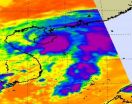
(Press-News.org) The northwestern Pacific Ocean is just as active as the Atlantic Ocean this hurricane season. The fourteenth tropical depression formed near Hainan Island, China this morning and its birth was captured by a NASA infrared satellite instrument. The NASA image showed the depression's strong thunderstorms near its center and east of its center.
NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Tropical Depression 14W (TD14W) today, October 5 at 06:05 UTC (2:05 a.m. EDT). Infrared imagery from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument onboard the Aqua satellite revealed a concentrated area of thunderstorms and strong convection (rapidly rising air that forms thunderstorms that power a tropical cyclone) around TD14W's center in the eastern quadrant of the storm. That convection in the east is a result of westerly wind shear blowing the convection and thunderstorms away from the storm's center.
Infrared imagery also indicated that those storms are weakening, because the cloud tops are now warming from previous imagery. Very cold thunderstorm cloud tops (colder than -60 Fahrenheit) indicate strong thunderstorms, very high into the troposphere, that likely have heavy rain associated with them. When AIRS detects that cloud top temperatures have warmed, it means the heights of the thunderstorms has dropped, meaning there's not as much power or uplift in the convection.
AIRS imagery also showed a poorly-defined low-level center of circulation in TD14W, and some of that deep convection (or thunderstorms) are pushed away from the eastern side of the center. That indicates wind shear (winds that buffet a storm and push it apart). When a storm doesn't stack up, and when part of the storm is displaced from the rest of it, it loses its organization and punch. That's what wind shear does, and is doing to TD14W and that wind shear is blowing at about 28 mph!
At 5 a.m. EDT, October 5, Tropical Depression 14W had maximum sustained winds near 34 mph. It was located over Hainan Island near 19.5 North and 109.4 East. Its winds were creating 9-foot high seas. TD14W was moving north at 6 mph. It is expected to make a turn to the north-northeast, make a brief landfall in the mainland of southern China. Once there, it is forecast to move east, then east-southeast, making a half-circle and head toward the eastern end of Hainan Island and dissipate.
INFORMATION:
NASA AIRS Satellite instrument sees Tropical Depression 14W form
2010-10-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New fossil suggests dinosaurs not so fierce after all
2010-10-06
A new species of dinosaur discovered in Arizona suggests dinosaurs did not spread throughout the world by overpowering other species, but by taking advantage of a natural catastrophe that wiped out their competitors.
The new dinosaur, named Sarahsaurus, was studied by an international team of scientists, including Robert R. Reisz, professor and chair of biology at the University of Toronto Mississauga, Tim Rowe, professor of paleontology at the University of Texas at Austin's Jackson School of Geosciences and Hans-Dieter Sues, curator of vertebrate paleontology at the ...
MAVEN mission to investigate how sun steals Martian atmosphere
2010-10-06
The Red Planet bleeds. Not blood, but its atmosphere, slowly trickling away to space. The culprit is our sun, which is using its own breath, the solar wind, and its radiation to rob Mars of its air. The crime may have condemned the planet's surface, once apparently promising for life, to a cold and sterile existence.
Features on Mars resembling dry riverbeds, and the discovery of minerals that form in the presence of water, indicate that Mars once had a thicker atmosphere and was warm enough for liquid water to flow on the surface. However, somehow that thick atmosphere ...
NASA'S Mars atmosphere mission given the green light to proceed to development
2010-10-06
GREENBELT, Md. – NASA's mission to investigate the mystery of how Mars lost much of its atmosphere passed a critical milestone on October 4, 2010. NASA has given approval for the development and 2013 launch of the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN) mission.
Clues on the Martian surface, such as features resembling dry riverbeds and minerals that only form in the presence of liquid water, suggest that Mars once had a denser atmosphere, which supported the presence of liquid water on the surface. As part of a dramatic climate change, most of the Martian atmosphere ...
Phillies, Rangers, Yanks, Giants to win, says NJIT math guru
2010-10-06
With the Major League Baseball Division Series set to begin, associate math professor Bruce Bukiet at NJIT is performing his analysis of the probability of each team advancing to the League Championship Series. "Going into these series, the Philadelphia Phillies have a 64 percent chance of defeating the Cincinnati Reds in their best of five game series," he said.
"The Texas Rangers, New York Yankees and San Francisco Giants have slight advantages to win series over their opponents, the Tampa Bay Rays, Minnesota Twins and Atlanta Braves respectively in the first round ...
Blood test could diagnose Alzheimer's disease, UT Southwestern researchers find
2010-10-06
DALLAS – Oct. 6, 2010 – A set of proteins found in blood serum shows promise as a sensitive and accurate way to diagnose Alzheimer's disease, researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center have found as part of a statewide study.
An analysis of the proteins, plus a clinical exam, proved 94 percent accurate in detecting suspected Alzheimer's and 84 percent accurate in ruling it out in people without the disease, the researchers said.
"This research uses a novel technology that makes it possible to analyze several biomarkers in a single blood sample in a cost-effective ...
Low testosterone linked to Alzheimer's disease
2010-10-06
ST. LOUIS -- Low levels of the male sex hormone, testosterone, in older men is associated with the onset of Alzheimer's disease, according to research by a team that includes a Saint Louis University scientist.
"Having low testosterone may make you more vulnerable to Alzheimer's disease," said John E. Morley, M.D., director of the division of geriatric medicine at Saint Louis University and a study co-investigator. "The take-home message is we should pay more attention to low testosterone, particularly in people who have memory problems or other signs of cognitive impairment."
The ...
Childrens Hospital LA discovers growth factor essential to epicardial cell function
2010-10-06
LOS ANGELES– In research that one day may lead to the discovery of how to regenerate tissue damaged by heart disease, investigators at Childrens Hospital Los Angeles have identified PDGF as a key factor in the proliferation and transformation of epicardial cells, one type of cell that surrounds heart muscle and contributes to vessels.
The study was published online September 21 in advance of the publication of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. Ching-Ling (Ellen) Lien, PhD, led a team of researchers at the Developmental ...
Study: Fish near coal-fired power plants have lower levels of mercury
2010-10-06
A new study from North Carolina State University finds that fish located near coal-fired power plants have lower levels of mercury than fish that live much further away. The surprising finding appears to be linked to high levels of another chemical, selenium, found near such facilities, which unfortunately poses problems of its own.
"We found that fish in lakes located at least 30 kilometers (km) from a coal-fired power plant had mercury levels more than three times higher than fish of the same species in lakes that are within 10 km of a plant," says Dana Sackett, a Ph.D. ...
Tour d'Afrique's New 2011 Samba Tango Cycling Adventure Dances Through Music-Loving Cultures From Rio de Janeiro to Buenos Aires
2010-10-06
Tour d'Afrique (http://www.tourdafrique.com/), a leader in cross-continent, multi-country cycling tours, invites riders to save space on their dance cards for an Aug. 14 to Sept. 18, 2011, Samba Tango Adventure http://www.tourdafrique.com/tours/sambatango spanning 3,150 km (1,950 miles) in 36 days from Rio de Janeiro to Buenos Aires.
The Full Tour per person rate of $3,900 offers the privilege of averaging 100 km per day in the saddle with six rest and sightseeing days sprinkled in. If full payment is made on or before Feb. 20, 2011, a discount of 5% applies.
Riders ...
The Culinary Studio: Metro Detroit's First Shared-Use Kitchen to Open in Southfield
2010-10-06
Calling all bakers, caterers, personal chefs and aspiring food entrepreneurs - The Culinary Studio will help local food-oriented businesses launch and grow without the burden of start-up costs. Fully equipped kitchens will be available at The Culinary Studio for hourly rental to food entrepreneurs and for special cooking events.
Located in the Applegate Shopping Center on Northwestern Highway in Southfield, Michigan, The Culinary Studio will have two state of the art commercial kitchens, with areas for preparing, packaging, catering and baking along with cooking classes. ...