Too little nitrogen may restrain plants' carbon storage capability, U of M paper shows
2012-10-03
(Press-News.org) MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL (10/02/2012) —Plants' ability to absorb increased levels of carbon dioxide in the air may have been overestimated, a new University of Minnesota study shows.
The study, published this week in the journal Nature Climate Change, shows that even though plants absorb large amounts of carbon dioxide and actually can benefit from higher levels of it, they may not get enough of the nutrients they need from typical soils to absorb as much CO2 as scientists had previously estimated. Carbon dioxide absorption is an important factor in mitigating fossil-fuel emissions.
The study, one of only three such long-term experiments in the world, is based on 13 years of research at the Cedar Creek Ecosystem Science Reserve north of the Twin Cities. U of M scientists Peter Reich and Sarah Hobbie monitored nearly 300 open-air plots planted with perennial grasses with varying levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide and soil nitrogen.
"Rather than building a time machine and comparing how ecosystems behave in 2070 – which is hard to do – we basically create the atmosphere of 2070 above our plots," Reich says.
The results suggest that limited levels of fertility typical in most soils likely eliminate a large fraction of the capacity of plants to scrub CO2 out of the atmosphere, Reich says. "It would be better if there were experiments like ours in tropical rain forest, temperate forest, and tundra, to see how well responses there match with what we have found. But as such experiments do not exist, our results play an important role in addressing this issue for ecosystems everywhere."
Reich is a Regents professor in the forest resources department of the university's College of Food, Agricultural and Natural Resource Sciences and Hobbie is a professor in the ecology, evolution and behavior department in the College of Biological Sciences. Both are fellows of the university's Institute on the Environment.
INFORMATION: END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2012-10-03
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- A technique that uses acoustic waves to sort cells on a chip may create miniature medical analytic devices that could make Star Trek's tricorder seem a bit bulky in comparison, according to a team of researchers.
The device uses two beams of acoustic -- or sound -- waves to act as acoustic tweezers and sort a continuous flow of cells on a dime-sized chip, said Tony Jun Huang, associate professor of engineering science and mechanics, Penn State. By changing the frequency of the acoustic waves, researchers can easily alter the paths of the cells.
Huang ...
2012-10-03
A study of widely used complimentary offers at Atlantic City casinos finds that common giveaways such as free rooms and dining credits are less profitable – and lead to unhealthy competition among casinos – than alternative comps such as free travel and parking.
The research, co-authored by Seul Ki Lee, an assistant professor at Temple University's School of Tourism and Hospitality Management, analyzed monthly promotional allowance and expenditure data from 11 casinos in the Atlantic City market from 2008 to 2010. Atlantic City is the second largest gaming market in ...
2012-10-03
TALLAHASSEE, Fla. - Despite a shared Latino heritage, there are significant differences in the overall health and the use of health-care services among Cuban-Americans, Mexican-Americans and Puerto Rican-Americans — even between men and women in the same subgroup — according to two recently published studies by Florida State University researchers.
The authors, led by College of Social Work Professor and Associate Dean Amy L. Ai, evaluated the physical and behavioral health, as well as the health care service usage, of all three major Latino subgroups in the United States. ...
2012-10-03
LOS ANGELES (Oct. 2, 2012) – Researchers at Cedars-Sinai's Maxine Dunitz Neurosurgical Institute have found that a blood vessel-building gene boosts the ability of human bone marrow stem cells to sustain pancreatic recovery in a laboratory mouse model of insulin-dependent diabetes.
The findings, published in a PLOS ONE article of the Public Library of Science, offer new insights on mechanisms involved in regeneration of insulin-producing cells and provide new evidence that a diabetic's own bone marrow one day may be a source of treatment.
Scientists began studying ...
2012-10-03
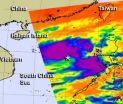
Infrared NASA satellite imagery revealed that the strongest thunderstorms within Tropical Storm Gaemi in the western North Pacific Ocean were located around the storm's center and in a band of thunderstorms east of the center.
On Oct. 2, 2012 at 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT) Tropical Storm Gaemi had maximum sustained winds near 40 knots (46 mph/74 kph). It was located about 515 nautical miles (592 miles/954 km) east of Hue, Vietnam, near 15.3 North latitude and 116.7 East longitude. Gaemi is moving to the southeast at 9 knots (10 mph/16.6 kph).
Infrared imagery from the AIRS ...
2012-10-03
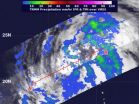
Wind shear is pushing the heaviest rainfall within Tropical Storm Maliksi east of the storm's center, and NASA's TRMM satellite captured it on Oct. 2 as it passed overhead from space.
When NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite passed over Tropical Storm Maliksi on Oct. 2 at 1206 UTC (8:06 a.m. EDT), the precipitation radar instrument detected light rainfall occurring over most of the storm. The heaviest rainfall was moderate was falling east of the center at a rate between .78 to 1.57 inches/20 to 40 mm per hour. There was a small area of heavy rainfall ...
2012-10-03
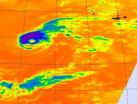
Forecasters know that Tropical Storm Nadine is a fighter as it continues to stay alive in the eastern Atlantic Ocean. Even satellite imagery shows Nadine's fighting spirit, because although Nadine is now a tropical storm, infrared data clearly shows that Nadine maintained an eye early on Oct. 2.
At 11 a.m. EDT on Oct. 2, Nadine remains a tropical storm and appears to be weakening. Nadine's maximum sustained winds were near 65 mph (100 kph). The center of Tropical Storm Nadine was located near latitude 34.2 north and longitude 37.5 west. Nadine is moving toward the east-southeast ...
2012-10-03
Researchers in Argentina report that women with multiple sclerosis (MS) who undergo assisted reproduction technology (ART) infertility treatment are at risk for increased disease activity. Study findings published in Annals of Neurology, a journal of the American Neurological Association and Child Neurology Society, suggest reproductive hormones contribute to regulation of immune responses in autoimmune diseases such as MS.
According to a 2006 report from the World Health Organization (WHO), MS affects 2.5 million individuals worldwide and is more common among women ...
2012-10-03
NEW YORK (Oct. 1, 2012) -- Parents should not worry that proposed changes to the medical criteria redefining a diagnosis of autism will leave their children excluded and deemed ineligible for psychiatric and medical care, says a team of researchers led by psychologists at Weill Cornell Medical College.
Their new study, published in the October 1 issue of the American Journal of Psychiatry, is the largest to date that has tried to unpack the differences between the diagnostic criteria for autism spectrum disorders in the fourth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical ...
2012-10-03
EAST LANSING, Mich. — Genetics may make some women more vulnerable to the pressure of being thin, a study led by Michigan State University researchers has found.
From size-zero models to airbrushed film stars, thinness is portrayed as equaling beauty across Western culture, and it's an ideal often cited as a cause of eating disorder symptoms in young women.
The researchers focused on the potential psychological impact of women buying into this perceived ideal of thinness, which they call thin-ideal internalization. Changes in self-perception and behavior, caused by ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Too little nitrogen may restrain plants' carbon storage capability, U of M paper shows