(Press-News.org) This gives new meaning to the complaint "I'm bored" — literally.
Canadian researchers — including a professor from the University of Guelph — have come up with a new, precise definition of boredom based on the mental processes that underlie the condition.
Although many people may see boredom as trivial and temporary, it actually is linked to a range of psychological, social and health problems, says Guelph psychology professor Mark Fenske. He's among authors of a new study in Perspectives on Psychological Science, published by the Association for Psychological Science.
Boredom at work can lead to serious accidents on the job. It's also linked to impulse control, causing everything from over-eating to alcohol abuse -- and even to mortality (think "bored to death").
"It's an amazingly under-studied area given how universal the experience is," Fenske said.
"The fact that it's difficult to define is, in part, why there has been so little research done. We need to have a common definition, something we all can agree on, of what boredom is."
A scientific definition is needed, not only to accommodate the different characteristics of boredom that have already been established, but also to bridge across a variety of theoretical perspectives, Fenske added.
The researchers, led by York University professor John Eastwood, set out to better understand the mental processes that fuel feelings of boredom.
They found that attention and awareness are keys to the aimless state. After reviewing existing psychological science and neuroscience studies, they defined boredom as "an aversive state of wanting, but being unable, to engage in satisfying activity," which arises from failures in one of the brain's attention networks.
In other words, you become bored when:
you have difficulty paying attention to the internal information, such as thoughts or feelings, or outside stimuli required to take part in satisfying activity;
you are aware that you're having difficulty paying attention; and
you blame the environment for your sorry state ("This task is boring"; "There is nothing to do").
"At the heart of it is our desire to engage with the world or some other mental activity, and that takes attention," Fenske said. "When we cannot do this —that seems to be what leads to frustration and the aversive state we call 'boredom.'"
The researchers hope their new definition and theoretical framework stimulates new research to help us better understand boredom and how to ease it and otherwise address its potential dangers.
Fenske joined U of G in 2007. In 2010, he published The Winner's Brain: 8 Strategies Great Minds Use to Achieve Success, co-written with Harvard Medical School psychologist Jeff Brown.
This new work also involved Alexandra Frischen, a former post-doctoral researcher of Fenske's, and Daniel Smilek of the University of Waterloo.
### END
Bored? Researchers shed light on why
2012-09-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Time bomb: Military ordnance in Gulf poses threat to shipping, says Texas A&M proffesor
2012-09-29
Millions of pounds of unexploded bombs and other military ordnance that were dumped decades ago in the Gulf of Mexico, as well as off the coasts of both the Atlantic and Pacific oceans, could now pose serious threats to shipping lanes and the 4,000 oil and gas rigs in the Gulf, warns two Texas A&M University oceanographers.
William Bryant and Neil Slowey, professors of oceanography who have more than 90 years of combined research experience in all of the Earth's oceans, along with fellow researcher Mike Kemp of Washington, D.C., say millions of pounds of bombs are scattered ...
IUCN adopts new 'Green List' to show species on the path to conservation success
2012-09-29
The IUCN World Conservation Congress has adopted a motion sponsored by the Wildlife Conservation Society and partners to create a Green List to assess conservation success. The Green List for Species would include species identified as 'fully conserved,' which are those that exist in ecologically significant numbers, interacting fully with other species in their ecosystems.
The motion was adopted at the World Conservation Congress, which was held this month in Jeju, Republic of Korea.
The aim of the Green List is to highlight species that are thriving parts of a healthy ...
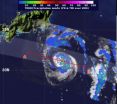
NASA sees super Typhoon Jelawat Affecting Japan
2012-09-29
Super Typhoon Jelawat is a large and powerful storm that has been bringing very rough seas to areas in the western North Pacific. NASA's Terra satellite passed over the monster storm and captured a visible image as it nears the big island of Japan.
NASA's Terra satellite passed over Super Typhoon Jelawat on Sept. 28 at 0238UTC (10:38 p.m. EDT, Sept. 27) and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer captured an infrared image as the storm approaches Okinawa, Japan.
Jelawat's center passed by Ishigaki-jima by 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT) on Sept. 28 and was approaching ...
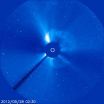
NASA sees sun unleash a wide, but benign, CME
2012-09-29
The sun erupted with a wide, Earth-directed coronal mass ejection (CME) on Sept. 27, 2012 at 10:25 p.m. EDT. CMEs are a phenomenon that can send billions of tons of solar particles into space that can reach Earth one to three days later, affecting electronic systems in satellites and on the ground. Experimental NASA research models estimate that the CME is traveling at around 700 miles per second and will reach Earth on Sept. 29.
CMEs of these speeds are usually benign. In the past, similar CMEs have caused auroras near the poles but have not caused disruption to electrical ...
NASA sees stubborn Nadine intensify into a hurricane again
2012-09-29
Infrared data from NASA's Aqua satellite today, Sept. 28, revealed strong convection and thunderstorms have built up again in Tropical Storm Nadine as it moved over warm waters in the Eastern Atlantic Ocean. That convection strengthened Nadine back into a hurricane today. Nadine has lasted over two weeks, but is nowhere near breaking the record for longest-lived tropical cyclone.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over long-lived Nadine on Sept. 28 at 0441 UTC (12:41 a.m. EDT) when it was still a tropical storm and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured ...
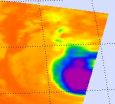
NASA sees Tropical Storm Miriam takes final bow, replaced by Norman
2012-09-29
The National Hurricane Center issued their last advisory on Miriam on Sept. 27 at 11 p.m. EDT when it became a remnant low pressure area. At that time, the center of post-tropical cyclone Miriam was located near latitude 22.0 north and longitude 116.7 west, just over 400 miles west of the southern tip of Baja California. Miriam had maximum sustained winds near 30 knots (35 mph/55 kmh).
NOAA's GOES-15 satellite captured an infrared image of Tropical Storm Miriam and a developing low pressure area in the Eastern Pacific on Sept. 28 at 1145 UTC (7:45 a.m. EDT), off the coast ...
NASA sees many things happening in Tropical Storm Ewiniar
2012-09-29
There are a number of things happening under the hood of Tropical Storm Ewiniar's clouds that have been deciphered by satellite data today, Sept. 28, 2012, and NASA's TRMM satellite has noticed one area of heavy rainfall remaining.
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite noticed light to moderate rainfall around most of the tropical storm, with the heaviest rainfall east of the center of circulation. Rainfall in that area was falling at a rate of 2 inches (50 mm) per hour).
Tropical Storm Ewiniar has a partially exposed low-level circulation center, ...
Notre Dame researchers part of team that discovered potentially dangerous new malaria mosquito
2012-09-29
University of Notre Dame entomologists are part of a team of researchers that recently discovered a potentially dangerous new malaria-transmitting mosquito. The as yet unnamed, and previously unreported, mosquito breeds in the western areas of Kenya and has an unknown DNA match to any of the existing malaria-transmitting species.
The Anopheles species of mosquitoes which transmits malaria in Africa is already widely studied by researchers. It prefers to rest indoors during the day and feed on humans during the night. Current malaria control programs, including spraying ...
Notre Dame receives $6.1 million NSF grant award to advance Quarknet Program
2012-09-29
The University of Notre Dame has received a five-year, $6.1 million award from the National Science Foundation to support the continuation of the nationwide QuarkNet program, which uses particle physics experiments to inspire students and provide valuable research, training and mentorship opportunities for high school teachers.
Through the QuarkNet program, physicists at Notre Dame, Fermilab and 50 other research institutions will continue to mentor teachers in research experiences, enabling them to teach the basic concepts of introductory physics in a context that high ...
Patient selection for bilateral total knee replacement needs improvement
2012-09-29
Because there are more risks with having a total knee replacement in both legs at the same time than having a knee replacement in one leg, doctors in recent years have been selecting younger and healthier patients for the bilateral procedure. Now a new study by researchers at Hospital for Special Surgery has revealed that although patients are younger and healthier than those undergoing only one-sided surgery, they are becoming sicker and some complication rates have risen.
"Although we are selecting younger people, we can't ignore the fact that the population in general ...