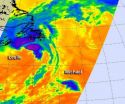
(Press-News.org) When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the Atlantic on Sept. 11 it caught Tropical Storm Leslie's clouds over Newfoundland and peanut-shaped Tropical Storm Michael to its southwest. The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured infrared data on Tropical Storms Leslie and Michael when it passed overhead on Sept. 11.
Michael Appears Peanut-Shaped on Satellite Imagery
Tropical Storm Michael forecast to become a remnant low later today, Sept. 11, but as of 11 a.m. EDT Michael still had maximum sustained winds near 45 mph (75 kmh). It was located about 1,090 miles (1,755 km) west of the Azores. Michael is moving to the north-northeast 23 mph (37 kmh) and this motion is expected to continue during the next day or so.
In the AIRS infrared image from around 1 a.m. EDT on Sept. 11, the strongest area of convection (and thunderstorms) appeared to be over Michael's north and eastern quadrants making the storm appear peanut-shaped on NASA satellite imagery. An infrared satellite image of Michael later on Sept. 11 showed that most of the convection has disappeared and Michael appeared as tight swirl of low clouds. Michael is over cool waters and in an environment of strong wind shear, two factors that are weakening the storm quickly. The National Hurricane Center forecast notes that Michael's remnants should then become absorbed by a front in the next day or two.
Tropical Storm Leslie Moving Away from Newfoundland
According to the Canadian Hurricane Centre, Leslie made landfall Tuesday, Sept. 10 in Fortune, Newfoundland, at about 8:30 a.m. AST (7:30 a.m. EDT) with maximum sustained winds near 40 mph (65 kmh). The Seattle Post Intelligencer newspaper reports power outages and flight cancellations. Canadian Broadcasting Corporation news reported heavy rainfall and wind gusts up to 82 mph (132 kmh) over the Avalon Peninsula, including St. John's that caused power outages, and downed trees. Leslie became a post-tropical cyclone as it begins to move away from Newfoundland.
The Canadian Hurricane Center discontinued the hurricane watch for southeastern Newfoundland early on Sept. 11, but a tropical storm warning is in effect for Newfoundland from Indian Harbour to Triton.
AIRS infrared imagery from 1 a.m. EDT on Sept. 11 showed strong thunderstorms around Leslie's center and in bands to the north of the center. At 11 a.m. EDT on Sept. 11, the center of post-tropical cyclone Leslie was located near latitude 49.4 north, longitude 53.6 west, about 130 miles (210 km) north-northwest of St. Johns Newfoundland. The post-tropical cyclone is moving toward the north-northeast at 45 mph (72 kmh).
By 12 p.m. EDT, satellite imagery showed that Leslie is now part of a cold front and is no longer a tropical cyclone. Post-tropical/extratropical cyclone is still producing a large area of tropical-storm-force winds primarily to the north and east of the center as it continues to move north-northeast at 39 knots. This system is forecast to remain a strong Post-tropical cyclone as it moves rapidly toward the northeast and east over the north Atlantic.
Leslie's remnants are expected to skirt southern Iceland on Thursday, Sept. 12 before heading toward Scotland sometime on Sept. 13.
INFORMATION:
NASA infrared data reveals fading Tropical Storm Leslie and peanut-shaped Michael
2012-09-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Yellow lights mean drivers have to make right choice -- if they have time
2012-09-12
A couple of years ago, Hesham Rakha misjudged a yellow traffic light and entered an intersection just as the light turned red. A police officer handed him a ticket.
"There are circumstances, as you approach a yellow light, where the decision is easy. If you are close to the intersection, you keep going. If you are far away, you stop. If you are almost at the intersection, you have to keep going because if you try to stop, you could cause a rear-end crash with the vehicle behind you and would be in the middle of the intersection anyway," said Rakha, professor of civil ...
Genetic make-up of children explains how they fight malaria infection
2012-09-12
Researchers from Sainte-Justine University Hospital Center and University of Montreal have identified several novel genes that make some children more efficient than others in the way their immune system responds to malaria infection. This world-first in integrative efforts to track down genes predisposing to specific immune responses to malaria and ultimately to identify the most suitable targets for vaccines or treatments was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences by lead author Dr. Youssef Idaghdour and senior author Pr. Philip Awadalla, whose ...
Scientists discover how the brain ages
2012-09-12
The ageing process has its roots deep within the cells and molecules that make up our bodies. Experts have previously identified the molecular pathway that react to cell damage and stems the cell's ability to divide, known as cell senescence.
However, in cells that do not have this ability to divide, such as neurons in the brain and elsewhere, little was understood of the ageing process. Now a team of scientists at Newcastle University, led by Professor Thomas von Zglinicki have shown that these cells follow the same pathway.
This challenges previous assumptions ...
Uncertain about health outcomes, male stroke survivors more likely to suffer depression than females
2012-09-12
Philadelphia, PA, September 12, 2012 – Post-stroke depression is a major issue affecting approximately 33% of stroke survivors. A new study published in the current issue of Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation reports that the level to which survivors are uncertain about the outcome of their illness is strongly linked to depression. The relationship is more pronounced for men than for women.
"Male stroke survivors in the US who subscribe to traditional health-related beliefs may be accustomed to, and value highly, being in control of their health," says ...
Information theory helps unravel DNA's genetic code
2012-09-12
DNA consists of regions called exons, which code for the synthesis of proteins, interspersed with noncoding regions called introns. Being able to predict the different regions in a new and unannotated genome is one of the biggest challenges facing biologists today. Now researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology in Delhi have used techniques from information theory to identify DNA introns and exons an order of magnitude faster than previously developed methods. The researchers were able to achieve this breakthrough in speed by looking at how electrical charges are ...
Going with the flow
2012-09-12
Scientists who study tissue engineering and test new drugs often need to sort, rotate, move, and otherwise manipulate individual cells. They can do this by prodding the cells into place with a mechanical probe or coaxing them in the desired direction with acoustic waves, electric fields, or flowing fluids. Techniques that rely on direct physical contact can position individual cells with a high level of precision while non-contact techniques are often faster for sorting large numbers of cells. An international team of researchers has now developed a way to manipulate cells ...
Less wear, longer life for memory storage device
2012-09-12
Probe storage devices read and write data by making nanoscale marks on a surface through physical contact. The technology may one day extend the data density limits of conventional magnetic and optical storage, but current probes have limited lifespans due to mechanical wear. A research team, led by Intel Corp., has now developed a long-lasting ultrahigh-density probe storage device by coating the tips of the probes with a thin metal film. The team's device features an array of 5,000 ultrasharp probes that is integrated with on-chip electronic circuits. The probes write ...
Weizmann Institute's mathematical model may lead to safer chemotherapy
2012-09-12
Cancer chemotherapy can be a life-saver, but it is fraught with severe side effects, among them an increased risk of infection. Until now, the major criterion for assessing this risk has been the blood cell count: if the number of white blood cells falls below a critical threshold, the risk of infection is thought to be high. A new model built by Weizmann Institute mathematicians in collaboration with physicians from the Meir Medical Center in Kfar Saba and from the Hoffmann-La Roche research center in Basel, Switzerland, suggests that for proper risk assessment, it is ...
New York & New Jersey Minority Supplier Development Council Presents Train Ride to Success: Networking on the Railroad on Friday, September 14
2012-09-12
The New York & New Jersey Minority Supplier Development Council (The Council) takes networking on the road on Friday, September 14 when corporate supplier diversity executives and minority business owners ride a New Jersey Transit train to New Brunswick at the annual "Train Ride to Success."
The Council's highly anticipated annual event kicks-off at New York Penn Station at 9:30am when the New York group meets to board the reserved railroad car. "Train Ride to Success" event concludes at 3:00pm in New Brunswick.
At "Train Ride to Success, ...
Lee Enterprises Consulting Group Adds Maritime Expert
2012-09-12
Lee Enterprises Alternative Fuels Consulting is pleased to announce the addition of Gerry Ellis as its maritime projects expert. Ellis has a B.Sc. in Nautical Science from Liverpool University in Liverpool, United Kingdom. He is the President of Miami based Ellis Maritime Consulting and one of the world's top experts in the maritime industry. Ellis is a Master Mariner, Class 1 (Unlimited) with over 30 years' experience in the marine industry. He has served as the VP of Marine & Technical Operations, Director of Compliance, Director of Port Development, Director of New ...