(Press-News.org) Inexperienced psychiatrists are less likely than their veteran peers to accurately predict violence by their patients, but a simple assessment checklist might help bridge that accuracy gap, according to new research from the University of Michigan.
Led by psychiatrist Alan Teo, M.D., a Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Clinical Scholar of the University of Michigan, researchers examined how accurate psychiatrists were at predicting assaults by acutely ill patients admitted to psychiatric units.
Their results found that inexperienced psychiatric resident doctors did no better than a coin flip, whereas veteran psychiatrists were 70 percent accurate in predicting risk of violence.
However, when a brief risk assessment tool was applied to the cases that the junior doctors evaluated, their level of accuracy jumped to 67 percent, or nearly as good as the more experienced psychiatrists. Results of the research were published online Sept. 1 in the journal Psychiatric Services.
"The tool we used, called the HCR-20-C, is remarkably brief and straightforward. Like a checklist a pilot might use before takeoff, it has just five items that any trained mental health professional can assess," Teo says.
In light of recent violent events, such as the movie theater shooting in Aurora, Colo,, earlier this summer, Teo says predicting violence risk in psychiatric patients is an increasingly important topic.
"Given public concern about this issue, I think teaching our budding psychiatrists and others how to use a practical tool like this, and encouraging its use in high-risk settings is a no-brainer," he says.
In the study, researchers were able to assess doctors' accuracy by comparing patients who had assaulted hospital staff members with similar patients who had not been violent.
Because all patients received a threat assessment when admitted to the psychiatric unit, the researchers were able to compare a patient's predicted violence risk with whether they actually had a documented assault while in the hospital.
Incidents of physical aggression typically included punching, slapping, or throwing objects, as well as yelling, directed at staff members of the hospital. The patients studied had severe illnesses, often schizophrenia, and had been involuntarily admitted to the hospital.
Teo says this study is the first to compare the predictive success of violence assessment between experienced and inexperienced psychiatrists. The results, he says, highlight the importance of emphasizing violence risk assessment in clinical training programs.
"If trainees are indeed less able than trained and experienced clinicians to accurately perform risk assessments for violence, it's important to figure out a way to improve their accuracy," he says. "Our study shows that evidence-based structured tools might have the potential to augment training and improve risk assessment."
###
Citation: Psychiatric Services, Sept. 1, 2012; doi: 10.1176/appi.ps.201200019
Other authors: Sarah R. Holley, Ph.D.; Mary Leary, M.D.; Dale E. McNiel, Ph.D.
Conflicts of interest: None.
Funding: This work was partly supported by the National Institute of Mental Health (grant R25 MH060482), a Minority Fellowship sponsored by the American Psychiatric Association and the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, and a Clinical and Translational Science Award (ULI RR024131) from the National Institutes of Health.
END
WCS invests in a diverse array of long term, seascape-scale and species-focused conservation strategies across the waters of 20 countries and all five oceans. We inspire millions to take action for the oceans through the New York Aquarium and all our parks in New York City. To achieve our long-term conservation goals, WCS marine conservationists work with local and national governments, as well as an array of partners to improve management of coastal fisheries, mitigate key threats to marine species, expand effective marine protected areas, enhance ocean industry sustainability, ...
A large meta-analysis conducted by researchers at Moffitt Cancer Center has concluded that breast cancer patients treated with chemotherapy are at risk for mild cognitive deficits after treatment. The meta-analysis, or analytic review of previously published studies, found that study participants on average had mild impairments in verbal abilities (such as difficulty choosing words) and visuospatial abilities (such as getting lost more easily). The study noted that cognitive functioning varies across survivors, with some reporting no impairments and others reporting more ...
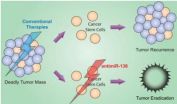
1. A*STAR scientists have identified a biomarker of the most lethal form of brain tumours in adults- glioblastoma multiforme. The scientists found that by targeting this biomarker and depleting it with a potential drug, they were able to prevent the progression and relapse of the brain tumour.
2. This research was conducted by scientists at A*STAR's Institute of Medical Biology led by Dr Prabha Sampath, Principal Investigator, in collaboration with A*STAR's Bioinformatics Institute (BII), and clinical collaborators from Medical University of Graz, Austria, and National ...
HOUSTON -- (Sept. 4, 2012) -- In the face of mounting evidence that cancer cells communicate, cooperate and even engage in collective decision-making, biophysicists and cancer researchers at Rice University, Tel Aviv University and Johns Hopkins University are suggesting a new strategy for outsmarting cancer through its own social intelligence.
"We need to get beyond the notion that cancer is a random collection of cells running amok," said Herbert Levine, co-director of Rice's Center for Theoretical Biological Physics (CTBP) and co-author of the cover article in this ...
HOUSTON – (Sept. 4, 2012) – Like tiny ships finding port in a storm, carbon atoms dock with the greater island of graphene in a predictable manner. But until recent research by scientists at Rice University, nobody had the tools to make that kind of prediction.
Electric current shoots straight across a sheet of defect-free graphene with almost no resistance, a feature that makes the material highly attractive to engineers who would use it in things like touchscreens and other electronics, said Rice theoretical physicist Boris Yakobson. He is co-author of a new paper about ...
Almost three quarters of disposed electrical household appliances in Spain are processed out of the Integrated Waste Management System (SIG). A study at the University of Salamanca exposes how many manufacturers are not registered in the established waste management system and avoid payment.
According to the European directive on waste electrical and electronic equipment, manufacturers of such products should recycle the waste they generate during their activity until reaching an annual level of 4 kg per inhabitant. However, in Spain the majority of unused equipment is ...
The governance of Canada's massive Mackenzie River Basin holds enormous national but also global importance due to the watershed's impact on the Arctic Ocean, international migratory birds and climate stability, say experts convening a special forum on the topic.
"Relevant parties in western Canada have recognized the need for a multi-party transboundary agreement that will govern land and water management in the Mackenzie River watershed. Successful collaboration will effectively determine the management regime for a watershed covering 1.8 million square kilometers or ...
1. No Nutritional or Safety Differences Between Organic and Conventional Foods
There is generally no difference in nutritional value or risk for bacterial contamination between organic and conventional foods, according to a new study being published in Annals of Internal Medicine, the flagship journal of the American College of Physicians (ACP). While the consumption of organic fruits and vegetables reduced exposure to any detectable pesticide residues by 30 percent, pesticide levels were generally within the allowable limits for safety.
Researchers conducted a systematic ...
MINNEAPOLIS – People whose blood sugar is on the high end of the normal range may be at greater risk of brain shrinkage that occurs with aging and diseases such as dementia, according to new research published in the September 4, 2012, print issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
"Numerous studies have shown a link between type 2 diabetes and brain shrinkage and dementia, but we haven't known much about whether people with blood sugar on the high end of normal experience these same effects," said study author Nicolas Cherbuin, ...
STANFORD, Calif. — You're in the supermarket eyeing a basket of sweet, juicy plums. You reach for the conventionally grown stone fruit, then decide to spring the extra $1/pound for its organic cousin. You figure you've just made the healthier decision by choosing the organic product — but new findings from Stanford University cast some doubt on your thinking.
"There isn't much difference between organic and conventional foods, if you're an adult and making a decision based solely on your health," said Dena Bravata, MD, MS, the senior author of a paper comparing the nutrition ...