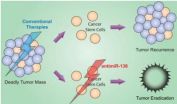
(Press-News.org) Researchers have discovered two gene variants that raise the risk of the pediatric cancer neuroblastoma. Using automated technology to perform genome-wide association studies on DNA from thousands of subjects, the study broadens understanding of how gene changes may make a child susceptible to this early childhood cancer, as well as causing a tumor to progress.
"We discovered common variants in the HACE1 and LIN28B genes that increase the risk of developing neuroblastoma. For LIN28B, these variants also appear to contribute to the tumor's progression once it forms," said first author Sharon J. Diskin, Ph.D., a pediatric cancer researcher at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia. "HACE1 and LIN28B are both known cancer-related genes, but this is the first study to link them to neuroblastoma."
Diskin and colleagues, including senior author John M. Maris, M.D., director of the Center for Childhood Cancer Research at Children's Hospital, published the study online Sept. 2 in Nature Genetics.
Striking the peripheral nervous system, neuroblastoma usually appears as a solid tumor in the chest or abdomen. It accounts for 7 percent of all childhood cancers, and 10 to 15 percent of all childhood cancer deaths.
The study team performed a genome-wide association study (GWAS), comparing DNA from 2,800 neuroblastoma patients with that of nearly 7,500 healthy children. They found two common gene variants associated with neuroblastoma, both in the 6q16 region of chromosome 6. One variant is within the HACE1 gene, the other in the LIN28B gene. They exert opposite effects: HACE1 functions as a tumor suppressor gene, hindering cancer, while LIN28B is an oncogene, driving cancer development.
The current study showed that low expression of HACE1, a tumor suppressor gene, and high expression of LIN28B, an oncogene, correlated with worse patient survival. To further investigate the gene's role, the researchers used genetic tools to decrease LIN28B's activity, and showed that this inhibited the growth of neuroblastoma cells in culture.
The new research builds on previous GWAS work by Children's Hospital investigators implicating other common gene variants as neuroblastoma oncogenes. As in the current study, these gene variants show a double-barreled effect, both initiating cancer and provoking its progression.
"In addition to broadening our understanding of the heritable component of neuroblastoma susceptibility, we think this research may suggest new therapies," Diskin added. "Our follow-up studies will focus on how we may intervene on these genes' biological pathways to develop more effective treatments."
INFORMATION:Financial support for this study came from the National Institutes of Health (grants CA124709, CA151869, HD026979, and CA136979), the Giulio D'Angio Endowed Chair, the Alex's Lemonade Stand Foundation, Andrew's Army Foundation, the PressOn Foundation, the Abramson Family Cancer Research Institute, Fondazione Italiana per la Lotta al Neuroblastoma and Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro, and the Center for Applied Genomics at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia. Co-authors with Diskin and Maris included researchers from institutions in Naples, Rende and Rome, Italy.
In addition to their positions at Children's Hospital, both Diskin and Maris are on the faculty of the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
"Common variation at 6q16 within HACE1 and LIN28B influence susceptibility to neuroblastoma," Nature Genetics, advance online publication, Sept. 2, 2012. doi:10.1038/ng.2387
About The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia: The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia was founded in 1855 as the nation's first pediatric hospital. Through its long-standing commitment to providing exceptional patient care, training new generations of pediatric healthcare professionals and pioneering major research initiatives, Children's Hospital has fostered many discoveries that have benefited children worldwide. Its pediatric research program is among the largest in the country, ranking third in National Institutes of Health funding. In addition, its unique family-centered care and public service programs have brought the 516-bed hospital recognition as a leading advocate for children and adolescents. For more information, visit http://www.chop.edu.
END
Coastline recession
The anticipated rise in sea levels due to climate change will result in coastlines receding worldwide through erosion. This is a known phenomenon that can in principle be calculated and predicted based on a given sea-level rise, by means of the so-called Bruun effect. However, things are a little more complicated when it comes to coastlines in the vicinity of inlets, such as river mouths, lagoons and estuaries. These places are affected by other factors, such as changes in rainfall due to climate change, and certain compensating effects (basin infilling).
Accurate ...
A lone rooster sees a lot of all the hens in the flock, but the hen with the largest comb gets a bigger dose of sperm - and thus more chicks. This sounds natural, but behind all this is humanity's hunger for eggs.
For thousands of years, people have tinkered with the development of domestic chickens. Through selective breeding for a few characteristics such as large muscle mass and increased egg-laying, we have at the same time caused numerous other radical changes in appearance and behaviour. A research group at Linköping University in Sweden has now shown how the size ...
A new fungal species, called 'Hebelomagriseopruinatum', has now officially been included in the list of species. The fungus, whose name can be translated into 'the grey-dewy tear leaf', was discovered on Zealand in Denmark during a mushroom-hunting tour headed by postdoc Jacob Heilman-Clausen from the University of Copenhagen.
During a mushroom-hunting excursion in 2009, postdoc Jacob Heilman-Clausen from the Center for Macroecology, Evolution and Climate at the Department of Biology, University of Copenhagen, was handed a very interesting looking fungus.
Following ...
Inexperienced psychiatrists are less likely than their veteran peers to accurately predict violence by their patients, but a simple assessment checklist might help bridge that accuracy gap, according to new research from the University of Michigan.
Led by psychiatrist Alan Teo, M.D., a Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Clinical Scholar of the University of Michigan, researchers examined how accurate psychiatrists were at predicting assaults by acutely ill patients admitted to psychiatric units.
Their results found that inexperienced psychiatric resident doctors did no ...
WCS invests in a diverse array of long term, seascape-scale and species-focused conservation strategies across the waters of 20 countries and all five oceans. We inspire millions to take action for the oceans through the New York Aquarium and all our parks in New York City. To achieve our long-term conservation goals, WCS marine conservationists work with local and national governments, as well as an array of partners to improve management of coastal fisheries, mitigate key threats to marine species, expand effective marine protected areas, enhance ocean industry sustainability, ...
A large meta-analysis conducted by researchers at Moffitt Cancer Center has concluded that breast cancer patients treated with chemotherapy are at risk for mild cognitive deficits after treatment. The meta-analysis, or analytic review of previously published studies, found that study participants on average had mild impairments in verbal abilities (such as difficulty choosing words) and visuospatial abilities (such as getting lost more easily). The study noted that cognitive functioning varies across survivors, with some reporting no impairments and others reporting more ...
1. A*STAR scientists have identified a biomarker of the most lethal form of brain tumours in adults- glioblastoma multiforme. The scientists found that by targeting this biomarker and depleting it with a potential drug, they were able to prevent the progression and relapse of the brain tumour.
2. This research was conducted by scientists at A*STAR's Institute of Medical Biology led by Dr Prabha Sampath, Principal Investigator, in collaboration with A*STAR's Bioinformatics Institute (BII), and clinical collaborators from Medical University of Graz, Austria, and National ...
HOUSTON -- (Sept. 4, 2012) -- In the face of mounting evidence that cancer cells communicate, cooperate and even engage in collective decision-making, biophysicists and cancer researchers at Rice University, Tel Aviv University and Johns Hopkins University are suggesting a new strategy for outsmarting cancer through its own social intelligence.
"We need to get beyond the notion that cancer is a random collection of cells running amok," said Herbert Levine, co-director of Rice's Center for Theoretical Biological Physics (CTBP) and co-author of the cover article in this ...
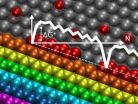
HOUSTON – (Sept. 4, 2012) – Like tiny ships finding port in a storm, carbon atoms dock with the greater island of graphene in a predictable manner. But until recent research by scientists at Rice University, nobody had the tools to make that kind of prediction.
Electric current shoots straight across a sheet of defect-free graphene with almost no resistance, a feature that makes the material highly attractive to engineers who would use it in things like touchscreens and other electronics, said Rice theoretical physicist Boris Yakobson. He is co-author of a new paper about ...
Almost three quarters of disposed electrical household appliances in Spain are processed out of the Integrated Waste Management System (SIG). A study at the University of Salamanca exposes how many manufacturers are not registered in the established waste management system and avoid payment.
According to the European directive on waste electrical and electronic equipment, manufacturers of such products should recycle the waste they generate during their activity until reaching an annual level of 4 kg per inhabitant. However, in Spain the majority of unused equipment is ...