(Press-News.org) There is still time to save the world's ailing coral reefs, if prompt and decisive action can be taken to improve their overall health, leading marine researchers say.
Writing in the journal Trends in Ecology and Evolution, eminent marine scientists from Australia and the USA have called for an international effort to improve the resilience of coral reefs, so they can withstand the impacts of climate change and other human activities.
"The world's coral reefs are important economic, social and environmental assets, and they are in deep trouble. How much trouble, and why, are critical research questions that have obvious implications for formulating policy and improving the governance and management of these tropical maritime resources," explains Jeremy Jackson from the Scripps Institution of Oceanography.
The key to saving the reefs lies in understanding why some reefs degenerate into a mass of weeds and never recover – an event known as a 'phase shift' – while on other reefs the corals manage to bounce back successfully, showing a quality known as resilience.
This underlines the importance of managing reefs in ways that promote their resilience, the researchers say.
They presented evidence that coral decline due to human activity has been going on for centuries, but has been particularly alarming in the past 50 years. In all some 125,000 square kilometres of the world's corals have disappeared so far.
The most recent global report card (2008) estimated that 19% of all reefs were effectively lost, another 15% were critical and likely to be lost in 10 years, and a further 20% are under threat from local human pressures (already experiencing 20% loss of corals). The remaining 46% of reefs were at low risk from direct human impacts, but were nevertheless vulnerable to climate change and ocean acidification.
"We have a very good scientific understanding of what causes reefs to decline – what we now need is a clearer picture of how to help them back onto the reverse trajectory," says lead author Professor Terry Hughes from the Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence for Coral Reef Studies at James Cook University.
Taking an optimistic view, the researchers argue there is compelling evidence from sites in Hawaii, Australia's Great Barrier Reef, the Caribbean, Bahamas and Philippines that the degradation and disappearance of corals can be arrested and reversed with the right management:
In Hawaii, where ending sewage discharges allowed corals in Kanehoe Bay to recover
In Australia, where weed-eating fish played a decisive role in keeping seaweed down while the corals fought back
In the Caribbean where recovering sea urchin populations are helping to keep down weed and allow corals to recover
In the Bahamas and Philippines, where controls on over fishing for parrot fish and other weed-eaters, also helped to restore coral cover.
"The coral reef crisis is a crisis of governance," says co-author Peter Mumby from the University of Queensland.
The team has formulated the scientific lessons from resilient reefs into a set of management advice which governments can adopt to give coral reefs a fighting chance:
Empower and educate local people to look after their own reefs
Change land uses that cause damaging runoff and sediment
Control not only fishing, but also fish markets to protect herbivorous fish
Integrate resilience science with reef management and support for local communities in restoring their reefs
Improve laws that protect coral reefs globally
"Confront climate change as the single most important issue for coral reef management and conservation by sharply reducing greenhouse gas emissions."
On climate change they caution: "Without urgent action, unchecked global warming and ocean acidification promise to be the ultimate policy failures for coral reefs. Although it is possible to promote the recovery of reefs following bouts of bleaching via local actions such as improving water-quality and protecting herbivores, these interventions alone cannot climate-proof reefs."
"The clear message from our research, and that of other marine scientists, is that the world's coral reefs can still be saved… if we try harder," Prof. Hughes says.
INFORMATION:
Their article "Rising to the challenge of sustaining coral reef resilience" by Terry P. Hughes, Nicholas A.J. Graham, Jeremy B.C. Jackson, Peter J. Mumby and Robert S. Steneck appears in the latest issue of Trends in Ecology and Evolution (TREE).
The future of Australia's and the world's coral reefs is the focus of a major scientific symposium in Canberra on October 7 and 8, at the Australian Academy of Science's Shine Dome.
Call to heal the world's coral reefs
2010-10-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Disability and Health Journal critically examines Americans with Disabilities Act
2010-10-08
New York, NY, October 6, 2010 – In recognition of the 20th anniversary of the enactment of the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), the October issue of Disability and Health Journal has brought together a series of articles to examine whether the ADA has in fact improved the health of people with disabilities. Areas of progress are identified, most notably acknowledging physical barriers and need for better staff training and communication about and with people with disabilities. However, there continue to be ongoing challenges, including recurrent barriers to health ...
Missing self-injury behavior in youths with eating disorders, Stanford/Packard study finds
2010-10-08
STANFORD, Calif. - An alarming number of adolescents already battling eating disorders are also intentionally cutting themselves, and health-care providers may be failing to diagnose many instances of such self-injury, according to a new study from Stanford University School of Medicine and Lucile Packard Children's Hospital.
The researchers found that 40.8 percent of patients with eating disorders in their study had documented incidents of intentionally harming themselves, most often by cutting and burning. What's more, the study suggests that inadequate clinical screening ...
Genetically modified crop resistance to pests benefits non-modified crop, U of Minnesota study finds
2010-10-08
Transgenic corn's resistance to pests has benefitted even non-transgenic corn, a new study led by scientists from the University of Minnesota shows.
The study, published in the Oct. 8 edition of the journal Science, found that widespread planting of genetically modified Bt corn throughout the Upper Midwest has suppressed populations of the European corn borer, historically one of corn's primary pests. This areawide suppression has dramatically reduced the estimated $1 billion in annual losses caused by the European corn borer, even on non-genetically modified corn. Bt ...
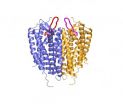
Scientists reveal first structure of a class of proteins that help guide blood cell movement
2010-10-08
LA JOLLA, CA – October 4, 2010 – Researchers have determined the structure of a protein that helps guide blood-forming stem cells, or hematopoetic stem cells. The protein is also one of the main receptors used by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) to get inside blood cells.
The findings are described in the October 7, 2010 issue of the journal Science.
The structure offers a detailed view of how the cell surface receptor, called CXCR4, interacts with molecules outside the cell. The results have implications for developing new drugs for hematopoetic stem cell transplantation, ...
Study details structure of potential target for HIV and cancer drugs
2010-10-08
VIDEO:
This model shows how HIV, in gray, might latch on to immune cell receptor molecules, allowing the virus to enter and infect the cell. The viral protein, gp120, shown in...
Click here for more information.
In a technical tour de force, structural biologists funded by the National Institutes of Health have determined the three-dimensional structure of a molecule involved in HIV infection and in many forms of cancer. The high-resolution structure sheds light on how the ...
Study cites illegal means, threats to farmers in company's bid to control China's forests
2010-10-08
Washington, DC/Beijing, China (7-8 October 2010)—A new study released today in Washington, DC and Beijing suggests that one of the world's largest and "greenest" paper companies, in concert with local officials and other middlemen, used illegal means to gain control over thousands of hectares of Chinese forestlands, with a goal of acquiring 120 thousand hectares for a eucalyptus plantation in the Guangxi Autonomous Region of southern China.
The authors say their research shows that the middlemen, acting on behalf of Finnish paper and pulp manufacturer Stora Enso, often ...
Female fish flaunt fins to attract a mate
2010-10-08
For the first time, biologists have described the evolution of the size of a female trait which males use to choose a partner. The research, published in the open access journal BMC Evolutionary Biology, shows that male cichlid fish prefer females with a larger pelvic fin and that this drives females to grow fins out of proportion with their body size.
Sebastian Baldauf from the University of Bonn, Germany, worked with a team of researchers to study the effects of female ornamentation in the African cichlid fish Pelvicachromis taeniatus. He said, "In contrast to the ...
Ultrasound device improves poor bone healing
2010-10-08
Ultrasound can speed the healing of fractures. A randomized controlled trial reported in the open access journal BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders has found that the use of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) in patients with tibial fractures which showed inadequate progress toward healing resulted in 34% greater bone mineral density (BMD) in the fracture area after 16 weeks than use of a sham device.
Jon E. Block, Ph.D. worked with a team of researchers from University Hospital Marburg and the University of Ulm, Germany, to test LIPUS in 51 patients and 50 controls. ...
Deceitful lily fools flies
2010-10-08
Scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology in Jena, Germany, have solved a case of fraud that has been pending for 40 million years. Arum palaestinum, also called the Solomon's lily, attracts drosophilids (vinegar flies) as pollinators by emitting odor molecules that resemble those produced during alcoholic fermentation of rotting fruit initiated by yeast. The plant accomplishes the illusion of yeast simply by producing six chemicals that - together in a specific mix - create the impression of fermentation in the fly brain. The produced volatiles include ...
Georgia Tech Information Security Center releases cyber threats forecast for 2011
2010-10-08
The Georgia Tech Information Security Center (GTISC), a national leader in information security research and education, today announced the release of the GTISC Emerging Cyber Threats Report for 2011, outlining the top three areas of security risk and concern for consumer and business Internet and computer users. The report was released today at the annual GTISC Security Summit on the Evolving Nature of Cyber Security Threats. The summit gathers leading industry and academic leaders who have distinguished themselves in the field of cyber security.
According to the report, ...