(Press-News.org) MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL (08/29/2012) —Can we have enough to eat and a healthy environment, too? Yes—if we're smart about it, suggests a study published in Nature this week by a team of researchers from the University of Minnesota and McGill University in Montreal.
Global demand for food is expected to double by 2050 due to population growth and increased standards of living. To meet this demand, it is often assumed we will need to expand the environmental burden of agriculture. The paper, based on analysis of agricultural data gathered from around the world, offers hope that with more strategic use of fertilizer and water, we could not only dramatically boost global crop yield, but also reduce the adverse environmental impact of agriculture.
"We have often seen these two goals as a trade-off: We could either have more food, or a cleaner environment, not both," says lead author Nathaniel Mueller, a researcher with the University of Minnesota's Institute on the Environment and a doctoral student in the College of Food, Agricultural and Natural Resource Sciences. "This study shows that doesn't have to be the case."
Mueller and colleagues used management and yield data for 17 major crops to take a big-picture look at how much water and nutrients it would take to bring underperforming farmlands to meet their food production potential. They also looked for places where fertilizer use could be cut down without substantially reducing crop yield. They found:
We could boost production 45 to 70 percent for most crops. The greatest opportunities for yield improvement are found in Eastern Europe, sub-Saharan Africa, East Asia, and South Asia.
Different inputs serve as limiting factors depending on the region and crop. Nutrients, for example, appear to be limiting corn production in Eastern Europe and West Africa and wheat production in Eastern Europe, while nutrients and water appear to limit rice production in Southeast Asia.
Worldwide, we could decrease nitrogen use 28 percent and phosphorus use 38 percent without adversely affecting yields for corn, wheat and rice. China stands out as a hot spot of nutrient overuse, but other areas, like the United States, Western Europe, and India, also have room to improve.
With strategic redistribution of nutrient inputs, we could bring underperforming lands worldwide to 75 percent of their production potential while only increasing global nitrogen use 9 percent and potassium use 34 percent—and reducing phosphorus use 2 percent.
The researchers caution that their analysis is at a coarse scale and that many other factors, including land characteristics, use of organic fertilizers, economics, geopolitics, water availability and climate change will influence actual gains in crop production and reductions in adverse environmental impacts. Nevertheless, they are encouraged by the strong indication that closing the "yield gap" on underperforming lands—previously identified as one of five promising points for meeting future food needs, along with halting farmland expansion in the tropics, using agricultural inputs more strategically, shifting diets and reducing food waste—holds great promise for sustainably boosting food security.
"These results show that substantial gains are indeed possible from closing the yield gap—and combining these efforts with improved management of existing lands can potentially reduce agriculture's environmental impact," Mueller says. "They also offer concrete suggestions as to where and how we can focus future efforts. This work should serve as a source of great encouragement and motivation for those working to feed the 9-billion-plus people anticipated to live on this planet in 2050 while protecting Earth's indispensible life support systems."
### END
Study shows hope of greater global food output, less environmental impact of agriculture
Just-released Nature paper shows more strategic use of nutrients and water on a global scale could boost production 45 to 70 percent for most crops
2012-08-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Collagen-seeking synthetic protein could lead doctors to tumor locations
2012-08-30
Johns Hopkins researchers have created a synthetic protein that, when activated by ultraviolet light, can guide doctors to places within the body where cancer, arthritis and other serious medical disorders can be detected.
The technique could lead to a new type of diagnostic imaging technology and may someday serve as a way to move medications to parts of the body where signs of disease have been found. In a study published in the Aug. 27-31 Online Early Edition of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the researchers reported success in using the synthetic ...
Controlling gait of horses may be possible, says key study from Texas A&M
2012-08-30
COLLEGE STATION Aug. 29, 2012 – Analysis of a specific mutation in a gene in horses that affects the ability of horses to use alternate gaits is strongly related to racing performance and is advantageous for harness-racing horses. In domestic horses, the mutation has had a major impact on their diversification, as the altered gait characteristics of a number of breeds apparently require this mutation, according to a study that includes a Texas A&M University researcher.
Gus Cothran, a professor in the Animal Genetic Lab of the College of Veterinary Medicine & Biomedical ...
Tropical Storm Kirk looks more like a comet on NASA infrared imagery
2012-08-30
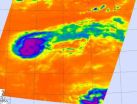
Tropical Storm Kirk looks more like a comet than a tropical storm in infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite because of wind shear. NASA infrared imagery also revealed powerful thunderstorms around the center of circulation which are indicators that Kirk will continue strengthening. Meanwhile, another low pressure area appears to be organizing in the eastern Atlantic, far to the southeast of Kirk.
Tropical Depression Kirk formed from the eleventh tropical depression of the Atlantic Ocean season. Tropical Depression 11 formed on Aug. 28 at 5 p.m. EDT about 1,270 miles ...
NASA sees Hurricane Isaac make double landfall in Louisiana
2012-08-30
Hurricane Isaac made two landfalls in southeastern Louisiana. Isaac's first landfall occurred in southeastern Louisiana on Aug. 28 at 7:45 p.m. EDT (1145 UTC), second landfall on Aug. 29 at 6 a.m. EDT (1000 UTC). NASA's TRMM satellite observed heavy rainfall in this slow moving storm, which leads to higher rainfall totals and flooding.
NASA and NOAA satellites continue to provide detailed information to forecasters at the National Hurricane Center. Hurricane Isaac's first landfall occurred at 7:45 p.m. EDT in extreme southeastern Louisiana, bringing strong winds and dangerous ...
'Nano machine shop' shapes nanowires, ultrathin films
2012-08-30
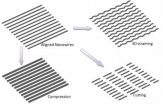
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. –A new "nano machine shop" that shapes nanowires and ultrathin films could represent a future manufacturing method for tiny structures with potentially revolutionary properties.
The structures might be "tuned" for applications ranging from high-speed electronics to solar cells and also may have greater strength and unusual traits such as ultrahigh magnetism and "plasmonic resonance," which could lead to improved optics, computers and electronics.
The researchers used their technique to stamp nano- and microgears; form tiny circular shapes out of ...
When to worry about kids' temper tantrums
2012-08-30
CHICAGO --- Temper tantrums in young children can be an early signal of mental health problems, but how does a parent or pediatrician know when disruptive behavior is typical or a sign of a serious problem?
New Northwestern Medicine research will give parents and professionals a new tool to know when to worry about young children's misbehavior. Researchers have developed an easy-to-administer questionnaire specifically designed to distinguish the typical misbehavior of early childhood from more concerning misbehavior. This will enable early identification and treatment ...
Tracing the Paralympic movement's 'freak show' roots
2012-08-30
(Edmonton) Danielle Peers has lived the thrill and pressure, revelled in competition and brought home hardware from the Paralympic Games. But beneath the cheers, the University of Alberta researcher questions whether the Paralympic movement is as empowering as its benevolent image.
The former Paralympian bronze medallist and women's wheelchair basketball world champion says the history of the Paralympic movement dates to the freak shows of the 19th century—and even today's modern games are a spectacle of curiosity that reinforces disability.
"The Paralympics is one ...
Scientist creates new cancer drug that is 10 times more potent
2012-08-30
VIDEO:
Mark W. Lee Jr., an assistant professor of chemistry at the University of Missouri, and his research team have used carboranes to enhance cancer-fighting drugs. They recently created one drug...
Click here for more information.
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- Legend has it that Ralph Waldo Emerson once said, "Build a better mousetrap, and the world will beat a path to your door." University of Missouri researchers are doing just that, but instead of building mousetraps, the scientists ...
WSU/USDA scientist creates test, treatment for malaria-like sickness in horses
2012-08-30
PULLMAN, Wash. - When Washington State University and U.S. Department of Agriculture veterinary scientist Don Knowles got word two years ago that a rare but deadly infection was discovered among a group of horses in south Texas, he felt a jolt of adrenaline. Not only were the horses infected with a parasitic disease similar to malaria in humans, but the epicenter of the outbreak was at no ordinary ranch.
It was the King Ranch, legendary for its world-class quarter horses, including former winners of the Triple Crown and Kentucky Derby. The 825,000 acre family-owned estate ...
NASA satellite sees remnants of Tropical Storm Bolaven racing over China and Russia
2012-08-30
Tropical Storm Bolaven made landfall on Aug. 28 and has been moving quickly over land while undergoing a transition. NASA's Terra satellite captured an image of the remnants of the ex-tropical storm mostly centered over eastern China.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA's Terra satellite captured this natural-color image of Tropical Storm Bolaven on August 29 at 0220 UTC. Some clouds still remain over North Korea and extend over the Sea of Japan as Bolaven's remnants continue speeding to the north-northeast at 29 knots (33.3 mph/53.7 kmh).
The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] Study shows hope of greater global food output, less environmental impact of agricultureJust-released Nature paper shows more strategic use of nutrients and water on a global scale could boost production 45 to 70 percent for most crops