(Press-News.org) CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – You may think you have your food all to yourself, but you're actually sharing it with a vast community of microbes waiting within your digestive tract. A new study from the University of North Carolina School of Medicine reveals some gut microbes increase the absorption of dietary fats, allowing the host organism to extract more calories from the same amount of food.
"This study is the first to demonstrate that microbes can promote the absorption of dietary fats in the intestine and their subsequent metabolism in the body," said senior study author John Rawls, PhD, associate professor in the Department of Cell and Molecular Physiology at UNC. "The results underscore the complex relationship between microbes, diet and host physiology."
Previous studies showed gut microbes aid in the breakdown of complex carbohydrates, but their role in dietary fat metabolism remained a mystery, until now. The research was published in the Sept 13, 2012 issue of the journal Cell Host & Microbe.
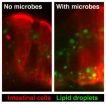
The study was carried out in zebrafish, which are optically transparent when young. By feeding the fish fatty acids tagged with fluorescent dye, the researchers were able to directly observe the absorption and transport of fats in the presence or absence of gut microbes.
The researchers pinpointed one group of bacteria — Firmicutes — as instrumental in increasing fat absorption. They also found the abundance of Firmicutes in the gut was influenced by diet: fish fed normally had more Firmicutes bacteria compared to fish that were denied food for several days. Other studies have linked a higher relative abundance of Firmicutes in the gut with obesity in humans.
"Our findings indicate that the gut microbiota can increase the host's ability to harvest calories from the diet by stimulating fat absorption," said the study's lead researcher, Ivana Semova, PhD, who was a graduate student at UNC at the time the study was conducted. "Another implication is that diet history could impact fat absorption by changing the abundance of certain microbes, such as Firmicutes, that promote fat absorption."
Although the study involved only fish, not humans, the researchers say it offers insights that could help inform new approaches to treating obesity and other disorders. For example, said Rawls, "If we can understand how specific gut bacteria are able to stimulate absorption of dietary fat, we may be able to use that information to develop new ways to reduce fat absorption in the context of obesity and associated metabolic diseases, and to enhance fat absorption in the context of malnutrition."
INFORMATION:
Study co-authors include Lantz Mackey of UNC, Juliana Carten and Steven Farber of the Carnegie Institution for Science, and Jesse Stombaugh and Rob Knight of the University of Colorado at Boulder.
Gut microbes help the body extract more calories from food
In a study using zebrafish, UNC researchers reveal how microbes in the intestine aid the uptake of fats -- and suggest how diet may influence our bodies' microbial communities.
2012-09-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Age, not underlying diagnosis, key factor in weight gain in children after tonsillectomy
2012-09-12
Potentially worrisome weight gains following tonsillectomy occur mostly in children under the age of 6, not in older children, a study by Johns Hopkins experts in otolaryngology- head and neck surgery shows.
Sudden increases in body mass index, or BMI, have been routinely observed for months after some of the more than half-million surgeries performed annually in the United States to remove the sore and swollen tissues at the back of the throat.
The Johns Hopkins study, in 115 children in the Baltimore region, is believed to be the first to dispel long-held beliefs ...
A celestial witch's broom?
2012-09-12
The Pencil Nebula is pictured in a new image from ESO's La Silla Observatory in Chile. This peculiar cloud of glowing gas is part of a huge ring of wreckage left over after a supernova explosion that took place about 11 000 years ago. This detailed view was produced by the Wide Field Imager on the MPG/ESO 2.2-metre telescope.
Despite the tranquil and apparently unchanging beauty of a starry night, the Universe is far from being a quiet place. Stars are being born and dying in an endless cycle, and sometimes the death of a star can create a vista of unequalled beauty as ...
Studies shed light on how to reduce the amount of toxins in plant-derived foods
2012-09-12
A number of environmental toxins pose considerable health threats to humans, and the heavy metal cadmium (Cd) ranks high on the list. Most of us are exposed to it through plant-derived foods such as grains and vegetables. Now, new research offers ways in which investigators can reduce the amount of Cd found in the food we eat, according to a review published online September 12th in the Cell Press journal Trends in Plant Science.
"Cadmium is virtually everywhere in the environment, and it is taken up into the human body and bioaccumulates for decades in the kidney," ...
Gut bacteria increase fat absorption
2012-09-12
Baltimore, MD —You may think you have dinner all to yourself, but you're actually sharing it with a vast community of microbes waiting within your digestive tract. A new study from a team including Carnegie's Steve Farber and Juliana Carten reveals that some gut microbes increase the absorption of dietary fats, allowing the host organism to extract more calories from the same amount of food.
Previous studies showed gut microbes aid in the breakdown of complex carbohydrates, but their role in dietary fat metabolism remained a mystery, until now. The research is published ...
Sandia, OurEnergyPolicy.org release 'Goals of Energy Policy' poll results
2012-09-12
LIVERMORE, Calif.— U.S. energy policy should simultaneously pursue security of its energy supply, economic stability and reduced environmental impacts, says a national poll of energy professionals jointly prepared by Sandia National Laboratories and OurEnergyPolicy.org.
The findings of the national poll, "The Goals of Energy Policy," show that the vast majority — more than 85 percent — of the 884 energy professionals surveyed prefer policymaking that pursues all three goals at once.
The poll asked the experts to allocate 100 points, representing a 100 percent policymaking ...
New paper addresses causes of shattering glass cookware; Margin of safety described as 'borderline'
2012-09-12
A new paper appearing in the September 2012 edition of the Bulletin of The American Ceramic Society for the first time provides a scientific explanation of why some glass cookware sold in the United States is more susceptible than others to "explosive" shattering and the possibility of exposing consumers to injury from flying glass shards.
Clear glass baking dishes and pots are a staple in many households around the world and have been since they were first introduced in 1915 to consumers by the Corning Glass Works, which created the Pyrex brand name. The original Pyrex ...
Old deeds, witness trees offer glimpse of pre-settlement forest in West Virginia
2012-09-12
PARSONS, W. Va., September 12, 2012 – Using old deeds and witness trees, a U.S. Forest Service scientist has created a glimpse of the composition of the forests that covered today's Monongahela National Forest before settlement and logging changed the landscape.
"European Settlement-Era Vegetation of the Monongahela National Forest, West Virginia" describes how a Forest Service scientist and her West Virginia University colleague answered questions about the composition of early forests using a unique dataset. The dataset was built with original deeds, metes and bounds ...
Predicting a die throw
2012-09-12
Vegas, Monte Carlo, and Atlantic City draw people from around the world who are willing to throw the dice and take their chances. Researchers from the Technical University of Lodz, Poland, have spotted something predictable in the seemingly random throw of the dice. By applying chaos theory and some high school level mechanics, they determined that by knowing the initial conditions – such as the viscosity of the air, the acceleration of gravity, and the friction of the table – it should be possible to predict the outcome when rolling the dice.
The researchers created ...
A carefully scheduled high-fat diet resets metabolism and prevents obesity
2012-09-12
New research from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem shows that a carefully scheduled high-fat diet can lead to a reduction in body weight and a unique metabolism in which ingested fats are not stored, but rather used for energy at times when no food is available.
The research was conducted by Prof. Oren Froy along with Prof. Zecharia Madar, research student Yoni Genzer and research fellow Dr. Hadas Sherman at the Institute of Biochemistry, Food Science and Nutrition, at the Hebrew University's Robert H. Smith Faculty of Agriculture, Food and Environment. The results ...
Epigenetics emerges powerfully as a clinical tool
2012-09-12
The research team led by Manel Esteller, director of the Cancer Epigenetics and Biology Program at the Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBELL), professor of genetics at the University of Barcelona and ICREA researcher, has updated the latest findings in applied epigenetics in a review paper published in Nature Reviews Genetics.
There is a growing need for better biomarkers that allow early detection of human diseases, especially cancer. The markers can improve primary prevention, diagnosis and prognosis of disease. Furthermore, it is possible to predict which ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
[Press-News.org] Gut microbes help the body extract more calories from foodIn a study using zebrafish, UNC researchers reveal how microbes in the intestine aid the uptake of fats -- and suggest how diet may influence our bodies' microbial communities.