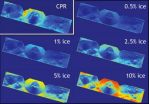
(Press-News.org) Small patches of ice could make up at most five to ten percent of material in walls of Shackleton crater.
Scientists using the Mini-RF radar on NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) have estimated the maximum amount of ice likely to be found inside a permanently shadowed lunar crater located near the moon's South Pole. As much as five to ten percent of material, by weight, could be patchy ice, according to the team of researchers led by Bradley Thomson at Boston University's Center for Remote Sensing, in Mass.
"These terrific results from the Mini-RF team contribute to the evolving story of water on the moon," says LRO's deputy project scientist, John Keller of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. "Several of the instruments on LRO have made unique contributions to this story, but only the radar penetrates beneath the surface to look for signatures of blocky ice deposits."
These are the first orbital radar measurements of Shackleton crater, a high-priority target for future exploration. The observations indicate an enhanced radar polarization signature, which is consistent with the presence of small amounts of ice in the rough inner wall slopes of the crater. Thomson and his colleagues reported the findings in a paper recently published in the journal Geophysical Research Letters.
"The interior of this crater lies in permanent shadow and is a 'cold trap'—a place cold enough to permit ice to accumulate," says Mini-RF's principal investigator, Ben Bussey of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md. "The radar results are consistent with the interior of Shackleton containing a few percent ice mixed into the dry lunar soil."
These findings support the long-recognized possibility that areas of permanent shadow inside polar impact craters are sites of the potential accumulation of water. Numerous lines of evidence from recent spacecraft observations have revised the view that the lunar surface is a completely dry, inhospitable landscape. Thin films of water and hydroxyl have been detected across the lunar surface using several space-borne near-infrared spectrometers. Additionally, orbital neutron measurements indicate elevated levels of near‐surface hydrogen in the polar regions; if in the form of water, this hydrogen would represent an average ice concentration of about 1.5% by weight in the polar regions.
The Shackleton findings are also consistent with those of the recent LCROSS spacecraft's controlled collision with a nearby permanently shadowed polar region near the lunar South Pole, which revealed evidence for water in the plume kicked up by its impact. A radar instrument flown on India's Chandrayaan-1 spacecraft in 2009 found evidence for ice deposits in craters at the lunar North Pole. Measurements of the albedo (surface reflectance) inside Shackleton crater using LRO's laser altimeter and far‐ultraviolet detector are also consistent with the presence of a small amount of ice.
"Inside the crater, we don't see evidence for glaciers like on Earth," says Thomson. "Glacial ice has a whopping radar signal, and these measurements reveal a much weaker signal consistent with rugged terrain and limited ice."
The radar measurements of Shackleton crater were made during three separate observations between December 2009 and June 2010. Radar illuminates shadowed regions and can detect deposits of water or ice, which have a distinctive radar polarization signature compared to the surrounding material. In addition, radar penetrates the terrain to depths of a meter or two and can measure water or ice buried beneath the surface. Radar measurements of Shackleton crater place an upper bound on the ice content of the uppermost meter of loose material of the crater's walls at between five and ten percent ice by weight.
"We are following up these tantalizing results with additional observations," says Bussey. "Mini-RF is currently acquiring new bistatic radar images of the moon using a signal transmitted by the Arecibo radio telescope in Puerto Rico. These bistatic images will help us distinguish between surface roughness and ice, providing further unique insights into the locations of volatile deposits."
The Mini-RF instrument, operated at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md., is one of seven instruments on board NASA's LRO spacecraft. NASA Goddard developed and manages the LRO mission. LRO's current Science Mission is implemented for NASA's Science Mission Directorate. NASA's Exploration Systems Mission Directorate sponsored LRO's initial one-year Exploration Mission that concluded in September 2010.
INFORMATION:
Walls of lunar crater may hold patchy ice, LRO radar finds
2012-08-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Stable isotopes are a universal tool
2012-08-31
Leipzig. More than 250 international scientists will be meeting in the first week of September in Leipzig to share their experiences on the latest methods and applications using stable isotopes. Stable isotopes are a tool that can be used in a wide range of areas in natural sciences and medicine as, with their help, it is possible to establish the origin of substances, and dynamic processes can be made visible. For example, it is possible to establish where a red wine really comes from, the cause of water damage, how the concentration of carbon dioxide at the South Pole ...
Analysis explores how religion and ethnicity shape the Asian-American vote
2012-08-31
As the nation's fastest-growing immigrant group, Asian Americans are likely to be a key constituency in the 2012 presidential election, but this community is far from a monolithic voting bloc, says Russell Jeung, associate professor of Asian American studies at San Francisco State University.
Jeung has published an analysis of Asian American voting patterns in the 2008 presidential election, including a breakdown of nine ethnic groups and 11 religious affiliations that make up the Asian American vote.
"Usually people act in a racial bloc or a religious bloc," Jeung ...
Monogamy and the immune system
2012-08-31
In the foothills of the Santa Cruz Mountains two closely related species of mice share a habitat and a genetic lineage, but have very different social lives. The California mouse (Peromyscus californicus) is characterized by a lifetime of monogamy; the deer mouse (Peromyscus maniculatus) is sexually promiscuous.
Researchers at the University of California Berkeley recently showed how these differences in sexual behavior impact the bacteria hosted by each species as well as the diversity of the genes that control immunity. The results were published in the May 2012 edition ...
Cardiovascular risk evaluation for all men should include assessment of sexual function
2012-08-31
(CHICAGO)-- Assessment of sexual function should be incorporated into cardiovascular risk evaluation for all men, regardless of the presence or absence of known cardiovascular disease, according to Dr. Ajay Nehra, lead author of a report by the Princeton Consensus (Expert Panel) Conference, a collaboration of 22 international, multispecialty researchers. Nehra is vice chairperson, professor and director of Men's Health in the Department of Urology at Rush University Medical Center in Chicago.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a red flag in younger men, less than 55 years of ...
Ancient genome reveals its secrets
2012-08-31
This release is available in German.
The analyses of an international team of researchers led by Svante Pääbo of the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany, show that the genetic variation of Denisovans was extremely low, suggesting that although they were present in large parts of Asia, their population was never large for long periods of time. In addition, a comprehensive list documents the genetic changes that set apart modern humans from their archaic relatives. Some of these changes concern genes that are associated with brain function ...
Microbes help hyenas communicate via scent
2012-08-31
EAST LANSING, Mich. — Bacteria in hyenas' scent glands may be the key controllers of communication.
The results, featured in the current issue of Scientific Reports, show a clear relationship between the diversity of hyena clans and the distinct microbial communities that reside in their scent glands, said Kevin Theis, the paper's lead author and Michigan State University postdoctoral researcher.
"A critical component of every animal's behavioral repertoire is an effective communication system," said Theis, who co-authored the study with Kay Holekamp, MSU zoologist. ...
Moving toward regeneration
2012-08-31
KANSAS CITY, MO—The skin, the blood, and the lining of the gut—adult stem cells replenish them daily. But stem cells really show off their healing powers in planarians, humble flatworms fabled for their ability to rebuild any missing body part. Just how adult stem cells build the right tissues at the right times and places has remained largely unanswered.
Now, in a study published in an upcoming issue of Development, researchers at the Stowers Institute for Medical Research describe a novel system that allowed them to track stem cells in the flatworm Schmidtea mediterranea. ...
Health reform: How community health centers could offer better access to subspecialty care
2012-08-31
FINDINGS:
The Affordable Care Act will fund more community health centers, making primary care more accessible to the underserved. But this may not necessarily lead to better access to subspecialty care.
In a new study, researchers from the David Geffen School of Medicine and Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Clinical Scholars program at UCLA and colleagues investigated the ways in which community health centers access subspecialty care. They identified six major models and determined which of those six offered the best access:
Tin cup ...
Researchers measure photonic interactions at the atomic level
2012-08-31
DURHAM, N.C. -- By measuring the unique properties of light on the scale of a single atom, researchers from Duke University and Imperial College, London, believe that they have characterized the limits of metal's ability in devices that enhance light.
This field is known as plasmonics because scientists are trying to take advantage of plasmons, electrons that have been "excited" by light in a phenomenon that produces electromagnetic field enhancement. The enhancement achieved by metals at the nanoscale is significantly higher than that achievable with any other material.
Until ...
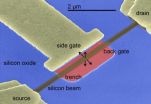
'Nanoresonators' might improve cell phone performance
2012-08-31
"There is not enough radio spectrum to account for everybody's handheld portable device," said Jeffrey Rhoads, an associate professor of mechanical engineering at Purdue University.
The overcrowding results in dropped calls, busy signals, degraded call quality and slower downloads. To counter the problem, industry is trying to build systems that operate with more sharply defined channels so that more of them can fit within the available bandwidth.
"To do that you need more precise filters for cell phones and other radio devices, systems that reject noise and allow signals ...