(Press-News.org) Serious gaming can be used to enhance surgical skills, but games developed or used to train medical professionals need to be validated before they are integrated into teaching methods, according to a paper in the October issue of the surgical journal BJS.
Researchers from The Netherlands reviewed 25 research studies covering 30 serious games published between 1995 and 2012.
"Many medical professionals may still have a rather out-dated view of the average gamer as being someone who is too young to vote, afraid of daylight and busy killing mystical dwarves in their parent's basement" says co-author Dr Marlies Schijven from the Department of Surgery at the Academic Medical Centre in Amsterdam.
"However, the reality is that the average game player is 37 years-old and there are almost three times as many women using games as boys aged 17 years or younger.
"Although game-based learning is becoming a new form of healthcare education, scientific research on its effectiveness is limited. The aim of this review was to identify the value of serious games for training professionals in medicine and, in particular, surgery."
Nineteen articles discussing 17 serious games specifically developed for educational purposes were identified by Dr Schijven and co-author Dr Maurits Graafland. Many of these covered team training in acute and critical care and dealing with mass casualty incidents, including nuclear events and hazardous materials. Others covered more specific areas of healthcare, such as training for coronary artery bypasses and knee joint surgery and assessing and resuscitating patients with burns.
Six studies assessed 13 commercially available games associated with, but not specifically developed for, improving skills relevant to the medical profession. They included sports, action, adventure and shooting games and were used to help surgeons improve their laparoscopic psychomotor skills.
The authors have made a number of observations as a result of their review. These include:
Serious games form an innovative approach towards the education of medical professionals and surgical specialities are eager to apply them for a range of training purposes.
Further research should define valid performance parameters and formally validate programmes before serious games can be seen as fully fledged teaching instruments for medical and surgical professionals.
Although a serious game does not necessarily have to be developed for an educational purpose to be an educational tool, such games cannot be seen as fully completed training resources.
Serious games allow multiple professionals to train simultaneously on one case and allow one professional to train multiple cases simultaneously. These skills are recognised as critical in reducing medical errors in dynamic high-risk environments, such as the operating room or emergency department.
Serious games can provide crisis resource training, with a large variety of cases, in a relatively cheap, readily available environment that provides a viable alternative to expensive simulators. Serious games also provide training environments for disaster situations and mass casualty incidents, including combat care.
Games need to be designed to fit into residency teaching programmes if they are to be used as a way of preventing medical errors.
Simulation and serious gaming represent ideal teaching methods to optimise the knowledge and skill of residents before they are entrusted with procedures in real patients. Educators and games designers should develop serious games that train professionals in order to maximise patient safety.
Although the cost of developing serious games can run into millions, this investment can be justified in terms of delivering better patient care and preventing errors and insurance companies could play a key role.
"Our review clearly shows that serious games can be used to provide surgeons with training in both technical and non-technical skills" says Dr Schijven. "However, games developed or used to train medical professionals need to be validated before they are integrated into surgical teaching programmes."
###The paper can be read free online at: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/bjs.8819/pdf
Note to editors
Systematic review of serious games for medical education and surgical skills training. Graafland et al BJS. 99, pp1322-1330. (October 2012). DOI: 10.1002/bjs.8819
With an impact factor of 4.606, BJS is the premier surgical journal in Europe and one of the top six surgical periodicals in the world. Its international readership is reflected in the prestigious international Editorial Board, supported by a panel of over 1200 reviewers worldwide. BJS features the very best in clinical and laboratory-based research on all aspects of general surgery and related topics. Developing areas such as minimally invasive therapy and interventional radiology are strongly represented. http://wileyonlinelibrary.com/journal/BJS
Wiley-Blackwell is the international scientific, technical, medical, and scholarly publishing business of John Wiley & Sons, with strengths in every major academic and professional field and partnerships with many of the world's leading societies. Wiley-Blackwell publishes nearly 1,500 peer-reviewed journals and 1,500+ new books annually in print and online, as well as databases, major reference works and laboratory protocols. For more information, please visit www.wileyblackwell.com or our new online platform, Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com), one of the world's most extensive multidisciplinary collections of online resources, covering life, health, social and physical sciences, and humanities.
Serious games could be integrated into surgical training subject to validation
2012-09-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
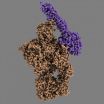
Chain reaction in the human immune system trapped in crystals
2012-09-11
VIDEO:
The animation shows how the MASP-2 (blue) attaches itself to the complement protein C4 (orange), and the structural rearrangements that occur in the C4 due to this. Note that although...
Click here for more information.
The complement system is part of the innate immune system and is composed of about 40 different proteins that work together to defend the body against disease-causing microorganisms. The complement system perceives danger signals in the body by recognising ...
More traffic deaths in wake of 9/11
2012-09-11
This press release is available in German.
In the wake of the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001, many Americans started driving more due to a fear of flying – and lost their lives in traffic accidents. But why did this happen more frequently in some states than in others? And why didn't Spanish driving habits change in the same way following the 2004 train bombings in Madrid? Wolfgang Gaissmaier and Gerd Gigerenzer from the Harding Center for Risk Literacy at the Max Planck Institute for Human Development in Berlin present new findings on this topic in the ...
Lights off? International experts call attention to dangers of exposure to light at night
2012-09-11
"The most important thing for us is to raise awareness of the dangers of artificial light at night and we have already come a long way now that the American Medical Association (AMA) recently announced its new policy recognizing adverse health effects of exposure to light at night and encouraging further research into the matter," said Prof. Abraham Haim, a leading authority on light pollution, who coordinated the 21st International Congress of Zoology (ICZ) that was held last week at the University of Haifa, Israel.
The panel of world experts discussed "Light Pollution ...
Researchers devise more accurate method for predicting hurricane activity
2012-09-11
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed a new method for forecasting seasonal hurricane activity that is 15 percent more accurate than previous techniques.
"This approach should give policymakers more reliable information than current state-of-the-art methods," says Dr. Nagiza Samatova, an associate professor of computer science at NC State and co-author of a paper describing the work. "This will hopefully give them more confidence in planning for the hurricane season."
Conventional models used to predict seasonal hurricane activity rely on classical ...
A minute crustacean invades the red swamp crayfish
2012-09-11
The small ostracod Ankylocythere sinuosa measures no more than half a millimetre in length and lives on other crayfish. And, Spanish scientists have discovered it for the first time in Europe. The finding suggests that it arrived along with the invader crayfish Procambarus clarkii some 30 years ago but it is still unknown whether it can invade other crustacean species or whether it benefits or damages the expansion of the already established red swamp crayfish.
The red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) originates from the USA and Mexico and has been present in the Iberian ...
Dartmouth research imparts momentum to mobile health
2012-09-11
Electronic Jewelry for Health
Bracelets and amulets are in the works at Dartmouth's Institute for Security, Technology, and Society (ISTS). Rather than items of mere adornment, the scientists and engineers are constructing personal mobile health (mHealth) devices—highly functional jewelry, as it were.
mHealth is a rapidly growing field where technology helps you or your physician monitor your health through mobile devices. This approach can offer more accurate and timely diagnoses as well as lower health costs. However, smartphones are often used to transmit collected ...
Aussie wasp on the hunt for redback spiders
2012-09-11
University of Adelaide researchers say a small wasp that scientists had forgotten about for more than 200 years is now making a name for itself – as a predator of Australia's most common dangerous spider, the redback.
The wasp (Agenioideus nigricornis) was first described scientifically in 1775 by Danish entomologist Johan Christian Fabricius, thanks to samples collected in Australia during Captain Cook's first great voyage (1768).
"Since then, scientists have largely forgotten about the wasp," says Professor Andy Austin from the University of Adelaide's Australian ...
Diet could combat adverse side-effects of quinine
2012-09-11
Scientists at The University of Nottingham say adverse side-effects caused by the anti-parasitic drug quinine in the treatment of malaria could be controlled by what we eat.
The research, carried out by Nottingham scientists on the University's campuses in the UK and Malaysia, indicates that natural variation in our levels of the amino acid, tryptophan, has a marked bearing on how we respond to quinine treatment. It appears that the lower our levels of tryptophan the more likely it is that we would suffer side-effects. And because tryptophan is an essential amino acid ...
A study analyzes the search for information in stock photography agencies
2012-09-11
VIDEO:
Research carried out at Universidad Carlos III in Madrid analyzes the search and visualization systems used by commercial stock photography agencies, whose estimated annual net sales reach over 150 billion...
Click here for more information.
Stock photography agencies, and not just those companies that dominate the digital photography market, are at the forefront of information search tools. "Their search, visualization and information downloading systems are extraordinarily ...
Vitamin C and beta-carotene might protect against dementia
2012-09-11
Forgetfulness, lack of orientation, cognitive decline… about 700, 000 Germans suffer from Alzheimer's disease (AD). Now researchers from the University of Ulm, among them the Epidemiologist Professor Gabriele Nagel and the Neurologist Professor Christine von Arnim, have discovered that the serum-concentration of the antioxidants vitamin C and beta-carotene are significantly lower in patients with mild dementia than in control persons. It might thus be possible to influence the pathogenesis of AD by a person's diet or dietary antioxidants. 74 AD-patients and 158 healthy ...