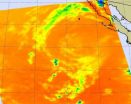
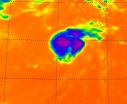
(Press-News.org) Post-tropical cyclone John has been "flushed" out of existence in the eastern Pacific Ocean, and infrared NASA imagery revealed warmer cloud top temperatures and virtually no precipitation from John's remnants on Sept. 4.
When NASA's Aqua satellite flew over post-tropical storm John on Sept. 4 at 21:23 UTC (5:23 p.m. EDT) the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument revealed that cloud top temperatures in the storm had warmed over the previous 24 hours. AIRS data also showed there was one very tiny area of convection (rising air that forms the thunderstorms that make up a tropical cyclone) in the southwestern quadrant of the entire low pressure area. The AIRS infrared data showed a circular swirl of clouds where temperatures were around 270 kelvin (26.3 F/-3.1 C), which are warm in terms of cloud top temperatures for thunderstorms. When cloud top temperatures reach the AIRS data threshold of -63F/-52C, they are considered strong thunderstorms.
The last advisory on John was issued by the National Hurricane Center on Sept. 4 at 2100 UTC (5 p.m. EDT), just before the AIRS image was captured by NASA's Aqua satellite. The 5 p.m. advisory put John's center about 505 miles west-northwest of Cabo San Lucas, Mexico, near 24.3 North and 117.7 West. John's maximum sustained winds were near 35 mph (55 kmh) and weakening. The remnants of John were moving to the northwest at 12 knots (13.8 mph/22.2 kmh) as the low pressure area continued to weaken. John is expected to dissipate later today.
INFORMATION:
NASA sees fading post-Tropical Cyclone John's warmer cloud tops
2012-09-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Alternatives to Medicare's fee-for-service payment system examined
2012-09-06
For years policymakers have attempted to replace Medicare's fee-for- service payment system with approaches that pay one price for an aggregation of services. The intent has been to reward providers for offering needed care in the most appropriate and cost-effective manner. But many of these programs have known pitfalls, says Stuart Altman, an economist and the Sol C. Chaikin Professor of National Health Policy at the Heller School for Social Policy and Management, Brandeis University.
On Friday, Sept. 7, Altman and his Heller school colleague Robert Mechanic, will ...
NASA imagery reveals strength in Tropical Storm Michael's 'arm'
2012-09-06
NASA's Aqua satellite shows that tiny Tropical Storm Michael had some strong thunderstorms wrapped around its center and in a band of thunderstorms in its northeastern "arm" or quadrant.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured in infrared image of Tropical Storm Michael on Sept. 5 at 0611 UTC (2:11 a.m. EDT) and noticed the strongest thunderstorms and coldest cloud top temperatures around the center of circulation and in a band of thunderstorms to the northeast of Michael's center. Those cloud top temperatures ...
Popular kids in US and Mexico more likely to smoke, USC studies show
2012-09-06
Be warned, popularity may cause lung cancer, heart disease, and emphysema.
New research from the University of Southern California (USC) and University of Texas finds that popular students in seven Southern California high schools are more likely to smoke cigarettes than their less popular counterparts.
The study, which appears online this week in the Journal of Adolescent Health, confirms trends observed in previous USC-led studies of students in the sixth through 12th grades across the United States and in Mexico.
"That we're still seeing this association more ...
Bright life on the ocean bed: Predators may even color code food
2012-09-06
Sinking through the inky ocean, it would seem that there is little light at depth: but you'd be wrong. 'In the mesopelagic realm [200 m] bioluminescence [light produced by animals] is very common', says Sönke Johnsen from Duke University, USA, explaining that many creatures are capable of producing light, yet rarely do so. But how much light do the inhabitants of the ocean floor (benthos) generate? Explaining that some bioluminescence is generated when organisms collide, Johnsen says, 'In the benthos you have a current moving over complicated ground with all the things ...
Deep-sea crabs grab grub using UV vision
2012-09-06
DURHAM, N.C. -- Crabs living half-a-mile down in the ocean, beyond the reach of sunlight, have a sort of color vision combining sensitivity to blue and ultraviolet light.
Their detection of shorter wavelengths may give the crabs a way to ensure they grab food, not poison.
"Call it color-coding your food," said Duke biologist Sönke Johnsen. He explained that the animals might be using their ultraviolet and blue-light sensitivity to "sort out the likely toxic corals they're sitting on, which glow, or bioluminesce, blue-green and green, from the plankton they eat, which ...
Minimally invasive surgery works well for abdominal aortic aneurysms, Mayo finds
2012-09-06
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- A minimally invasive procedure known as endovascular repair used for abdominal aortic aneurysms has a low rate of complications, even in high-risk patients such as those with kidney, heart or lung problems, a Mayo Clinic study shows. Researchers found that even when aneurysms ruptured, endovascular repair had lower mortality rates than open-abdominal surgery, the other treatment option. The findings are being presented at the Midwestern Vascular Surgical Society Annual Meeting, Sept. 6-8, in Milwaukee, Wis.
An abdominal aortic aneurysm is a weakened ...
Bacteria on marine sponges can develop capacity to move and inhibit biofilm formation
2012-09-06
BALTIMORE, MD (September 6, 2012)—A new study shows that when enough bacteria get together in one place, they can make a collective decision to grow an appendage and swim away. This type of behavior has been seen for the first time in marine sponges, and could lead to an understanding of how to break up harmful bacterial biofilms, such as plaque on teeth or those found on internal medical devices like artificial heart valves.
Bacteria have ways of communicating with each other, and scientists have now identified a new signaling system that, when there is a critical mass ...
Moffitt Cancer Center researchers find acidic pH microenvironments in tumors aid tumor cell survival
2012-09-06
Researchers at Moffitt Cancer Center and colleagues at the University of South Florida and Wayne State University have discovered that tumor cell survival relies on adaptation to acidic conditions in the tumor microenvironment. Their research investigating the effects of acidity on breast and pancreatic cancer cell lines revealed the importance of autophagy in acidic microenvironments and suggests that a successful treatment strategy might be based on this autophagic dependence.
The study appears as the cover story for the Aug. 15 issue of Cancer Research, a publication ...
Positive American Youth, Inc. Announces 5th ANNUAL "PAY DAY" 2012 For Kids
2012-09-06
Positive American Youth, Inc. (P.A.Y. USA), chaired by Atlanta radio personality Maurice "Reec" Swiney announces the 2012 5th Annual PAY USA "PAY DAY". The yearly event which benefits metro Atlanta children & their families will be held, Saturday Sept. 29th @ Atlanta Metro College. The fun begins at 11 am and lasts until 4 pm.
The purpose of the "PAY DAY" event is to promote the importance of education, healthcare, community involvement, and perseverance to urban children. "We are proud to say last years' event was very successful," ...
Crime Victims First Announces the 3rd Annual Jam for Justice "No Violence Day"
2012-09-06
Crime Victims First (www.crimevictimsfirst.org) proclaims October 21, 2012 a "No Violence Day," and announces our 3rd Annual Jam for Justice Music Festival (www.jam4justice.org). This is our annual event to increase awareness and to offer a family event to celebrate all that our community does on behalf of crime victims. The event is free. The Keynote Speaker is Meg Garvin, Executive Director at the National Crime Victim Law Institute. Meg is also our 2012 Outstanding Community Service Award Winner. The music festival features Quenby and the West of Wayland Band ...