(Press-News.org) A new model system of the cellular skeletons of living cells is akin to a mini-laboratory designed to explore how the cells' functional structures assemble. A paper about to be published in EPJ E by physicist Volker Schaller and his colleagues from the Technical University Munich, Germany, presents one hypothesis concerning self-organisation. It hinges on the findings that a homogeneous protein network, once subjected to stresses generated by molecular motors, compacts into highly condensed fibres.
The contractile machinery inside cells is arguably the most prominent example of cells' ability to self-organise cellular proteins into highly ordered functional structures involved in cell division or cell migration, for example.
The authors attempt to elucidate how such highly self-organised structures emerge from a less ordered and homogeneous collection of constituent proteins. Namely, such proteins are actin filaments — one of the main scaffold proteins in cells made of biopolymers — and associated molecular motors. The latter exerts forces by pressing along the filament, an energy consuming process.
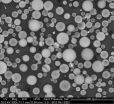
Schaller and colleagues reconstituted a minimal model system of the cellular skeleton consisting of actin filaments held together by cross-linking proteins and molecular motors. They found that this minimal system is sufficient to reproduce similar self-organisation processes observed in nature.
In particular, they showed that a homogeneous network of actin filaments held together by the cross-linking protein α-actinin can rapidly be reorganised by molecular motor proteins. It contracts to form a highly heterogeneous set of compact fibres consisting of millions of individual filaments, resembling scaffold structures inside the cellular skeleton.
The authors also realised that the efficiency of this reorganisation process, and therefore the length scale of the fibres created, directly depend on motor activity. Thus, the fibres can range between 5μm and up to 100μm in length for low and high motor activity, respectively.
###
Reference
V. Schaller, B. Hammerich, A. R. Bausch, Active compaction of crosslinked driven filament networks, European Physical Journal E 35: 81, DOI 10.1140/epje/i2012-12081-2
For more information, please visit www.epj.org
The full-text article is available to journalists on request.
Self-forming biological scaffolding
A model system that can interpret the role of cross-linking proteins
2012-09-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Angling for gold
2012-09-19
A study on how gold atoms bond to other atoms using a model that takes into account bonds direction has been carried out by physicist Marie Backman from the University of Helsinki, Finland, and colleagues. These findings, which are about to be published in EPJ B, are a first step toward better understanding how gold binds to other materials through strong, so-called covalent, bonds.
What scientists need is an empirical model, based on a so-called potential, that describes the gold-gold bond in a reliable way. Most previous models only accounted for interactions in the ...
Barack Obama good for Israel; Barack Hussein Obama less so
2012-09-19
President Obama's middle name, Hussein, makes Israelis – both Jewish and Arab – perceive him as less pro-Israeli, reveals a new study conducted by the University of Haifa and the University of Texas. The study has just been published in the journal Political Behavior. "Even though the Israeli public has extensive information about the American President and his positions, their opinions can still be swayed by cultural cues, such as a name that in this case is perceived as Arabic," says Dr. Israel Waismel-Manor of the University of Haifa who co-authored the study.
Similar ...
NEIKER and INRA discover that BDA symptoms in grapevine leaves are a sign of esca
2012-09-19
This press release is available in Spanish.Scientists at the Basque Institute of Agricultural Research and Development, NEIKER-Tecnalia, and the National Institute of Agricultural Research in Bordeaux (INRA) have come to the conclusion that alleged symptoms of 'black dead arm' (BDA) on grapevine leaves are, in fact, those of esca disease in its initial phase. Esca and BDA are diseases that affect the trunk of vines and cause serious losses to the wine-making and grape-growing sectors every year.
The symptoms produced by esca and BDA in vine leaves are reminiscent of ...
Preemies' brains reap long-term benefits from Kangaroo Mother Care
2012-09-19
This press release is available in French.Quebec City, September 19, 2012—Kangaroo Mother Care -- a technique in which a breastfed premature infant remains in skin-to-skin contact with the parent's chest rather than being placed in an incubator -- has lasting positive impact on brain development, revealed Université Laval researchers in the October issue of Acta Paediatrica. Very premature infants who benefited from this technique had better brain functioning in adolescence -- comparable to that of adolescents born at term -- than did premature infants placed in incubators.
Earlier ...
Stop diabetes with insulin tablets
2012-09-19
Type 1 diabetes is the autoimmune form of diabetes, in which the patients' insulin-producing beta cells are destroyed by their own immune system.
"We know that if a person has two autoantibodies and one of them is against insulin, there is a 50 per cent risk that they will develop type 1 diabetes within five years. It doesn't matter how old you are", says Åke Lernmark, Professor of Experimental Diabetes Research at Lund University in Sweden.
"There are indications that oral insulin may prevent or delay the clinical onset of type 1 diabetes among individuals with autoantibodies ...
Fighting melanoma's attraction to the brain
2012-09-19
The process of metastasis, by which cancer cells travel from a tumor site and proliferate at other sites in the body, is a serious threat to cancer patients. According to the National Cancer Institute, most recurrences of cancer are metastases rather than "new" cancers.
Virtually all types of cancer can spread to other parts of the body, including the brain. Once metastatic melanoma cells are entrenched in the brain, patients typically have only a few months to live.
Now Prof. Isaac Witz and his team at Tel Aviv University's Department of Cell Research and Immunology ...
Carbon dioxide from water pollution, as well as air pollution, may adversely impact oceans
2012-09-19
Carbon dioxide (CO2) released into the oceans as a result of water pollution by nutrients — a major source of this greenhouse gas that gets little public attention — is enhancing the unwanted changes in ocean acidity due to atmospheric increases in CO2. The changes may already be impacting commercial fish and shellfish populations, according to new data and model predictions published today in ACS's journal, Environmental Science & Technology.
William G. Sunda and Wei-Jun Cai point out that atmospheric levels of CO2, the main greenhouse gas, have increased by about 40 ...
A TECNALIA study reveals the loss of nanomaterials in surface treatments caused by water
2012-09-19
This press release is available in Spanish.Researchers at TECNALIA recently published a study in the prestigious science magazine, Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, which reveals the emission of nanomaterials caused by water runoff on surfaces containing nanomaterials. These surface treatments are employed in numerous consumption and construction products, so evidences of the presence of engineered nanomaterials are beginning to appear in the environment. Concerns about their toxicity for human or the environment rose in the last years, so further studies are required.
The ...
Revolutionary ultrathin, flat lens: Smartphones as thin as a credit card?
2012-09-19
Scientists are reporting development of a revolutionary new lens — flat, distortion-free, so small that more than 1,500 would fit across the width of a human hair — capable in the future of replacing lenses in applications ranging from cell phones to cameras to fiber-optic communication systems. The advance, which could lead to smart phones as thin as a credit card, appears in ACS' journal Nano Letters.
Federico Capasso and colleagues explain that the lenses used to focus light in eyeglasses, microscopes and other products use the same basic technology dating to the late ...
Toward a better material for hip replacement and other joint implants
2012-09-19
In an advance toward a new generation of improved hip and other joint replacements, scientists are describing development of a potential implant material that flexes more like natural bone, fosters the growth of bone that keeps implants firmly in place and is less likely to fail and require repeat surgery. Their study on these so-called tantalum nanotube materials appears in ACS Applied Material & Interfaces.
Hongyi Li, Jinshu Wang and Zhenting Zhang explain that the metal tantalum has advantages over titanium, stainless steel and other metals used in the current generation ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
[Press-News.org] Self-forming biological scaffoldingA model system that can interpret the role of cross-linking proteins