(Press-News.org)
VIDEO:
This movie compares the blood flow dynamics in a cross-section of the foot between a healthy individual and a diabetic patient with PAD. Differences are clearly visible in both the...
Click here for more information.
WASHINGTON, Aug. 30, 2012—For many diabetics, monitoring their condition involves much more than adhering to a routine of glucose sensing and insulin injections. It also entails carefully monitoring the ongoing toll this disease takes on their body.
An innovative new optical diagnostic tool created by Columbia University researchers and reported today in the Optical Society's (OSA) open-access journal Biomedical Optics Express may soon make it easier to diagnose and monitor one of the most serious complications of diabetes, peripheral arterial disease (PAD). PAD, which is marked by a narrowing of the arteries caused by plaque accumulation, frequently results in insufficient blood flow to the body's extremities and increases a person's risk for heart attack and stroke.
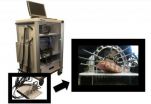
This new noninvasive imaging technique – known as dynamic diffuse optical tomography imaging (DDOT) – uses near-infrared light to map the concentration of hemoglobin in the body's tissue. This mapping can reveal how effectively blood is flowing to patients' hands and feet.
"Currently, there are no good methods to assess and monitor PAD in diabetic patients," explains Andreas Hielscher, Ph.D., professor of Biomedical and Electrical Engineering and Radiology, and director of the Biophotonics and Optical Radiology Laboratory at Columbia University.
"Patients with PAD experience foot pain, called 'claudication,' while walking," adds Gautam Shrikhande, M.D., assistant professor of surgery, and director of the Vascular Laboratory at Columbia's Medical Center. "This pain continues, even at rest, as the disease progresses. In more advanced stages, PAD patients develop sores or ulcers that won't heal. Then, cell death, a.k.a. 'gangrene,' occurs and amputation is often the only solution. It's extremely important to diagnose PAD early, because medication and lifestyle changes can alleviate the disease."
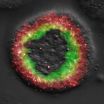
This is where DDOT can help. "We've successfully used DDOT to detect PAD in the lower extremities," says Michael Khalil, a Ph.D. candidate working with Hielscher at Columbia. "One key reason why DDOT shows so much promise as a diagnostic and monitoring tool is that, unlike other methods, it can provide maps of oxy, deoxy and total hemoglobin concentration throughout the foot and identify problematic regions that require intervention."
"Using instrumentation for fast image acquisition lets us observe blood volume over time in response to stimulus such as a pressure cuff occlusion or blockage," said Hielscher.
To map and monitor the presence of hemoglobin, the protein that carries oxygen in the blood, red and near-infrared light is shone at different angles around areas that are susceptible to arterial disease. These specific wavelengths of light are then absorbed or scattered, depending on the concentration of hemoglobin.
"In the case of tissue, light is absorbed by hemoglobin. Since hemoglobin is the main protein in blood, we can image blood concentrations within the foot without using a contrast agent," Hielscher points out. Contrast agents pose the risk of renal failure in some cases, so the ability to monitor PAD without using a contrast agent is a great advantage.
Since more than 25 million people — or 8 percent of the population — in the United States are diabetic, this diagnostic tool has the potential to make it significantly simpler to diagnose and monitor diabetics with PAD in the future.
Khalil, Hielscher, and colleagues hope to bring their diagnostic tool to market and into clinics within the next 3 years.
INFORMATION:
Paper: "Dynamic diffuse optical tomography imaging of peripheral arterial disease," Biomedical Optics Express, Vol. 3, Issue 9, pp. 2288-2298 (2012). http://www.opticsinfobase.org/boe/abstract.cfm?uri=boe-3-9-2288
EDITOR'S NOTE: High-resolution images and a brief video clip are available to members of the media upon request. Contact Angela Stark, astark@osa.org.
About Biomedical Optics Express
Biomedical Optics Express is OSA's principal outlet for serving the biomedical optics community with rapid, open-access, peer-reviewed papers related to optics, photonics and imaging in the life sciences. The journal scope encompasses theoretical modeling and simulations, technology development, and biomedical studies and clinical applications. It is published by the Optical Society and edited by Joseph A. Izatt of Duke University. Biomedical Optics Express is an open-access journal and is available at no cost to readers online at http://www.OpticsInfoBase.org/BOE.
About OSA
Uniting more than 130,000 professionals from 175 countries, the Optical Society (OSA) brings together the global optics community through its programs and initiatives. Since 1916 OSA has worked to advance the common interests of the field, providing educational resources to the scientists, engineers and business leaders who work in the field by promoting the science of light and the advanced technologies made possible by optics and photonics. OSA publications, events, technical groups and programs foster optics knowledge and scientific collaboration among all those with an interest in optics and photonics. For more information, visit www.osa.org.
Shedding new light on one of diabetes' most dangerous complications
New optical instrument helps diagnose, monitor peripheral arterial disease
2012-08-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Increased sediment and nutrients delivered to bay as Susquehanna reservoirs near sediment capacity
2012-08-30
Reservoirs near the mouth of the Susquehanna River just above Chesapeake Bay are nearly at capacity in their ability to trap sediment. As a result, large storms are already delivering increasingly more suspended sediment and nutrients to the Bay, which may negatively impact restoration efforts.
Too many nutrients rob the Bay of oxygen needed for fish and, along with sediment, cloud the waters, disturbing the habitat of underwater plants crucial for aquatic life and waterfowl.
"The upstream reservoirs have served previously to help reduce nutrient pollutant loads to ...
Kidney stenting lowers blood pressure in patients with severe hypertension
2012-08-30
Patients with uncontrolled renovascular hypertension saw a significant improvement in their blood pressure with renal artery stent deployment. The multicenter HERCULES trial, evaluating the safety and effectiveness of the RX Herculink Elite Stent, found that patients with higher blood pressure levels at baseline had the most dramatic reduction in blood pressure following intervention. Trial details appear in Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions, a journal published by Wiley on behalf of the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI).
Narrowing ...
Water pipe smoking has the same respiratory effects as smoking cigarettes
2012-08-30
A new study published in the journal Respirology reveals that water pipe smoking, such as hookah or bong smoking, affects lung function and respiratory symptoms as much as cigarette smoking.
Most users of water pipes and many physicians believe that smoking through a water pipe filters out the toxic components of tobacco and is considerably less harmful than smoking cigarettes.
Led by Mohammad Hossein Boskabady, MD, PhD, of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, researchers set out to compare lung function and respiratory symptoms among water pipe smokers, deep or ...
Immunodeficient patients with secondary lung disease benefit from combined chemotherapy
2012-08-30
A team of researchers at the Medical College of Wisconsin and Children's Hospital of Wisconsin Research Institute defined a new treatment for a potentially fatal lung disease in patients with a primary immunodeficiency known as common variable immunodeficiency (CVID).The findings are published in the Journal of Clinical Immunology.
Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) is the most common primary immunodeficiency that requires regular treatment with medication, specifically immunoglobulin (antibodies) replacement therapy. With immunoglobulin therapy, deaths from infection ...
A model for development
2012-08-30
PASADENA, Calif.—As an animal develops from an embryo, its cells take diverse paths, eventually forming different body parts -- muscles, bones, heart. In order for each cell to know what to do during development, it follows a genetic blueprint, which consists of complex webs of interacting genes called gene regulatory networks.
Biologists at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) have spent the last decade or so detailing how these gene networks control development in sea-urchin embryos. Now, for the first time, they have built a computational model of one ...
Does wisdom really come with age? It depends on the culture
2012-08-30
"Wisdom comes with winters," Oscar Wilde once said. And it's certainly comforting to think that aging benefits the mind, if not the body. But do we really get wiser as time passes?
There are many way to define what exactly wisdom is, but previous literature suggests that having wisdom means that you are also good at resolving conflict. But conflict is not handled the same way across cultures. Americans have been shown to emphasize individuality and solve conflict in a direct manner, such as by using direct persuasion. In contrast, the Japanese place a greater emphasis ...
Viruses could be the key to healthy corals
2012-08-30
Corals are an invaluable part of the marine ecosystem, fostering biodiversity and protecting coastlines. But they're also increasingly endangered. Pathogenic bacteria, along with pollution and harmful fishing practices, are one of the biggest threats to the world's coral populations today.
One of the solutions to the crisis may lie in human medicine. Prof. Eugene Rosenberg of Tel Aviv University's Department of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology, working in collaboration with Dr. Ilil Atad of his own laboratory and Prof. Yossi Loya of TAU's Department of Zoology, ...
No-till farming helps capture snow and soil water
2012-08-30
A smooth blanket of snow in the winter can help boost dryland crop productivity in the summer, and no-till management is one way to ensure that blanket coverage, according to U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) research.
Agricultural Research Service (ARS) soil scientist David Huggins conducted studies to determine how standing crop residues affect snow accumulation and soil water levels across entire fields. ARS is USDA's chief intramural scientific research agency, and this work supports the USDA priority of responding to climate change.
Huggins, who works at ...
'Hulk' protein, Grb10, controls muscle growth
2012-08-30
Bethesda, MD — Scientists have moved closer toward helping people grow big, strong muscles without needing to hit the weight room. Australian researchers have found that by blocking the function of a protein called Grb10 while mice were in the womb, they were considerably stronger and more muscular than their normal counterparts. This discovery appears in the September 2012 issue of The FASEB Journal. Outside of aesthetics, this study has important implications for a wide range of conditions that are worsened by, or cause muscle wasting, such as injury, muscular dystrophy, ...
Wayne State's new flexible electronics technology may lead to new medical uses
2012-08-30
DETROIT — A Wayne State University researcher has developed technology that opens new possibilities for health care and medical applications of electronic devices.
Yong Xu, associate professor of electrical and computer engineering in the College of Engineering, has developed a simple technology compatible with silicon-on-insulator (SOI) complementary-metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) processes for making flexible electronics. "A Silicon-On-Insulator Complementary-Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Compatible Flexible Electronics Technology," published recently in Applied Physics ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
New study reveals asynchronous land–ocean responses to ancient ocean anoxia
Ctenophore research points to earlier origins of brain-like structures
Tibet ASγ experiment sheds new light on cosmic rays acceleration and propagation in Milky Way
AI-based liquid biopsy may detect liver fibrosis, cirrhosis and chronic disease signals
Hope for Rett syndrome: New research may unlock treatment pathway for rare disorder with no cure
How some skills become second nature
SFU study sheds light on clotting risks for female astronauts
UC Irvine chemists shed light on how age-related cataracts may begin
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia researchers emphasize benefits and risks of generative AI at different stages of childhood development
Why conversation is more like a dance than an exchange of words
With Evo 2, AI can model and design the genetic code for all domains of life
Discovery of why only some early tumors survive could help catch and treat cancer at very earliest stages
Study reveals how gut bacteria and diet can reprogram fat to burn more energy
Mayo Clinic researchers link Parkinson's-related protein to faster Alzheimer's progression in women
Trends in metabolic and bariatric surgery use during the GLP-1 receptor agonist era
Loneliness, anxiety symptoms, depressive symptoms, and suicidal ideation in the all of us dataset
A decision-support system to personalize antidepressant treatment in major depressive disorder
Thunderstorms don’t just appear out of thin air - scientists' key finding to improve forecasting
Automated CT scan analysis could fast-track clinical assessments
New UNC Charlotte study reveals how just three molecules can launch gene-silencing condensates, organizing the epigenome and controlling stem cell differentiation
Oldest known bony fish fossils uncover early vertebrate evolution
High‑performance all‑solid‑state magnesium-air rechargeable battery enabled by metal-free nanoporous graphene
[Press-News.org] Shedding new light on one of diabetes' most dangerous complicationsNew optical instrument helps diagnose, monitor peripheral arterial disease