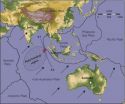
(Press-News.org) SALT LAKE CITY Sept. 26, 2012 – Seismologists have known for years that the Indo-Australian plate of Earth's crust is slowly breaking apart, but they saw it in action last April when at least four faults broke in a magnitude-8.7 earthquake that may be the largest of its type ever recorded.
The great Indian Ocean quake of April 11, 2012 previously was reported as 8.6 magnitude, and the new estimate means the quake was 40 percent larger than had been believed, scientists from the University of Utah and University of California, Santa Cruz, report in the Sept. 27 issue of the journal Nature.
The quake was caused by at least four undersea fault ruptures southwest of Sumatra, Indonesia, within a 2-minute, 40-second period. It killed at least two people, and eight others died from heart attacks. The quake was felt from India to Australia, including throughout South Asia and Southeast Asia.
If the four ruptures were considered separate quakes, their magnitudes would have been 8.5, 7.9, 8.3 and 7.8 on the "moment magnitude" scale used to measure the largest quakes, the scientists report.
The 8.7 main shock broke three faults that were parallel but offset from each other – known as en echelon faults – and a fourth fault that was perpendicular to and crossed the first fault.
The new study concludes that the magnitude-8.7 quake and an 8.2 quake two hours later were part of the breakup of the Indian and Australian subplates along a yet-unclear boundary beneath the Indian Ocean west of Sumatra and southeast of India – a process that started roughly 50 million years ago and that will continue for millions more.
"We've never seen an earthquake like this," says study co-author Keith Koper, an associate professor geophysics and director of the University of Utah Seismograph Stations. "This is part of the messy business of breaking up a plate. … This is a geologic process. It will take millions of years to form a new plate boundary and, most likely, it will take thousands of similar large quakes for that to happen."
All four faults that broke in the 8.7 quake and the fifth fault that ruptured in the 8.2 quake were strike-slip faults, meaning ground on one side of the fault moves horizontally past ground on the other side.
The great quake of last April 11 "is possibly the largest strike-slip earthquake ever seismically recorded," although a similar size quake in Tibet in 1950 was of an unknown type, according to the new study, which was led by two University of California, Santa Cruz, seismologists: graduate student Han Yue and Thorne Lay, a professor of Earth and planetary sciences. The National Science Foundation funded the study.
The 8.7 jolt also "is probably the largest intraplate [within a single tectonic plate of Earth's crust] ever seismically recorded," Lay, Yue and Koper add. Most of Earth's earthquakes occur at existing plate boundaries.
The researchers cannot be certain the April great quake was the largest intraplate quake or the largest strike-slip quake because "we are comparing it against historic earthquakes long before we had modern seismometers," says Koper.
Why the Great Quake Didn't Unleash Major Tsunamis
Koper says the 2012 quakes likely were triggered, at least in part, by changes in crustal stresses caused by the magnitude-9.1 Sumatra-Andaman earthquake of Dec. 26, 2004 – a jolt that generated massive tsunamis that killed most of the 228,000 victims in the Indian Ocean region.
The fact the 8.7 and 8.2 quakes were generated by horizontal movements along seafloor strike-slip faults – not by vertical motion along thrust faults – explains why they didn't generate major tsunamis. The 8.7 quake caused small tsunamis, the largest of which measured about 12 inches in height at Meulaboh, Indonesia, according to the U.S. Geological Survey.
Without major tsunamis, the great earthquake caused "very little damage and death, especially for this size of an earthquake, because it happened in the ocean and away from coastlines," and on strike-slip faults, says Koper.
The researchers studied the quake using a variety of methods to analyze the seismic waves it generated. Because the same data can be interpreted in various ways, Koper says it is conceivable that more than four fault segments broke during the 8.7 quake – conceivably five or even six – although four fault ruptures is most likely.
Breaking Up is Hard to Do
The Indo-Australian plate is breaking into two or perhaps three pieces (some believe a Capricorn subplate is separating from the west side of the Indian subplate). The magnitude-8.7 and 8.2 great quakes on April 11 occurred over a broad area where the India and Australian subplates are being sheared apart.
"What we're seeing here is the Indo-Australian plate fragmenting into two separate plates," says Lay.
The breakup of the northeast-moving Indo-Australian plate is happening because it is colliding with Asia in the northwest, which slows down the western part of the plate, while the eastern part of the plate continues moving more easily by diving or "subducting" under the island of Sumatra to the northeast. The subduction zone off Sumatra caused the catastrophic 2004 magnitude-9.1 quake and tsunami.
Seismic analysis shows the April 11 quakes "involve rupture of a very complex network of faults, for which we have no documented precedent in recorded seismic history," the researchers write.
The analysis revealed this sequence for the faults ruptures that generated the 8.7 quake, and the estimated fault rupture lengths and slippage amounts:
-- The quake began with the 50-second rupture of a fault extending west-northwest to east-southeast, with an epicenter a few hundred miles southwest of Sumatra. The fault ruptured along a roughly 90-mile length, breaking "bilaterally" both west-northwestward and east-southeastward, and also at least 30 miles deep, "almost ripping through the whole plate," Koper says. The seafloor on one side of the fault slipped about 100 feet past the seafloor on the fault's other side.
-- The second fault, which slipped about 25 feet, began to rupture 40 seconds after the quake began. This rupture extended an estimated 60 miles to 120 miles north-northeast to south-southwest – perpendicular to the first fault and crossing it.
-- The third fault was parallel to the first fault and about 90 to the miles southwest of it. It started breaking 70 seconds after the quake began and ruptured along a length of about 90 miles. This fault slipped about 70 feet.
-- The fourth fault paralleled the first and third faults, but was to the northwest of both of them. It began to rupture 145 seconds after the quake began and continued to do so for 15 seconds until the quake ended after a total time of 2 minutes and 40 seconds. The fault rupture was roughly 30 miles to 60 miles long. The ground on one side of this fault slipped about 20 feet past ground on the other side.
INFORMATION:
University of Utah Communications
201 Presidents Circle, Room 308
Salt Lake City, Utah 84112-9017
(801) 581-6773 fax: (801) 585-3350
www.unews.utah.edu
Big quake was part of crustal plate breakup
Study shows huge jolt measured 8.7, ripped at least 4 faults
2012-09-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study reveals complex rupture process in surprising 2012 Sumatra quake
2012-09-27
SANTA CRUZ, CA--The massive earthquake that struck under the Indian Ocean southwest of Sumatra on April 11, 2012, came as a surprise to seismologists and left them scrambling to figure out exactly what had happened. Analysis of the seismic waves generated during the event has now revealed a complicated faulting process unlike anything seen before.
"Nobody was anticipating an earthquake of this size and type, and the complexity of the faulting surprised everybody I've spoken to about this," said Thorne Lay, professor of Earth and planetary sciences at the University of ...
Men on the mind: Study finds male DNA in women's brains
2012-09-27
SEATTLE – Male DNA is commonly found in the brains of women, most likely derived from prior pregnancy with a male fetus, according to first-of-its-kind research conducted at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center. While the medical implications of male DNA and male cells in the brain are unknown, studies of other kinds of microchimerism – the harboring of genetic material and cells that were exchanged between fetus and mother during pregnancy – have linked the phenomenon to autoimmune diseases and cancer, sometimes for better and other times for worse.
The study findings ...
Pregnancy generates maternal immune-suppressive cells that protect the fetus
2012-09-27
A new study published online in the journal Nature suggests it might be possible to develop vaccines to prevent premature birth and other pregnancy complications. If so, such vaccines would be the first intended to stimulate the subset of regulatory CD4 T cells that suppress the immune response.
Current vaccines are specifically designed to stimulate T cell subsets that activate the immune response.
The study, led by a researcher at Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, shows the immune system of a pregnant mother stimulates cells that selectively prevent ...
Researchers define 2 categories of multiple sclerosis patients
2012-09-27
BOSTON, MA—There are approximately 400,000 people in the United States with multiple sclerosis. Worldwide, the number jumps to more than 2.1 million people. Rather than a one-size-fits-all approach to treating the millions with multiple sclerosis, what if doctors could categorize patients to create more personalized treatments? A new study by researchers at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) may one day make this idea a reality in the fight against the debilitating autoimmune disease.
A research team led by Philip De Jager, MD, PhD, BWH Department of Neurology, senior ...
Touch-sensitive tentacles catapult prey into carnivorous plant traps
2012-09-27
Swift predators are common in the animal world but are rare in the plant kingdom. New research shows that Drosera glanduligera, a small sundew from southern Australia, deploys one of the fastest and most spectacular trapping mechanisms known among carnivorous plants.
The study, published Sep. 26 in the open access journal PLOS ONE, is a collaboration between the Plant Biomechanics Group at the University of Freiburg and private sundew cultivators from Weil am Rhein, and provides the first experimental demonstration of fast-moving snap tentacles in sundew plants propelling ...
Large 2012 earthquake triggered temblors worldwide for nearly a week
2012-09-27
This year's largest earthquake, a magnitude 8.6 temblor on April 11 centered in the East Indian Ocean off Sumatra, did little damage, but it triggered quakes around the world for at least a week, according to a new analysis by seismologists from the University of California, Berkeley, and the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS).
The April 11 quake was unusually large – the tenth largest in the last 100 years and, similar to a few other recent large quakes, triggered small quakes during the three hours it took for seismic waves to travel through Earth's crust.
The new study ...
Cannabis withdrawal symptoms might have clinical importance
2012-09-27
Cannabis users have a greater chance of relapse to cannabis use when they experience certain withdrawal symptoms, according to research published Sep. 26 in the open access journal PLOS ONE led by David Allsop of the National Cannabis Prevention and Information Centre (NCPIC) at the University of New South Wales.
The authors tested a group of dependent cannabis users over a two week period of abstinence for impairment related to their withdrawal symptoms. Findings were correlated with the probability of relapse to cannabis use during the abstinence period, and the level ...
First evidence of fetal DNA persisting in human brain tissue
2012-09-27
Small portions of male DNA, most likely left over in a mother's body by a male fetus can be detected in the maternal brain relatively frequently, according to a report published Sep. 26 in the open access journal PLOS ONE by William Chan of Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center and his colleagues.
The process, called fetal 'microchimerism (Mc)', is common in other tissues such as blood, but this is the first evidence of male Mc in the human female brain. Microchimerism can be both beneficial and harmful to maternal health, since it is associated with processes such ...
Viewing gender-specific objects influences perception of gender identity
2012-09-27
Spending too much time looking at high heels may influence how a viewer perceives the gender of an androgynous face, according to new research published Sep. 26 in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Amir Homayoun Javadi of Technische Universität, Dresden and his colleagues. The study sheds new light on how the objects surrounding us may influence our perceptions of gender.
The authors found that when people view objects highly associated with one gender, like high heels for women or electric shavers for men, for a short period of time and are then asked to identify the ...
Psychology of equine performance and the biology behind laminitis
2012-09-27
Achieving the best performance from a horse is the goal of not just professional riders, but also the millions of amateur and hobby riders all over the world. A new article published in BioMed Central's open access journal BMC Veterinary Research looks at the issues surrounding training, competition environment and practices, and how the psychology of horse mood, emotion and temperament can be used to enhance performance. A sister article looks at the devastating disease laminitis, and finds that the anti-inflammatory protein apolipoprotein A-IV (APOA-IV) is raised in chronic ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
UCSB researcher bridges the worlds of general relativity and supernova astrophysics
Global exchange of knowledge and technology to significantly advance reef restoration efforts
Vision sensing for intelligent driving: technical challenges and innovative solutions
To attempt world record, researchers will use their finding that prep phase is most vital to accurate three-point shooting
AI is homogenizing human expression and thought, computer scientists and psychologists say
Severe COVID-19, flu facilitate lung cancer months or years later, new research shows
Housing displacement, employment disruption, and mental health after the 2023 Maui wildfires
GLP-1 receptor agonist use and survival among patients with type 2 diabetes and brain metastases
Solid but fluid: New materials reconfigure their entire crystal structure in response to humidity
New research reveals how development and sex shape the brain
New discovery may improve kidney disease diagnosis in black patients
What changes happen in the aging brain?
Pew awards fellowships to seven scientists advancing marine conservation
Turning cancer’s protein machinery against itself to boost immunity
Current Pharmaceutical Analysis releases Volume 22, Issue 2 with open access research
Researchers capture thermal fluctuations in polymer segments for the first time
16-year study finds major health burden in single‑ventricle heart
Disposable vapes ban could lead young adults to switch to cigarettes, study finds
[Press-News.org] Big quake was part of crustal plate breakupStudy shows huge jolt measured 8.7, ripped at least 4 faults