(Press-News.org) August 28, 2012, Shenzhen, China – The international research team led by Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences and BGI have completed the genome sequence and analysis of a diploid cotton-- Gossypium raimondii. The cotton genome provides an invaluable resource for the study and genetic improvement of cotton quality and output, and sheds new lights on understanding the genetic characteristics and evolutionary mechanism underlying cotton and its close relatives. The study was published online in Nature Genetics. (http://www.nature.com/ng/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/ng.2371.html).
Cotton, also known as "white gold", is an important cash crop worldwide. Its fiber is one of the oldest fibers under human cultivation, which traces over 7,000 years old recovered from archaeological sites. The cotton production provides income for approximately 100 million families, and approximately 150 countries are involved in cotton import and export. Additionally, in scientific research, cotton also serves as an excellent model system for studying polyploidization, cell elongation and cell wall biosynthesis.
In this study, researchers sequenced the genome of G. raimondii by the next-generation sequencing technology, yielding a draft cotton genome with 103.6-fold genome coverage. Over 73% of the assembled sequences were anchored on 13 G. raimondii chromosomes. They identified 2,355 syntenic blocks in the G. raimondii genome, and found that approximately 40% of the paralogous genes were present in more than 1 block, which suggests that this cotton genome has undergone substantial chromosome rearrangement during its evolution.
Through comprehensive comparison and analysis, researchers observed that one paleohexaploidization event occurred in the G. raimondii genome at approximately 130.8 million years ago, while the event is commonly found in eudicots. They also found the evidence to support a cotton–specific whole–genome duplication event occurred at approximately 13-20 million years ago.
Cotton is known to produce a unique group of terpenoids such as gossypol. The accumulated gossypol and related sesquiterpenoids produced by cotton in pigment glands can be as a resistance against pathogens and herbivores. The majority of cotton sesquiterpenoids are derived from a common precursor which is synthesized by (+)- δ -cadinene synthase (CDN) in gossypol biosynthesis. Through the phylogenetic analysis on G. raimondii and eight other sequenced plant genomes, they found that the cotton, and probably Theobroma cacao, were the only sequenced plant species that possess an authentic CDN1 gene family for gossypol biosynthesis.
Furthermore, the transcriptomic comparison between the fiber-bearing G. hirsutum and the non-fibered G. raimondii demonstrated that three synthases are important for cotton fiber development, including sucrose synthase (Sus), 3-ketoacyl-CoA synthase (KCS) and 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid oxidase (ACO). Meanwhile, the MYB and bHLH transcription factors preferentially expressed in fiber may be useful to explain the molecular mechanisms that are in charge of governing fiber initiation and early cell growth.
Zhiwen Wang, Project Manager at BGI, said, "The completed G. raimondii genome provides a good reference for accelerating the genomic research on tetraploid cotton species such as G. hirsutum and G. barbadense. It also will lay a solid foundation for researchers to further boost cotton quality and productivity by comprehensively exploring the genetic mechanisms underlying cotton fiber initiation, gossypol biosynthesis and resistance against pathogens and herbivores."
###
About BGI
BGI was founded in Beijing, China on September 9th, 1999 with the mission of being a premier scientific partner to the global research community. The goal of BGI is to make leading-edge genomic science highly accessible through its investment in infrastructure that leverages the best available technology, economies of scale, and expert bioinformatics resources. BGI, and its affiliates, BGI Americas, based in Cambridge, MA and BGI Europe, based in Copenhagen. Denmark, have established partnerships and collaborations with leading academic and government research institutions as well as global biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies, supporting a variety of disease, agricultural, environmental, and related applications.
BGI has established a proven track record of excellence, delivering results with high efficiency and accuracy for innovative, high-profile research which has generated over 200 publications in top-tier journals such as Nature and Science. These accomplishments include sequencing one percent of the human genome for the International Human Genome Project, contributing 10 percent to the International Human HapMap Project, carrying out research to combat SARS and German deadly E. coli, playing a key role in the Sino-British Chicken Genome Project, and completing the sequence of the rice genome, the silkworm genome, the first Asian diploid genome, the potato genome, and, most recently, 1000 genomes and human Gut metagenome. For more information about BGI, please visit www.genomics.cn.
Contact Information:
Zhiwen Wang
Project Manager
BGI
wangzhiwen@genomics.cn
www.genomics.cn
Bicheng Yang
Public Communication Officer
BGI
+86-755-82639701
yangbicheng@genomics.cn
www.genomics.cn
Chinese scientists successfully crack the genome of diploid cotton
The latest study was published online in Nature Genetics
2012-08-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The FAME 2 trial
2012-08-28
Munich, Germany – August 28 2012: Patients with stable coronary artery disease (CAD) had a lower need for urgent revascularisation when receiving fractional flow reserve (FFR)-guided PCI plus the best available medical therapy (MT) than when receiving MT alone. The results, from a final analysis of the FAME 2 trial, were presented today during a Hot Line session of ESC Congress 2012 in Munich. Treatment guided by fractional flow reserve assessment helped reduce the risk of urgent revascularisation by a factor of eight.
The FAME 2 (FFR-Guided Percutaneous Coronary Intervention ...
Zebrafish study explains why the circadian rhythm affects your health
2012-08-28
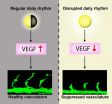
Disruptions to the circadian rhythm can affect the growth of blood vessels in the body, thus causing illnesses such as diabetes, obesity, and cancer, according to a new study from Linköping University and Karolinska Institutet in Sweden.
The circadian rhythm is regulated by a "clock" that reacts to both incoming light and genetic factors.
In an article now being published in the scientific journal Cell Reports, it is demonstrated for the first time that disruption of the circadian rhythm immediately inhibit blood vessel growth in zebra fish embryos.
Professor Yihai Cao ...
Global platelet reactivity and high risk ACS patients
2012-08-28
Global platelet reactivity is more effective than responsiveness to clopidogrel in identifying acute coronary syndrome (ACS) patients at high risk of ischemic events, according to research presented at ESC Congress 2012.
The results from the RECLOSE 2-ACS study were presented by Dr Rossella Marcucci from the University of Florence.
The Responsiveness to Clopidogrel and Stent thrombosis 2 – ACS (RECLOSE 2-ACS) study is a prospective, observational, referral centre cohort study of 1,789 patients with acute coronary syndromes undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention ...
Botany student proves 'New England Banksia' a distinct species
2012-08-28
The New England Banksia is largely restricted to the eastern edge of the New England Tableland, and is common in places along Waterfall Way. Ms Stimpson's research has raised this flowering plant, until now classified as a variety of the Hairpin Banksia (B. spinulosa), to the taxonomic level of a distinct species. The study was published in the open access journal PhytoKeys.
"I love the Proteaceae – the family of flowering plants that includes the Banksia and Grevillea genera in Australia and Protea in South Africa," Ms Stimpson said. "Surprisingly, molecular evidence ...
Women 40% less likely to die after TAVI than men
2012-08-28
Munich, Germany – August 27 2012: Women with severe aortic stenosis are 40% less likely to die after transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) than men, reveals the latest data from the largest study to date of gender differences in outcomes after TAVI. The findings were presented at ESC Congress 2012 by Professor Karin Humphries from St. Paul's Hospital.
More than 1.5 million people in the US suffer from aortic stenosis, a progressive disease where the aortic valve becomes obstructed, leading to life-threatening heart problems. If left untreated, half of all patients ...
TAVI improves quality of life in patients with severe aortic stenosis for at least 1 year
2012-08-28
Munich, Germany – August 28 2012: Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) leads to meaningful improvements in health-related quality of life in patients with severe aortic stenosis that are maintained for at least 1 year, according to a study presented at ESC Congress 2012. The results from the German transcatheter aortic valve interventions registry were presented by Professor Till Neumann, MD, from Essen, Germany.
Aortic stenosis is the most common valvular heart disease with increasing incidence especially with regard to the ageing of the population. Today, ...
Lifestyle changes could prevent 400 cardiac events and 200 deaths in Swedish PCI patients
2012-08-28
Munich, Germany – August 27 2012: Up to 400 cardiac events and 200 deaths in Swedish PCI patients could be avoided by following a heart healthy lifestyle, according to research from the SPICI study presented at ESC Congress 2012. The results were presented at ESC press conference by Professor Joep Perk from Linnaeus University and at the scientific session by Dr Roland CARLSSON.
The benefits of adherence to a heart healthy lifestyle in combination with drug treatment after an acute myocardial infarction treated with coronary artery balloon intervention (PCI) have recently ...
Smoking after stroke increases death risk by 3-fold
2012-08-28
Munich, Germany – August 28 2012: Patients who resume smoking after a stroke increase their risk of death by three-fold, according to research presented at ESC Congress 2012 by Professor Furio Colivicchi from San Filippo Neri Hospital. The researchers also found that the earlier patients resume smoking, the greater their risk of death with one year.
"It is well established that smoking increases the risk of having a stroke," said Professor Colivicchi. "Quitting smoking after an acute ischemic stroke may be more effective than any medication in reducing the risk of further ...
African research identifies strong candidate for possible single-dose malaria cure
2012-08-28
A recently discovered compound from the aminopyridine class not only has the potential to become part of a single-dose cure for all strains of malaria, but might also be able to block transmission of the parasite from person to person, according to a research collaboration involving the Medicines for Malaria Venture (MMV), based in Switzerland, and the Drug Discovery and Development Centre (H3-D) at the University of Cape Town, South Africa. On the basis of initial results it was selected by MMV for further development – making it the first compound researched on African ...
Personalized antiplatelet treatment improves outcome after PCI
2012-08-28
Munich, Germany – August 26 2012: Personalized antiplatelet treatment leads to better outcomes than standard antiplatelet treatment in patients undergoing coronary stent implantation, according to results from the MADONNA study presented at ESC Congress 2012. The findings were presented by Dr Jolanta Siller-Matula from Medical University of Vienna.
Standard antiplatelet treatment in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) consists of a dual antiplatelet therapy with aspirin and an ADP receptor inhibitor such as clopidogrel.
But measurements of platelet ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Chinese scientists successfully crack the genome of diploid cottonThe latest study was published online in Nature Genetics