(Press-News.org) CHICAGO --- More can be done to properly manage the care of American children with food allergies, especially when it comes to diagnostic testing and recognizing non-visual symptoms of severe allergic reactions, according to a new Northwestern Medicine study.
"Every child with a food allergy should be diagnosed by a physician, have access to life-saving medication such as an epinephrine autoinjector and receive confirmation of the disease through diagnostic testing," said lead author Ruchi Gupta, M.D., an associate professor of pediatrics at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine and a physician at the Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago. "Not all children are receiving this kind of care."
The study was published online in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, the official publication of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology.
Data in this study is from a randomized online survey of U.S. households with children with symptoms consistent with a mild-to-severe food allergy. It's the first paper of its kind to offer insight on how pediatric food allergies are typically diagnosed and what can be done to streamline the management of the disease and keep affected children safe.
Here are key findings from the study:
70 percent report receiving a physician's diagnosis for their child's food allergy
Lower income and minority households were more likely to have a child with an undiagnosed food allergy.
Of the physician-diagnosed children, 32 percent did not receive diagnostic testing --- such as a blood, skin or oral food challenge test.
A skin test was the most popular diagnostic test with 46 percent. A blood test was second with 39 percent.
Only 1 in 5 of reported that their child received an oral food challenge test --- the gold standard of food allergy diagnoses.
"An oral food challenge might be scary for parents because their child is being fed the allergenic food," Gupta said. "Some physicians think the risks outweigh the benefits, but it is the best tool we have to diagnose a food allergy."
Here are key findings on the kind of reactions children had to the top nine food allergies, which are: egg, finfish, milk, peanut, sesame, shellfish, soy, tree nut and wheat:
Cutaneous symptoms, such as hives, puffy eyes or lips, and eczema occurred in 80 percent of food-induced anaphylactic reactions.
During severe, life-threatening reactions, hives only occurred in 40 percent of the cases and puffy eyes or lips in 34 percent of the cases.
"Not all food allergy reactions start with swelling or a rash," Gupta said. "If you suspect your child has eaten something they're allergic to and you don't see a visible sign of a reaction, you need to think about what might be going on internally."
Here are some questions to ask a child after a suspected accidental ingestion of an allergenic food:
Does your throat feel tight?
Are you having trouble breathing?
Do you feel dizzy or faint?
Does your stomach hurt?
"This study shows why it's vital that children receive an accurate diagnosis, and that parents and other caregivers know the signs of a severe reaction and are equipped to respond immediately," said Mary Jane Marchisotto, executive director of the Food Allergy Initiative (FAI), which provided financial support for the study. "We urge families to visit www.faiusa.org, where they will find the information and tools they need to understand and cope with food allergies."
INFORMATION:
A nonprofit founded in 1998 by concerned parents and grandparents, FAI is the world's largest private funder of food allergy research.
END
Toronto – Tax collectors and insurance agencies trying to boost honest reporting could improve compliance simply by asking people to sign their forms at the beginning instead of at the end.
That's because attesting to the truthfulness of the information before a form is filled out tends to activate people's moral sense, making it harder for them to fudge their numbers after, says a new paper.
"Based on our previous research we knew that an honour code is useful, but we were wondering how much the location mattered," says Nina Mazar, an assistant professor of marketing ...
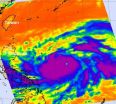
Tropical Storm Sanba exploded in intensity between Sept. 12 and 13, becoming a major Category 4 Typhoon on the Saffir-Simpson Scale. NASA's Aqua satellite captured infrared data that showed a large area of powerful thunderstorms around the center of circulation, dropping heavy rain over the western North Pacific Ocean.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Super Typhoon Sanba on Sept. 13 at 0447 UTC (12:47 a.m. EDT). The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an infrared image of Sanba and found an eye about 20 nautical miles (23 miles/37 km) wide, surrounded ...
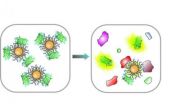
AMHERST, Mass. – In the fight against cancer, knowing the enemy's exact identity is crucial for diagnosis and treatment, especially in metastatic cancers, those that spread between organs and tissues. Now chemists led by Vincent Rotello at the University of Massachusetts Amherst have developed a rapid, sensitive way to detect microscopic levels of many different metastatic cell types in living tissue. Findings appear in the current issue of the journal ACS Nano.
In a pre-clinical non-small-cell lung cancer metastasis model in mice developed by Frank Jirik and colleagues ...
A new study finds that smart growth approaches to urban planning could substantially reduce the number of miles that residents drive in a year. The research was published this week in The B.E. Journal of Economic Analysis and Policy.
Smart growth focuses on the development of compact, walkable cities with houses and jobs located close together. By shortening residents' commutes, this form of urban design aims to cut transportation-related energy use and greenhouse gas emissions. California is already pursuing smart growth in order to meet emissions reductions set by the ...
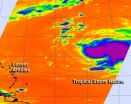
Tropical Storm Nadine is struggling against wind shear and some dry air. Infrared satellite imagery from NASA showed that Nadine's most powerful thunderstorms were being pushed east of the center.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Nadine early on Sept. 13 and saw several factors that indicated the storm was still struggling to achieve hurricane status.
Infrared data from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) that flies aboard Aqua found the strongest thunderstorms with very cold cloud temperatures (colder than -63F/-52C) were being pushed east of Nadine's ...
Gardeners and landscapers may want to rethink their fall tree plantings. Warming temperatures have already made the U.S. Department of Agriculture's new cold-weather planting guidelines obsolete, according to Dr. Nir Krakauer, assistant professor of civil engineering in The City College of New York's Grove School of Engineering.
Professor Krakauer developed a new method to map cold-weather zones in the United States that takes rapidly rising temperatures into account. Analyzing recent weather data, he overhauled the Department of Agriculture's latest plant zone map released ...
Researchers have developed new software that can rapidly calculate the carbon footprints of thousands of products simultaneously, a process that up to now has been time consuming and expensive. The methodology should help companies to accurately label products, and to design ways to reduce their environmental impacts, said Christoph Meinrenken, the project's leader and associate research scientist at Columbia University's Earth Institute and Columbia Engineering. A new study, published online in the Journal of Industrial Ecology, describes the methodology.
The project ...
In a ribbon-cutting ceremony on Sept. 12, 2012, the U.S. Commerce Department's National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) unveiled a new laboratory designed to demonstrate that a typical-looking suburban home for a family of four can generate as much energy as it uses in a year. Following an initial year-long experiment, the facility will be used to improve test methods for energy-efficient technologies and develop cost-effective design standards for energy-efficient homes that could reduce overall energy consumption and harmful pollution, and save families money ...
Nanoengineers at the University of California, San Diego have developed a novel technology that can fabricate, in mere seconds, microscale three dimensional (3D) structures out of soft, biocompatible hydrogels. Near term, the technology could lead to better systems for growing and studying cells, including stem cells, in the laboratory. Long-term, the goal is to be able to print biological tissues for regenerative medicine. For example, in the future, doctors may repair the damage caused by heart attack by replacing it with tissue that rolled off of a printer.
Reported ...
Children of immigrants are outperforming children whose family trees have deeper roots in the United States, learning more in school and then making smoother transitions into adulthood, according to sociologists at The Johns Hopkins University.
Researchers Lingxin Hao and Han S. Woo tracked nearly 11,000 children from as young as age 13 into their early 30s, coming from families with diverse backgrounds. When comparing children with similar socioeconomic status and school conditions, Hao and Woo found that the best students, and later the most successful young adults, ...