(Press-News.org) Children exposed to diethyl phthalate (DEP) and butylbenzyl phthalate (BBzP)—phthalate chemicals commonly found in personal care and plastic products—have elevated risk of asthma-related airway inflammation, according to researchers at Columbia Center for Children's Environmental Health (CCCEH) at the Mailman School of Public Health.
Of the 244 children aged 5 to 9 in the study, all had detectable levels of phthalates in their urine although these varied over a wide range. Higher levels of both phthalates were associated with higher levels of nitric oxide in exhaled breath, a biological marker of airway inflammation. The association between BBzP exposure and airway inflammation was especially strong among children who had recently reported wheeze, a common symptom of asthma. Results were recently published online in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine.
"While many factors contribute to childhood asthma, our study shows that exposure to phthalates may play a significant role," says Allan Just, PhD, first author on the new CCCEH study and current postdoctoral researcher at the Harvard School of Public Health.
Dr. Just and co-investigators looked at children enrolled in the CCCEH Mothers and Newborns study. All live in Northern Manhattan and the South Bronx where asthma prevalence is high. Exposure to phthalates was measured through a urine test, and the level of nitric oxide in the child's exhaled breath was quantified as a marker of airway inflammation.
The study is the first to use exhaled nitric oxide in a study of phthalate exposure in children. By using the biomarker in exhaled breath, the researchers overcame a significant hurdle. "Many asthma patients only have asthma exacerbations a few times a year, making it difficult to discern short-term associations between environmental exposures and the disease," explains Matthew Perzanowski, PhD, senior author and Associate Professor of Environmental Health Sciences at the Mailman School. "To solve this problem, we used nitric oxide, which has been shown to be a reliable marker of airway inflammation in response to known asthma triggers like vehicle emissions."
Phthalates are used widely in consumer products, including plastics, vinyl flooring, and personal care products, making exposure ubiquitous in the United States and other developed nations. Phthalates enter the body through ingestion, inhalation, and absorption through the skin. However, past research has suggested inhalation to be a particularly important route of exposure to the two phthalates associated with airway inflammation in this study. Several phthalates are known to disrupt the endocrine system and early-life exposure has been linked not only to asthma but also to adverse neurobehavioral and reproductive effects. A recent study by Dr. Just and other CCCEH investigators found that prenatal exposure to BBzP was linked with increased risk of childhood eczema.
###The research was supported by funding from the National Institutes of Health grants R01 ES014393, R01 ES013163, P01 ES09600, R01 ES008977, and P30 ES009089; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency grants R827027, RD832141, RD834509, and EPA STAR graduate fellowship FP-91712001 for Allan C. Just; the John and Wendy Neu Family Foundation and other private funding sources.
Additional authors include Robin M. Whyatt, Rachel L. Miller, Andrew G. Rundle, Qixuan Chen, Antonia M. Calafat, Adnan Divjan, Maria J. Rosa, Hanjie Zhang, Frederica P. Perera, and Inge F. Goldstein.
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Children exposed to 2 phthalates have elevated risk of asthma-related airway inflammation
2012-09-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Telaprevir: Added benefit in certain patients with hepatitis C
2012-09-05
The drug telaprevir (trade name: Incivo®) has been available for treatment of chronic hepatitis C infection of genotype 1 since autumn 2011. In an early benefit assessment pursuant to the "Act on the Reform of the Market for Medicinal Products" (AMNOG), the German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) examined whether telaprevir offers an added benefit compared with the present standard therapy.
According to the findings of the assessment, the new drug telaprevir offers advantages in various groups of patients with chronic hepatitis C infection ...
New study examines how ocean energy impacts life in the deep sea
2012-09-05
Durham, NC — A new study of deep-sea species across the globe aims to understand how natural gradients in food and temperature in the dark, frigid waters of the deep sea affect the snails, clams, and other creatures that live there.
Similar studies have been conducted for animals in the shallow oceans, but our understanding of the impact of food and temperature on life in the deep sea — the Earth's largest and most remote ecosystem — has been more limited.
The results will help scientists understand what to expect in the deep sea under future climate change, the researchers ...
Gender equality influences how people choose their partners
2012-09-05
Men and women clearly have different strategies for picking sexual partners, but the reason why differences exist is less clear. The classic explanation for these differences has been that men's and women's brains have evolved to make certain choices, but a new study in Psychological Science, a publication of the Association for Psychological Science, suggests that evolution is only part of the answer.
To be a 'success' in evolutionary terms, women need to have access to resources for raising offspring, and men need to have access to fertile females. Researchers have ...
AGU: Glacial thinning has sharply accelerated at major South American icefields
2012-09-05
WASHINGTON –For the past four decades scientists have monitored the ebbs and flows of the icefields in the southernmost stretch of South America's vast Andes Mountains, detecting an overall loss of ice as the climate warms. A new study, however, finds that the rate of glacier thinning has increased by about half over the last dozen years in the Southern Patagonian Icefield, compared to the 30 years prior to 2000.
"Patagonia is kind of a poster child for rapidly changing glacier systems," said Michael Willis, lead author of the study and a research associate at Cornell ...
Teens tell different tales about themselves depending on gender
2012-09-05
COLUMBIA, Mo. — During adolescence, the stories young people tell about themselves reflects their development of a personal identity and sense of self, and those autobiographical narratives vary depending on the teens' gender, according to a University of Missouri psychologist and her colleagues. Parents can use this knowledge of how teens talk about themselves to help understand the tumultuous transitions of their children into adults.
"Autobiographical stories tell us details about adolescent psychology that questionnaires and observations of behavior cannot," said ...
Study in mice discovers injection of heat-generating cells reduces belly fat
2012-09-05
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The injection of a tiny capsule containing heat-generating cells into the abdomens of mice led those animals to burn abdominal fat and initially lose about 20 percent of belly fat after 80 days of treatment.
Researchers conducting the study were surprised to see that the injected cells even acted like "missionaries," converting existing belly fat cells into so-called thermogenic cells, which use fat to generate heat.
Over time, the mice gained back some weight. But they resisted any dramatic weight gain on a high-fat diet and burned away more than ...
Study: How a high-fat diet and estrogen loss leads women to store more abdominal fat than men
2012-09-05
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A high-fat diet triggers chemical reactions in female mice that could explain why women are more likely than men to gain fat in the abdomen after eating excess saturated fat, new research suggests. The study also sheds light on why women gain fat following menopause.
Scientists identified events in female mice that start with the activation of an enzyme and end with the formation of visceral fat – fat that accumulates around internal organs and is linked to a higher risk for Type 2 diabetes, heart disease and cancer.
At least one function for this ...
Young Crossover Tenor Carlos Aponte Releases His Album: Attimo
2012-09-05
Puerto Rican Young Crossover Tenor Carlos Aponte recently presented 'Attimo', an album that features 11 of the world's most memorable songs with new musical and vocal arrangements in English, Spanish, Italian, and German.
Since his appearance on the acclaimed NBC TV show America's Got Talent, Carlos has been busy at public and private performances in Puerto Rico, the United States and also internationally such as Costa Rica and China.
'Attimo' (Italian for 'Moment') includes a Spanish version of the smash hit 'You Raise Me Up (Por Ti Sere),' as well as other outstanding ...
Rate of women with pregnancy-associated cancer on the increase
2012-09-05
The rate of pregnancy-associated cancer is increasing and is only partially explained by the rise in older mothers suggests new research published today (5 September) in BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology.
A large Australian study looked at 781,907 women who gave birth in New South Wales (NSW) between 1994 and 2008 which corresponds to 1,309,501 maternities. Women with pregnancy-associated cancer, where the initial diagnosis of cancer is made during pregnancy or within 12 months of delivery, are compared to women without cancer.
A total of ...
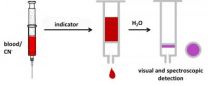
Rapid response in cases of smoke poisoning
2012-09-05
The main cause of cyanide poisoning is smoke inhalation in closed spaces during fires. Cyanides, the salts of hydrocyanic acid, inhibit cellular respiration and may lead to coma or death. The rapid administration of a cyanide antidote is essential for successful treatment. Previously, detecting cyanide in the blood took up to an hour and could only be performed in the laboratory, a lengthy process that is poorly suited for emergency situations. As a result, emergency doctors and paramedics are forced to administer antidotes based solely on presumptive diagnoses. Now, chemists ...