(Press-News.org) Attention men: The day may be coming soon when you can take your own birth control pill with no side effects, according to a study done by a group of scientists that includes a Texas A&M University researcher.
Qinglei Li, an assistant professor in Texas A&M's College of Veterinary Medicine & Biomedical Sciences, is part of a team of researchers led by Martin Matzuk at Baylor College of Medicine and James Bradner at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute who made the discovery, and their work is published in the journal Cell.
Working on mice, the team found that a compound called JQ1 acts as an inhibitor to sperm production and also sperm mobility.
"Both of these are needed for fertility, but JQ1 prevents both," Li says of the findings.
"It stopped the sperm production very dramatically. More good news is that there appear to be no side effects whatsoever. Once the JQ1 was no longer given to the mice, they were back to their normal reproduction rates, and it did not affect mating behavior or the health of the offspring."
Though the mice were given injections, the team believes that a pill could eventually be developed for the same results.
A male contraceptive pill has been talked about for decades, but so far none has been successfully created despite a strong demand.
While many men might be reluctant to take out the trash or ask for directions if they are lost, recent studies have shown that about 70 percent of men would be willing to take a birth control pill if it were available.
One drawback to many female contraceptives is that they sometimes interfere with hormones, especially estrogen. But Li says the team is confident that JQ1 does not affect testosterone levels in men, and appears to have no other side effects as well.
As with many discoveries, the JQ1 compound appears to have come about by accident.
It was originally used for anti-cancer treatments, but researchers found it was also an excellent compound in controlling fertility.
"This is an exciting step in male contraception," Li adds.
"A compound with more specificity will be needed before clinical trials can be done for humans. It does not mean a male birth control just yet, but it is a great step forward in that direction."
###
About Research at Texas A&M University:
As one of the world's leading research institutions, Texas A&M is in the vanguard in making significant contributions to the storehouse of knowledge, including that of science and technology. Research conducted at Texas A&M represents an annual investment of more than $700 million. That research creates new knowledge that provides basic, fundamental and applied contributions resulting in many cases in economic benefits to the state, nation and world.
Media contact: Keith Randall, News & Information Services, at (979) 845-4644 or keith-randall@tamu.edu or Qinglei Li at (979) 862-2009 or QLi@cvm.tamu.edu
For more news about Texas A&M University, go to http://tamutimes.tamu.edu/
Follow us on Twitter at http://twitter.com/tamu/
The National Human Genome Research Institute today announced the results of a five-year international study of the regulation and organization of the human genome. The project is named ENCODE, which stands for the Encyclopedia of DNA Elements. In conjunction with the release of those results, the Journal of Biological Chemistry has published a series of reviews that focus on several aspects of the findings.
"The ENCODE project not only generated an enormous body of data about our genome, but it also analyzed many issues to better understand how the genome functions in ...
The most-studied mass extinction in Earth history happened 65 million years ago and is widely thought to have wiped out the dinosaurs. New University of Washington research indicates that a separate extinction came shortly before that, triggered by volcanic eruptions that warmed the planet and killed life on the ocean floor.
The well-known second event is believed to have been triggered by an asteroid at least 6 miles in diameter slamming into Mexico's Yucatán Peninsula. But new evidence shows that by the time of the asteroid impact, life on the seafloor – mostly species ...
Montreal, September 5, 2012 – Being the last one picked for the team, getting left out of the clique of cool girls, having no one to sit with at lunch… For children, social exclusion can impact everything from emotional well being to academic achievements.
But what does it mean for the kids doing the excluding? Is the cure a one-size-fits-all approach that requires kids to include others, regardless of the situation at hand? Not necessarily, says new research from a professor now at Concordia University.
Unlike previous studies where researchers created hypothetical ...
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Only about 1 percent of the human genome contains gene regions that code for proteins, raising the question of what the rest of the DNA is doing. Scientists have now begun to discover the answer: About 80 percent of the genome is biochemically active, and likely involved in regulating the expression of nearby genes, according to a study from a large international team of researchers.
The consortium, known as ENCODE (which stands for "Encyclopedia of DNA Elements"), includes hundreds of scientists from several dozen labs around the world. Using genetic ...
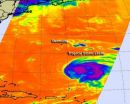
Infrared data from NASA's Aqua satellite shows that Tropical Storm Leslie has been causing problems for itself.
Tropical Storm Leslie has been on a slow track in the Atlantic, and because of that, the storm is kicking up cooler waters from below the ocean surface. Those cooler waters were seen in infrared imagery on Sept. 5 at 0611 UTC (2:11 a.m. EDT) taken by the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite. The cooler waters are responsible for Leslie's slow strengthening. Sea surface temperatures need to be at least as warm ...
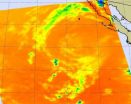
Post-tropical cyclone John has been "flushed" out of existence in the eastern Pacific Ocean, and infrared NASA imagery revealed warmer cloud top temperatures and virtually no precipitation from John's remnants on Sept. 4.
When NASA's Aqua satellite flew over post-tropical storm John on Sept. 4 at 21:23 UTC (5:23 p.m. EDT) the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument revealed that cloud top temperatures in the storm had warmed over the previous 24 hours. AIRS data also showed there was one very tiny area of convection (rising air that forms the thunderstorms that ...
For years policymakers have attempted to replace Medicare's fee-for- service payment system with approaches that pay one price for an aggregation of services. The intent has been to reward providers for offering needed care in the most appropriate and cost-effective manner. But many of these programs have known pitfalls, says Stuart Altman, an economist and the Sol C. Chaikin Professor of National Health Policy at the Heller School for Social Policy and Management, Brandeis University.
On Friday, Sept. 7, Altman and his Heller school colleague Robert Mechanic, will ...
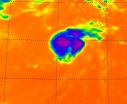
NASA's Aqua satellite shows that tiny Tropical Storm Michael had some strong thunderstorms wrapped around its center and in a band of thunderstorms in its northeastern "arm" or quadrant.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured in infrared image of Tropical Storm Michael on Sept. 5 at 0611 UTC (2:11 a.m. EDT) and noticed the strongest thunderstorms and coldest cloud top temperatures around the center of circulation and in a band of thunderstorms to the northeast of Michael's center. Those cloud top temperatures ...
Be warned, popularity may cause lung cancer, heart disease, and emphysema.
New research from the University of Southern California (USC) and University of Texas finds that popular students in seven Southern California high schools are more likely to smoke cigarettes than their less popular counterparts.
The study, which appears online this week in the Journal of Adolescent Health, confirms trends observed in previous USC-led studies of students in the sixth through 12th grades across the United States and in Mexico.
"That we're still seeing this association more ...
Sinking through the inky ocean, it would seem that there is little light at depth: but you'd be wrong. 'In the mesopelagic realm [200 m] bioluminescence [light produced by animals] is very common', says Sönke Johnsen from Duke University, USA, explaining that many creatures are capable of producing light, yet rarely do so. But how much light do the inhabitants of the ocean floor (benthos) generate? Explaining that some bioluminescence is generated when organisms collide, Johnsen says, 'In the benthos you have a current moving over complicated ground with all the things ...