(Press-News.org) Diverse symptoms associated with autism could be explained by unreliable activity of neurons in the brain in response to basic, nonsocial sensory information, according to a study published by Cell Press on September 19th in the journal Neuron. The new findings suggest that autism is a disorder of general neural processing and could potentially provide an explanation for the origins of a range of psychiatric and neurological disorders.
"Within the autism research community, most researchers are looking for either a dysfunctional brain region or inadequate connections between brain regions," says lead study author Ilan Dinstein of Carnegie Mellon University. "We're taking a different approach and thinking about how a general characteristic of the brain could be different in autism—and how that might lead to behavioral changes."
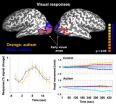
Autism is a developmental disorder marked by social deficits, communication problems, and repetitive behaviors. Two previous studies suggested that the neural responses of individuals with autism are more variable than those of control subjects during visual and motor tasks. Building on this past evidence, Dinstein and his collaborators have now shown that multiple sensory systems within these individuals show noisy responses, suggesting that widespread behavioral abnormalities could arise from a basic dysfunction in neural processing that emerges during development.
In the study, adults with autism participated in functional magnetic resonance imaging experiments in which their brain activity was measured under three different conditions: while they watched moving dots on a screen, listened to tone beeps, and felt air puffs on their hands. The neural responses to all three types of sensory information were less reliable across trials in individuals with autism than in control subjects.
The findings suggest that autism could result from fundamental defects in general neural processing rather than a collection of independent problems that affect different brain regions. "Unreliable neural activity is a general property that could have a profound impact on the function of many brain systems and could underlie a range of cognitive and social abnormalities," says study author Marlene Behrmann of Carnegie Mellon University. "So we think that this problem could play a role not only in autism, but also potentially in other disorders such as epilepsy and schizophrenia."
###
Dinstein et al.: "Unreliable evoked responses in autism."
Video: Marlene Behrmann, Professor of Psychology, and IIan Dinstein, Postdoctoral Researcher, from Carnegie Mellon University's Department of Psychology discuss their study "Autistic Adults have Unreliable Neural Sensory Responses" publishing in Neuron.
Autism symptoms could arise from unreliable neural responses
2012-09-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Autistic adults have unreliable neural responses, Carnegie Mellon-led research team finds
2012-09-19
VIDEO:
New research led by Carnegie Mellon University neuroscientists takes the first step towards deciphering the connection between general brain function and the emergent behavioral patterns in autism. Published in...
Click here for more information.
PITTSBURGH— Autism is a disorder well known for its complex changes in behavior — including repeating actions over and over and having difficulty with social interactions and language. Current approaches to understanding ...
Neuroscientists investigate lotteries to study how the brain evaluates risk
2012-09-19
People are faced with thousands of choices every day, some inane and some risky. Scientists know that the areas of the brain that evaluate risk are the same for each person, but what makes the value assigned to risk different for individuals? To answer this question, a new video article in Journal of Visualized Experiments (JoVE) uses functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to characterize subjective risk assessment while subjects choose between different lotteries to play. The article, a joint effort from laboratories at Yale School of Medicine and New York University, ...
Nearly half of kidney recipients in live donor transplant chains are minorities
2012-09-19
The largest U.S. multicenter study of living kidney transplant donor chains showed that 46 percent of recipients are minorities, a finding that allays previous fears that these groups would be disadvantaged by expansion of the donor pool through this type of exchange process.
The study of a series of chain transplantations performed from February 2008 to June 2011 at 57 centers nationwide included 272 kidney transplants that paired organ donors who were incompatible with their relatives with strangers providing organs for altruistic reasons or with others donating an ...
Warming ocean could start big shift of Antarctic ice
2012-09-19
Fast-flowing and narrow glaciers have the potential to trigger massive changes in the Antarctic ice sheet and contribute to rapid ice-sheet decay and sea-level rise, a new study has found.
Research results published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences reveal in more detail than ever before how warming waters in the Southern Ocean are connected intimately with the movement of massive ice-sheets deep in the Antarctic interior.
"It has long been known that narrow glaciers on the edge of the Antarctica act as discrete arteries termed ice streams, ...
Did a 'forgotten' meteor have a deadly, icy double-punch?
2012-09-19
When a huge meteor collided with Earth about 2.5 million years ago and fell into the southern Pacific Ocean it not only could have generated a massive tsunami but also may have plunged the world into the Ice Ages, a new study suggests.
A team of Australian researchers says that because the Eltanin meteor – which was up to two kilometres across - crashed into deep water, most scientists have not adequately considered either its potential for immediate catastrophic impacts on coastlines around the Pacific rim or its capacity to destabilise the entire planet's climate system.
"This ...
Specialist urologists should handle vasectomy reversal cases says 10-year study
2012-09-19
Vasectomy reversals should be carried out by urology specialists with access to appropriate micro-surgical training and assisted reproductive technologies and not general urology surgeons, according to research published in the October issue of BJUI.
The findings are based on a series of surveys carried out among consultant members of the British Association of Urological Surgeons (BAUS) over a ten-year period.
"It is clear from our research that couples should not be seen by urologists with diverse interests, but by those with appropriate knowledge of all of the ...
Vall d’Hebron, VHIO and SOLTI head up an international 'dream team' against breast cancer
2012-09-19
Barcelona, 19 September 2012. The Vall d'Hebron Breast Cancer Unit, the Vall d'Hebron Institute of Oncology (VHIO) and SOLTI, an academic breast cancer research group , are heading up a multi-centre international study involving four Spanish and three North American research centres*. The aim of the study is to investigate whether BKM120, a drug that inhibits the PI3K pathway (phosphatidylinositol-3-Kinase) can be an effective treatment against triple-negative breast cancer.
At present it is known that breast cancer can be classified into different subtypes with varying ...
War causes mental illness in soldiers
2012-09-19
One in every two cases of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in soldiers remains undiagnosed. This is the conclusion reached by a working group led by Hans-Ulrich Wittchen et al. They report their study in the current issue of Deutsches Ärzteblatt International (Dtsch Arztebl Int 2012; 109(35): 559), which is a special issue focusing on the prevalence of psychological stress in German army soldiers. In a second original article, results reported by Jens T Kowalski and colleagues show that more female soldiers contact the psychosocial support services provided by Germany's ...
How close were we to armageddon? 50 years on, why should we still study the Cuban Missile Crisis?
2012-09-19
Why, fifty years on, is the Cuban Missile Crisis still a subject of considerable fascination for academics and professionals alike? Should we still be studying it, and if so, how? These are just some of the questions addressed in a special issue in the journal International Relations, published by SAGE.
As one of the most intensely studied events of the twentieth century, the Cuban Missile Crisis could suffer from "over examination", yet as Guest Editor Len Scott, Professor of International Politics and Dean of Social Science at Aberystwyth University, remarks: "While ...
Self-forming biological scaffolding
2012-09-19
A new model system of the cellular skeletons of living cells is akin to a mini-laboratory designed to explore how the cells' functional structures assemble. A paper about to be published in EPJ E by physicist Volker Schaller and his colleagues from the Technical University Munich, Germany, presents one hypothesis concerning self-organisation. It hinges on the findings that a homogeneous protein network, once subjected to stresses generated by molecular motors, compacts into highly condensed fibres.
The contractile machinery inside cells is arguably the most prominent ...