(Press-News.org) DNA barcoding developed by University of Guelph researchers has proven up to 88 per cent effective in authenticating natural health products, according to a new U of G study.
The study appears in the latest issue of Food Research International.
It's a crucial finding because the health product industry is under-regulated worldwide and mislabelling poses economic, health, legal and environmental implications, says study author Mehrdad Hajibabaei.
"Currently there is no other broadly applicable tool that can identify the species used in both animal and plant natural health products as rapidly and cost-effectively," said Hajibabaei, a U of G integrative biology professor and director of technology development for the Guelph-based Biodiversity Institute of Ontario (BIO).
Up to about 80 per cent of people in developed countries use natural health products, including vitamins, minerals and herbal remedies. In Canada, these products have been regulated since 2004. But regulators face a backlog of licence applications, and thousands of products on the market lack a full product licence. In the U.S. and the U.K., regulatory problems involving natural health products have affected consistency and safety.
Authenticating natural product capsules or tablets -- containing dried fragments rather than whole specimens -- poses challenges.
DNA barcoding allows scientists to use short standardized regions of genetic material to identify species and compare them to reference genetic sequences, said Hajibabaei.
The technique works for all life stages and even for fragments of organisms, allowing scientists to ID even dried contents of a small pill.
"DNA barcoding provides a simple and efficient method for accurate identification and can play a key role in developing a more robust protocol for their regulation," Hajibabaei said.
For the study, researchers tested 95 plant and animal products bought in Toronto and New York City. Samples included capsules, tablets, roots, extracts, teas and shredded products. The researchers also sampled for products containing widely used shark tissue or ginseng.
Fully 81 per cent of natural health products made from animals correctly matched their commercial label. The rest contained everything from cheaper alternatives to fragments of protected species. One product labelled as tiger shark fins actually contained a catfish species.
Several of the identified shark species are on the "red list" of the International Union for the Conservation of Nature.
Half of the plant products labelled as Korean ginseng – which is more expensive and is sold for different medicinal benefits than other types – were really American ginseng.
Besides Hajibabaei, the study was headed by Lauren Wallace, a former President's Scholar at U of G and now a doctoral student at McMaster University. Wallace received a summer research fellowship from the Ontario Genomics Institute in 2010 to work on the BIO project.
Other researchers were Stephanie Boilard, now a technician in Hajibabaei's lab; graduate students Shannon Eagle and Jennifer Spall; and post-doc Shadi Shokralla.
Three of the researchers were using DNA barcoding for the first time. "Ultimately, the study showcases the utility of DNA barcodes for use in the real world," Hajibabaei said.
### The BIO is a hub for barcoding research worldwide and leads the International Barcode of Life (www.ibol.org) project to develop a DNA barcode reference library. Another project based at the institute is Biomonitoring 2.0 (www.biomonitoring2.org), which uses barcoding and DNA sequencing for large-scale environmental assessment.
This research has been funded by the federal government through Genome Canada and the Ontario Genomics Institute.
Study: DNA barcoding can ID natural health products
2012-09-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ASGE initiative addresses endoscopy simulators for training and skill assessment
2012-09-20
OAK BROOK, Ill. – September 19, 2012 – The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy's (ASGE) Preservation and Incorporation of Valuable Endoscopic Innovations (PIVI) initiative addresses the use of endoscopy simulators for training and assessing skills in an article appearing in the September issue of GIE: Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, ASGE's monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal. This PIVI is one in a series of statements defining the diagnostic or therapeutic threshold that must be met for a technique or device to become considered appropriate for incorporation ...
Split-dose preparation for colonoscopy increases precancerous polyp detection rates
2012-09-20
OAK BROOK, Ill. – September 19, 2012 – A new study from researchers at the Mayo Clinic Arizona showed that system-wide implementation of a split-dose preparation as the primary choice for colonoscopy significantly improved both polyp detection rates and adenoma (precancerous polyp) detection rates, overall quality of the preparation, and colonoscopy completion rates. The study appears in the September issue of GIE: Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, the monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal of the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE).
Colorectal cancer develops ...
Researchers identify possible key to slow progression toward AIDS
2012-09-20
One of the big mysteries of AIDS is why some HIV-positive people take more than a decade to progress to full-blown AIDS, if they progress at all.
Although the average time between HIV infection and AIDS in the absence of antiretroviral treatment is about 10 years, some individuals succumb within two years, while so-called slow progressors can stay healthy for 20 years or longer.
Researchers already know that many slow progressors carry a gene called HLA-B*57 (B57), an immune gene variant that is found in less than 5 percent of the general population but in 40 to ...
Research suggests promise of cell therapy for bowel disease
2012-09-20
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – Sept. 19, 2012 – New research shows that a special population of stem cells found in cord blood has the innate ability to migrate to the intestine and contribute to the cell population there, suggesting the cells' potential to treat inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
"These cells are involved in the formation of blood vessels and may prove to be a tool for improving the vessel abnormalities found in IBD," said lead author Graca Almeida-Porada, M.D., Ph.D., a professor at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center's Institute for Regenerative Medicine. The ...
Misinformation: Psychological Science shows why it sticks and how to fix it
2012-09-20
Childhood vaccines do not cause autism. Barack Obama was born in the United States. Global warming is confirmed by science. And yet, many people believe claims to the contrary.
Why does that kind of misinformation stick? A new report published in Psychological Science in the Public Interest, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science, explores this phenomenon. Psychological scientist Stephan Lewandowsky of the University of Western Australia and colleagues highlight the cognitive factors that make certain pieces of misinformation so "sticky" and identify some ...
Ultra-distant galaxy spied amidst cosmic 'Dark Ages'
2012-09-20
Pasadena, CA— With the combined power of NASA's Spitzer and Hubble Space Telescopes, as well as a cosmic magnification effect, a team of astronomers, including Carnegie's Daniel Kelson, have spotted what could be the most distant galaxy ever seen. Light from the young galaxy captured by the orbiting observatories was emitted when our 13.7-billion-year-old universe was just 500 million years old. Their work is published September 20 by Nature.
The far-off galaxy existed within an important era when the universe just emerged from the so-called cosmic Dark Ages. During this ...
Robotic tuna is built by Homeland Security
2012-09-20
No question about it… they're very good at what they do. But they don't take well to orders, especially those to carry out inspection work in oily or dangerous environments, or in any kind of harsh environment, for that matter. Still, they're one of the fastest and most maneuverable creatures on the planet, having extraordinary abilities at both high and low speeds due to their streamlined bodies and a finely tuned muscular/sensory/control system.
This impressive creature is the humble tuna fish.
The Department of Homeland Security's (DHS) Science and Technology ...
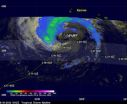
NASA satellite sees fading rainfall in Tropical Storm Nadine
2012-09-20
Tropical Storm Nadine continues to bring rains and winds to the Azores in the eastern Atlantic Ocean, but that rainfall continues to diminish according to data from NASA satellites. NASA's unmanned Global Hawk aircraft is also exploring the storm today, Sept. 19.
A tropical storm warning is in effect on Sept. 19 for the islands of Flores, Corvo, Faial, Pico, Sao Jorge, Graciosa, Terceira, Sao Miguel and Santa Maria in the Azores.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite flew over Nadine on Sept. 19 at 1013 UTC (6:13 a.m. EDT) and captured data on rainfall ...
Arctic sea ice hits smallest extent in satellite era
2012-09-20
The frozen cap of the Arctic Ocean appears to have reached its annual summertime minimum extent and broken a new record low on Sept. 16, the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) has reported. Analysis of satellite data by NASA and the NASA-supported NSIDC at the University of Colorado in Boulder showed that the sea ice extent shrunk to 1.32 million square miles (3.41 million square kilometers).
The new record minimum measures almost 300,000 square miles less than the previous lowest extent in the satellite record, set in mid-September 2007, of 1.61 million square ...
Climate scientists put predictions to the test
2012-09-20
Climate-prediction models show skills in forecasting climate trends over time spans of greater than 30 years and at the geographical scale of continents, but they deteriorate when applied to shorter time frames and smaller geographical regions, a new study has found.
Published in the Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, the study is one of the first to systematically address a longstanding, fundamental question asked not only by climate scientists and weather forecasters, but the public as well: How good are Earth system models at predicting the surface air temperature ...