
A greener way to fertilize nursery crops
2012-08-28
This press release is available in Spanish.
A U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientist has found a "green" alternative to a type of fertilizer additive that is believed to contribute to the accumulation of heavy metals in waterways.
Ornamental nursery and floral crops require micronutrients like iron, manganese, copper and zinc. But fertilizers that provide these micronutrients often include synthetically produced compounds that bind with the micronutrients so they are available in the root zone.
The most commonly used compounds, known as chelating agents, ...
George Washington University Computational Biology Director solves 200-year-old oceanic mystery
2012-08-28
WASHINGTON — The origin of Cerataspis monstrosa has been a mystery as deep as the ocean waters it hails from for more than 180 years. For nearly two centuries, researchers have tried to track down the larva that has shown up in the guts of other fish over time but found no adult counterpart. Until now.
George Washington University Biology Professor Keith Crandall cracked the code to the elusive crustacean's DNA this summer. His findings were recently published in the journal "Ecology and Evolution," and his research was funded by the National Science Foundation and the ...
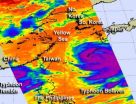
NASA sees Typhoon Bolaven dwarf Typhoon Tembin
2012-08-28
NASA satellites are providing imagery and data on Typhoon Tembin southwest of Taiwan, and Typhoon Bolaven is it barrels northwest through the Yellow Sea. In a stunning image from NASA's Aqua satellite, Bolaven appears twice as large as Tembin.
NASA's Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument that flies onboard the Terra satellite captured a remarkable image of Typhoon Tembin being dwarfed by giant Typhoon Bolaven at 0240 UTC on Aug. 27, 2012. The visible image shows that the island of Taiwan appears to be squeezed between the two typhoons, while ...
Plants unpack winter coats when days get shorter
2012-08-28
EAST LANSING, Mich. — Mechanisms that protect plants from freezing are placed in storage during the summer and wisely unpacked when days get shorter.
In the current issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Michael Thomashow, University Distinguished Professor of molecular genetics, demonstrates how the CBF (C-repeat binding factor) cold response pathway is inactive during warmer months when days are long, and how it's triggered by waning sunlight to prepare plants for freezing temperatures.
The CBF cold response pathway was discovered by Thomashow's ...
Parents and readers beware of stereotypes in young adult literature
2012-08-28
COLUMBIA, Mo. — A newly defined genre of literature, "teen sick-lit," features tear-jerking stories of ill adolescents developing romantic relationships. Although "teen sick-lit" tends to adhere to negative stereotypes of the ill and traditional gender roles, it also explores the taboo realm of sexuality, sickness and youth, says the University of Missouri researcher who named the genre in a recent study. Readers and their parents should be aware of how the presentation of disease and disability in these stories can instill prejudices and enforce societal norms in young ...
Divorced parents in hostile relationships use technology to sabotage communication, MU study finds
2012-08-28
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Separated and divorced couples are increasingly using emails, texting and social media to communicate with their ex-partners about their children. However, when ex-spouses use that technology to withhold or manipulate information, the children are the ones who suffer most, according to a University of Missouri family studies expert. A new study suggests divorce counselors should teach separated parents effective ways to use communication technology in order to maintain healthy environments for their children.
Lawrence Ganong, a professor of human development ...
Speaking 2 languages also benefits low-income children
2012-08-28
Living in poverty is often accompanied by conditions that can negatively influence cognitive development. Is it possible that being bilingual might counteract these effects? Although previous research has shown that being bilingual enhances executive functioning in middle-class children, less is known about how it affects lower income populations.
In a study forthcoming in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science, psychological scientist Pascale Engel de Abreu of the University of Luxembourg and colleagues examine the effects of speaking ...
ASGE initiative examines real-time imaging of Barrett's esophagus
2012-08-28
OAK BROOK, Ill. – August 27, 2012 – The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy's (ASGE) Preservation and Incorporation of Valuable Endoscopic Innovations (PIVI) initiative examines real-time imaging of Barrett's esophagus in an article appearing in the August issue of GIE: Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, ASGE's monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal. This PIVI is one in a series of statements defining the diagnostic or therapeutic threshold that must be met for a technique or device to become considered appropriate for incorporation into clinical practice.
Barrett's ...
Working moms spend less time daily on kids' diet, exercise, study finds
2012-08-28
When it comes to cooking, grocery shopping and playing with children, American moms with full-time jobs spend roughly three-and-half fewer hours per day on these and other chores related to their children's diet and exercise compared to stay-at-home and unemployed mothers, reports a new paper by a Cornell University health economist.
Male partners do little to make up the deficit: Employed fathers devote just 13 minutes daily to such activities and non-working fathers contribute 41 minutes, finds the study, which will be printed in the December issue of Economics and ...