(Press-News.org) The rate of pregnancy-associated cancer is increasing and is only partially explained by the rise in older mothers suggests new research published today (5 September) in BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology.
A large Australian study looked at 781,907 women who gave birth in New South Wales (NSW) between 1994 and 2008 which corresponds to 1,309,501 maternities. Women with pregnancy-associated cancer, where the initial diagnosis of cancer is made during pregnancy or within 12 months of delivery, are compared to women without cancer.
A total of 1,798 pregnancy-associated cancers were identified from the total number of maternities corresponding to an overall incidence rate of 137.3 per 100,000 maternities. The research found that between 1994 and 2008 the incidence rate of pregnancy-associated cancer increased from 112.3 to 191.5 per 100,000 maternities.
During this period maternal age also increased. The percentage of women aged 35 years and over increased from 13.2% to 23.6% in New South Wales.
Despite this the research found that only 14% of the increase was explained by increasing maternal age. The research looked at independent risk factors for pregnancy-associated cancer including older maternal age, Australian-born, socio-economic status, multiparity, multiple pregnancy and prior diagnosis of cancer.
The authors state that improved diagnostic techniques, detection and increased interaction with health services during pregnancy may contribute to higher incidence rates of pregnancy-associated cancer. They also say that the genetic and environmental origins of pregnancy-associated cancers are likely to pre-date the pregnancy, however the hormones and growth factors necessary for fetal growth may accelerate tumour growth.
The most common cancers were melanoma of skin, breast cancer, thyroid and other endocrine cancers, gynaecological and lymphohaematopoeitic cancers. However it must be noted that Australia has the highest incidence of melanoma in the world.
In addition the study looked at pregnancy outcomes and found that cancer during pregnancy was associated with a significantly increased risk of caesarean section, planned preterm birth and large-for-gestational-age infants.
Professor Christine Roberts, Clinical and Population Perinatal Health Research, Kolling Institute of Medical Research, University of Sydney, New South Wales and co-author of the paper said:
"This is a large study and looks at contemporary data. The trend for women to postpone childbearing has raised concerns about the incidence of cancer in pregnancy increasing.
"Although maternal age was a strong risk factor for cancer, increasing maternal age explained only some of the increase in cancer incidence. Pregnancy increases women's interaction with health services and the possibility for diagnosis is therefore increased. Furthermore, pregnancy may actually influence tumour growth."
John Thorp, BJOG Deputy-Editor-in-Chief added:
"Pregnancy is a time when a woman comes into contact with healthcare workers more frequently than normal and this may play a part in certain cancers being picked up more. The most common cancer was melanoma of the skin which it must be noted is more common in Australia than other countries."
INFORMATION: END
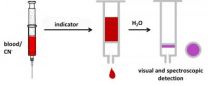
The main cause of cyanide poisoning is smoke inhalation in closed spaces during fires. Cyanides, the salts of hydrocyanic acid, inhibit cellular respiration and may lead to coma or death. The rapid administration of a cyanide antidote is essential for successful treatment. Previously, detecting cyanide in the blood took up to an hour and could only be performed in the laboratory, a lengthy process that is poorly suited for emergency situations. As a result, emergency doctors and paramedics are forced to administer antidotes based solely on presumptive diagnoses. Now, chemists ...
An archaeologist from the University of Sheffield has revealed the origin and trading routes of razor-sharp stone tools 4,200 years ago in Syria.
Ancient sites and cultural heritage are under threat in Syria due to the current conflict. An interdisciplinary research team hopes this new discovery, which has major implications for understanding the world's first empire, will help to highlight the importance of protecting Syria's heritage.
Obsidian, naturally occurring volcanic glass, is smooth, hard, and far sharper than a surgical scalpel when fractured, making it a ...
Evolving to become less aggressive could be key to saving the Tasmanian devil – famed for its ferocity – from extinction, research suggests. The species is being wiped out by Devil Facial Tumour Disease (DFTD), a fatal infectious cancer spread by biting. The new study, published in the British Ecological Society's Journal of Animal Ecology, found the less often a devil gets bitten, the more likely it is to become infected with the cancer.
According to lead author Dr Rodrigo Hamede of the University of Tasmania: "Our results – that devils with fewer bites are more likely ...
Medicare payment reforms mandated in the Affordable Care Act (ACA) for postacute care have great potential to lower costs without harming patients, a new study reports.
However, researchers caution, policymakers will need to be vigilant to ensure that these cuts don't result in one-time savings that revert to rising costs.
"We expect that the Affordable Care Act's dramatic cuts in payments to providers for postacute care will lead to decreased utilization and lower spending," said David Grabowski, Harvard Medical School professor of health care policy and lead author ...
Is there a "gender gap" in the views of professional economists? A new national study finds that while most economists agree on core economic concepts, values and methods, they differ along gender lines in their views on important economic policy.
The study – believed to be the first systematic analysis of male and female economists' views on a wide variety of policy issues – surveyed hundreds of members of the American Economic Association. The research team found that despite having similar training and adherence to core economic principles and methodology, male and ...
The Earth and the planets of our solar system are not alone in the universe. Over the past few decades, the hunt for extrasolar planets has yielded incredible discoveries, and now planetary researchers have a new tool—simulated models of how planets are born.
Most planets form when a molecular cloud collapses into a young star. The leftover gas and dust form a disk around the star, and the particulates inside the disk begin to collide and coalesce over millions of years, forming larger and larger objects until a planet eventually takes shape.
Sally Dodson Robinson, ...
Los Angeles, CA (September 4, 2012) While the effects of sexualized media on young women has long been debated, a new study finds that women who read sex-related magazine articles from popular women's magazines like Cosmopolitan are less likely to view premarital sex as a risky behavior. Additionally, the women who are exposed to these articles are more supportive of sexual behavior that both empowers women and prioritizes their own sexual pleasure. This study was published in a recent article from Psychology of Women Quarterly (published by SAGE).
Study authors Janna ...
The Pink Double Dandy peony, the Double Peppermint petunia, the Doubled Strawberry Vanilla lily and nearly all roses are varieties cultivated for their double flowers.
The blossoms of these and other such plants are lush with extra petals in place of the parts of the flower needed for sexual reproduction and seed production, meaning double flowers – though beautiful – are mutants and usually sterile.
The genetic interruption that causes that mutation helped scientists in the 1990s pinpoint the genes responsible for normal development of sexual organs stamens and carpels ...
Disease-free survival for invasive ductal breast cancer (IDC) patients may be easier to predict with the help of F-18-fludeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (PET)/computed tomography (CT) scans, according to research published in the September issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. New data show that high maximum standard uptake value (SUVmax) of F-18-FDG in the lymph nodes prior to treatment could be an independent indicator of disease recurrence.
"Many studies have revealed that breast cancer patients with axillary lymph node metastasis have a significantly ...
New Rochelle, NY, September 4, 2012—The use of RNA in nanotechnology applications is highly promising for many applications, including the development of new therapeutic compounds. Key technical challenges remain, though, and the challenges and opportunities associated with the use of RNA molecules in nanotechnology approaches are presented in a review article in Nucleic Acid Therapeutics, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. The article is available free online at the Nucleic Acid Therapeutics website.
Peixuan Guo and colleagues, University of Kentucky, ...