US invested $139 billion in health research in 2009
Research spending stagnant since 2005 as portion of health costs
2010-10-08
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON—October 7, 2010—The U.S. invested $139 billion last year in health research from all public and private sources, according to Research!America's latest annual estimate. That amount represents only 5.6% of the $2.47 trillion overall U.S. health spending in 2009—or 5.6¢ of every health dollar—which varies no more than 0.2% from 2005 levels.
The estimate is available here: http://www.researchamerica.org/uploads/healthdollar09.pdf.
The 2009 investment grew by only 0.1% over 2008. This small increase can be attributed largely to the federal stimulus funding for research provided through the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009. Federal research investment was nearly $46.8 billion in 2009, up from $38.6 billion in 2008.
"America's economic destiny lies in innovation, but other countries are stepping up, investing more and thus challenging our lead," said former Congressman John Edward Porter, Research!America's chair. "We need to invest in our federal research agencies for the long term. Our economic competitiveness and our future standard of living depend on it."
The effects of the economic recession can be seen throughout the other sectors that fund health research and development—industry, universities, state and local governments, philanthropic foundations, voluntary health associations, and independent research institutes—where such investment remained essentially flat or declined in 2009. Industry was the largest source of health research funding in 2009 at $74.3 billion, down slightly from the prior year's $74.8 billion. All other sources combined invested $17.8 billion, compared with $17.1 billion in 2008.
Mary Woolley, president and CEO of Research!America, said, "We need to make the research and development tax credit permanent as an incentive to the private research enterprise, which builds upon the essential work of our federal research agencies. We need this and other incentives and investments to support the full pipeline of research, so research can get the job done and deliver on its promise of treating, curing and preventing disease, as well as raising health care quality and lowering cost."
###
Research!America has issued estimates of the U.S. investment in health research since 2002. All reports in the series are available online at www.researchamerica.org/research_investment.
Research!America is the nation's largest not-for-profit public education and advocacy alliance working to make research to improve health a higher national priority. Founded in 1989, Research!America is supported by member organizations representing 125 million Americans. Visit www.researchamerica.org.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2010-10-08
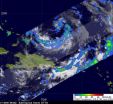
NASA satellites have collected data as the Atlantic Ocean's Tropical Depression 17 has undergone two changes in less than 24 hours. Since Oct. 6, the depression has strengthened and has tropical storm-force winds and has morphed from a sub-tropical storm into a tropical storm.
After a United States Air Force Reserve reconnaissance flight subtropical depression seventeen was upgraded by the National Hurricane Center (NHC) to subtropical storm Otto on Oct. 6 at 5 p.m. EDT (2100 UTC). On Oct. 6 and 7, NASA's TRMM and Aqua satellites were flying overhead measuring very cold, ...
2010-10-08
Saturn's icy moon Enceladus should not be one of the most promising places in our solar system to look for extraterrestrial life. Instead, it should have frozen solid billions of years ago. Located in the frigid outer solar system, it's too far from the sun to have oceans of liquid water -- a necessary ingredient for known forms of life -- on its surface.
Some worlds, like Mars or Jupiter's moon Europa, give hints that they might harbor liquid water beneath their surfaces. Mars is about 4,200 miles across and Europa almost 2,000 miles across. However, with a diameter ...
2010-10-08
PHILADELPHIA - Heart muscle cells do not normally replicate in adult tissue, but multiply with abandoned during development. This is why the loss of heart muscle after a heart attack is so dire—you can't grow enough new heart muscle to make up for the loss.
A team of researchers at the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine describe the interconnections between three-molecules that control fetal, heart-muscle-cell proliferation in a mouse model that will help cardiologists better understand the natural repair process after heart attacks and help scientists learn ...
2010-10-08
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — University of Illinois chemistry professor Alexander Scheeline wants to see high school students using their cell phones in class. Not for texting or surfing the Web, but as an analytical chemistry instrument.
Scheeline developed a method using a few basic, inexpensive supplies and a digital camera to build a spectrometer, an important basic chemistry instrument. Spectrophotometry is one of the most widely used means for identifying and quantifying materials in both physical and biological sciences.
"If we want to measure the amount of protein in ...
2010-10-08
An approach pioneered by researchers at North Carolina State University gives scientists new insight into the way silicon bonds with other materials at the atomic level. This technique could lead to improved understanding of and control over bond formation at the atomic level, and opportunities for the creation of new devices and more efficient microchips.
Manufacturers build silicon-based devices from layers of different materials. Bonds – the chemical interaction between adjacent atoms – are what give materials their distinctive characteristics. "Essentially, a bond ...
2010-10-08
New Haven, Conn.—A team of Yale University scientists has engineered the cell wall of the Staphylococcus aureus bacteria, tricking it into incorporating foreign small molecules and embedding them within the cell wall.
The finding, described online in the journal ACS Chemical Biology this week, represents the first time scientists have engineered the cell wall of a pathogenic "Gram-positive" bacteria—organisms responsible not only for Staph infections but also pneumonia, strep throat and many others. The discovery could pave the way for new methods of combating the bacteria ...
2010-10-08
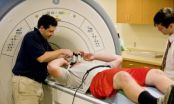
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - A study by researchers at Purdue University suggests that some high school football players suffer undiagnosed changes in brain function and continue playing even though they are impaired.
"Our key finding is a previously undiscovered category of cognitive impairment," said Thomas Talavage, an expert in functional neuroimaging who is an associate professor of biomedical engineering and electrical and computer engineering and co-director of the Purdue MRI Facility.
The findings represent a dilemma because they suggest athletes may suffer a form ...
2010-10-08
(Garrison, NY) The researcher whose revelations about unethical U.S. studies on syphilis in Guatemala in the 1940's led to apologies from the Obama administration last week has written a commentary for Bioethics Forum, the Hastings Center's online publication. She calls for the need to learn from history to better protect human subjects in the developing world.
Susan M. Reverby, a professor at Wellesley College, describes how she unearthed documents about the study by accident while doing research for a book on the Tuskegee syphilis study. The documents, hidden in the ...
2010-10-08
Talk about a walk on the wild side: University of Notre Dame researcher Joshua Shrout is co-author of a new paper that shows that bacteria are capable of "standing up" and moving while vertical.
Shrout, assistant professor of civil engineering and geological sciences and a member of the Eck Institute for Global Health, has been studying the surface motility of bacteria since 2004. In 2008, UCLA researcher Gerard Wong suggested that an undergraduate bioengineering senior design group that he was advising track the bacterium Shrout was studying. After some interesting patterns ...
2010-10-08
"Better and faster results!" is the clarion call for scientists and engineers to continually strive to improve their research tools. Of the tools used to study material structures at the atomic and molecular scales, there is none finer than Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and its daughter technology Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). Now, the latest development from the research group of one of the word's foremost authorities on NMR/MRI technology promises NMR/MRI results that are better and faster than ever before – a million times faster!
Through a combination ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] US invested $139 billion in health research in 2009
Research spending stagnant since 2005 as portion of health costs