(Press-News.org) Inhaled pain relief appears to be effective in reducing pain intensity and in giving pain relief in the first stage of labour, say Cochrane researchers. These conclusions came from a systematic review that drew data from twenty-six separate studies that involved a total of 2,959 women, and are published in The Cochrane Library.
Many women would like to have a choice in pain relief during labour and would also like to avoid invasive methods of pain management. Inhaling a mixture of oxygen and either a flurane derivative or nitrous oxide reduces pain, but enable the mother to remain awake and able to swallow normally. This form of pain relief is easy to take, can be started in less than a minute and becomes effective within a minute.
The review found that women who used nitrous oxide had more pain relief than those who had no analgesic at all. The women do need to be warned, though, that this gas can cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, dizziness and drowsiness. If fluranes were available, using them gave a more powerful effect than nitrous oxide, while at the same time having fewer side-effects.
While fluranes can only be given to women under supervision of an educated analgesia professional, nitrous oxide can be administered by midwives. "This is probably the main reason why flurane use is not widespread and also why little research is done on this form of inhaled analgesia for the management of labour pain," says lead author Trudy Klomp, who works at the Department of Midwifery Science and the EMGO Institute for Health and Care Research at VU University Medical Center, Amsterdam
The researchers believe that a more widespread use of nitrous oxide could help many women who at the moment do not have any option for pain relief, but where there are appropriately trained anaesthesia professions flurane is the preferred gas to use.
"We need to apply some caution to these findings as there was a lot of variation in the analyses of pain intensity and of pain relief between the studies and some of the trials involved small numbers of women," says Klomp. "But despite these limitations, inhaled analgesia's ability to significantly reduce pain intensity and increase pain relief indicates that it can help women in labour, particularly those who want pain relief but do not want more intensive forms such as epidurals."
The authors call for more trials to be conducted that involve larger numbers of women and look particularly at which forms of anaesthetic give a woman a greater sense of control in labour, satisfaction with the whole childbirth experience and ease in moving on to breastfeeding.
###
Inhaled pain relief in early labor is safe and effective
2012-09-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Latinos more vulnerable to fatty pancreas, Type 2 diabetes, Cedars-Sinai study shows
2012-09-11
LOS ANGELES – Latinos are more likely to store fat in the pancreas and are less able to compensate by excreting additional insulin, a Cedars-Sinai study shows.
The research examining overweight, prediabetic patients, published online by Diabetes Care, is part of a focus by Cedars-Sinai's Heart Institute, Biomedical Imaging Research Institute and Diabetes and Obesity Research Institute, to identify biological measures that could help predict which patients are likely to develop type 2 diabetes.
"Prevention of diabetes is our goal," said Richard Bergman, PhD, director ...
Study provides insight into why severely obese women have difficulty getting pregnant from IVF
2012-09-11
Boston – One third of American women of childbearing age are battling obesity, a condition that affects their health and their chances of getting pregnant. Obese women often have poor reproductive outcomes, but the reasons why have not been clearly identified. Now, a novel study led by Catherine Racowsky, PhD, director of the Assisted Reproductive Technologies Laboratory at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH), and performed by Ronit Machtinger, M.D., of BWH, in collaboration with Catherine Combelles, PhD, of Middlebury College, gains further insight into the underlying ...
U of Toronto-led team induces high-temperature superconductivity in a semiconductor with Scotch tape
2012-09-11
September 10, 2012-- Issued by the UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO
Under strict embargo by Nature Communications until Tuesday, September 11, 11 a.m. EST
An international team led by University of Toronto physicists has developed a simple new technique using Scotch poster tape that has enabled them to induce high-temperature superconductivity in a semiconductor for the first time. The method paves the way for novel new devices that could be used in quantum computing and to improve energy efficiency.
"Who would have thought simply sticking things together can generate entirely ...
New discovery related to gum disease
2012-09-11
A University of Louisville scientist has found a way to prevent inflammation and bone loss surrounding the teeth by blocking a natural signaling pathway of the enzyme GSK3b, which plays an important role in directing the immune response.
The discovery of UofL School of Dentistry researcher David Scott, PhD, and his team recently published on-line first in the journal Molecular Medicine. The finding not only has implications in preventing periodontal disease, a chronic inflammatory disease that causes tooth loss, but also may have relevance to other chronic inflammatory ...
Breast cancer risks acquired in pregnancy may pass to next 3 generations
2012-09-11
Chemicals or foods that raise estrogen levels during pregnancy may increase cancer risk in daughters, granddaughters, and even great-granddaughters, according to scientists from Virginia Tech and Georgetown University.
Pregnant rats on a diet supplemented with synthetic estrogen or with fat, which increases estrogen levels, produce ensuing generations of daughters that appear to be healthy, but harbor a greater than normal risk for mammary cancer, the researchers report in today's Nature Communications.
Although the findings have not yet been validated in humans, the ...
Unnecessary oil disasters
2012-09-11
The BP oil disaster in the Gulf of Mexico 2010 could have been avoided if the experiences of earlier disasters had been put to use, researcher Charles Woolfson, Linköping university, claims. The United States government is now accusing BP of gross negligence and deliberate misconduct, and taking the company to court.
On April 20, 2010, the Deepwater Horizon oil rig exploded in the ocean south of the southern coast of the US. The explosion led to the deaths of eleven people and an unfathomable environmental catastrophe.
Charles Woolfson, former professor of Labour Sociology ...
Serious games could be integrated into surgical training subject to validation
2012-09-11
Serious gaming can be used to enhance surgical skills, but games developed or used to train medical professionals need to be validated before they are integrated into teaching methods, according to a paper in the October issue of the surgical journal BJS.
Researchers from The Netherlands reviewed 25 research studies covering 30 serious games published between 1995 and 2012.
"Many medical professionals may still have a rather out-dated view of the average gamer as being someone who is too young to vote, afraid of daylight and busy killing mystical dwarves in their parent's ...
Chain reaction in the human immune system trapped in crystals
2012-09-11
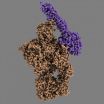
VIDEO:
The animation shows how the MASP-2 (blue) attaches itself to the complement protein C4 (orange), and the structural rearrangements that occur in the C4 due to this. Note that although...
Click here for more information.
The complement system is part of the innate immune system and is composed of about 40 different proteins that work together to defend the body against disease-causing microorganisms. The complement system perceives danger signals in the body by recognising ...
More traffic deaths in wake of 9/11
2012-09-11
This press release is available in German.
In the wake of the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001, many Americans started driving more due to a fear of flying – and lost their lives in traffic accidents. But why did this happen more frequently in some states than in others? And why didn't Spanish driving habits change in the same way following the 2004 train bombings in Madrid? Wolfgang Gaissmaier and Gerd Gigerenzer from the Harding Center for Risk Literacy at the Max Planck Institute for Human Development in Berlin present new findings on this topic in the ...
Lights off? International experts call attention to dangers of exposure to light at night
2012-09-11
"The most important thing for us is to raise awareness of the dangers of artificial light at night and we have already come a long way now that the American Medical Association (AMA) recently announced its new policy recognizing adverse health effects of exposure to light at night and encouraging further research into the matter," said Prof. Abraham Haim, a leading authority on light pollution, who coordinated the 21st International Congress of Zoology (ICZ) that was held last week at the University of Haifa, Israel.
The panel of world experts discussed "Light Pollution ...