(Press-News.org) A simple new test, in which the patient swallows a string, can monitor treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis as effectively as an invasive, expensive and uncomfortable procedure that risks complications, particularly in children.
Researchers from the University of Illinois at Chicago College of Medicine, working in collaboration with clinician-investigators at the University of Colorado Denver/Children's Hospital Colorado and Lurie Children's Hospital in Chicago, reported their findings in a study published recently online in the journal Gut.
Eosinophilic esophagitis, or EoE, is a food-allergy inflammatory disease of the esophagus in both children and adults. While rare, it is steadily increasing in incidence. In EoE, inflammatory cells in the body called eosinophils attack the esophagus. The esophagus narrows until food cannot pass, causing painful impactions.
"Most cases are first encountered in the emergency room, where a child is brought in because something he ate is caught in his esophagus," says Steven Ackerman, UIC professor of biochemistry and molecular genetics and co-principal investigator on the study.
Eosinophils produce specific proteins. Because these inflammatory cells are not normally found in the esophagus, these proteins serve as biomarkers and can indicate the extent of inflammation in the esophagus.
Currently, physicians diagnose EoE and monitor its treatment by endoscopy. A lighted, flexible instrument is inserted down the esophagus and used to obtain six to eight tissue samples for biopsy from sections along its length from throat to stomach.
A child may require 10, 15, or even 20 such procedures over three or four years, say two of the report's authors, co-principal investigator Dr. Glenn Furuta, professor of pediatrics at the University of Colorado at Denver, and Dr. Amir Kagalwalla, associate professor of pediatrics at Northwestern University.
The new method, the Esophageal String Test, or EST, uses a capsule containing a yard-long string. One end of the string is taped to the patient's cheek before the capsule is swallowed, and the string spools out of the dissolving capsule, stretching through the esophagus, the stomach and the small intestine. The string becomes coated with digestive tract secretions and can be removed for analysis.
Ackerman and Furuta tested samples from the string in the esophagus region looking for eosinophil proteins to show evidence of inflammation. Levels detected by the string test and by biopsy were both shown to indicate disease accurately.
The researchers recruited 41 patients ages 7-20, who were to undergo endoscopy and biopsy. Participants swallowed the capsule the night before endoscopy, and the string was removed just prior to that procedure. The researchers believe the string may not need to remain in place for so long, and the test could be performed in a single visit to the doctor's office.
Although the string test may never completely replace endoscopy-with-biopsy, particularly for diagnosis, the authors conclude, "it certainly has the potential to significantly improve the evaluation and treatment of patients who require repeated assessments."
INFORMATION:
This study was supported by grants or gifts form NIH-R21AID79925, Thaser Research Fund, NIH/NICATS Colorado CCTS grant Ul1 TR000154, Shell, Mandell, Boyd and Savoie Families, American Gastroenterological Association, Campaign Urging Research for Eosinophilic Diseases, Buckeye Foundation, Pappas Foundation, American Partnership for Eosinophic Disorders, Sandhill Scientific, Mayo Foundation and NIH HL058732 and the SCRR K26 RR0109709 and NIH- 1UL1RR025741.
For more information about the University of Illinois Hospital & Health Sciences System,
visit http://www.hospital.uillinois.edu.
END
MAYWOOD, Ill. – Gender-specific group therapy is effective for treating depressed women with Type 2 diabetes, according to a study published in the latest issue of the Annals of Behavioral Medicine and funded by the National Institute of Nursing Research. Evidence suggests that antidepressants may disrupt blood-sugar control and can be associated with increased weight gain; therefore, other treatment options are needed for depression.
"Using antidepressants to treat depression, although important, can be associated with side effects that make compliance an issue for people ...
Amsterdam, The Netherlands, October 3, 2012 – Milk consumption has been linked to improved health, with decreased risks of diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and colon cancer. A group of scientists in Sweden found that lactoferricin4-14 (Lfcin4-14), a milk protein with known health effects, significantly reduces the growth rate of colon cancer cells over time by prolonging the period of the cell cycle before chromosomes are replicated. In a new study, investigators report that treatment with Lfcin4-14 reduced DNA damage in colon cancer cells exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. ...
STANFORD, Calif. — Not everyone is able to be hypnotized, and new research from the Stanford University School of Medicine shows how the brains of such people differ from those who can easily be.
The study, published in the October issue of Archives of General Psychiatry, uses data from functional and structural magnetic resonance imaging to identify how the areas of the brain associated with executive control and attention tend to have less activity in people who cannot be put into a hypnotic trance.
"There's never been a brain signature of being hypnotized, and we're ...
The fifteenth tropical depression of the Atlantic Ocean hurricane season was born on Oct. 3 an NASA's Terra satellite captured an image of it as it came to be.
NASA's Terra satellite passed over newborn Tropical Depression 15 on Oct. 3 at 8:52 a.m. EDT in the central Atlantic Ocean and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument captured an image of the storm. Shortly after the image was created, forecasters at the National Hurricane Center looking at the MODIS and other satellite data determined that the low pressure area had become a depression.
On ...
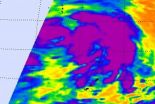
NASA's Aqua satellite took an infrared "picture" of Tropical Storm Maliksi in the western North Pacific Ocean and identified the strongest part of the storm being east of its center.
On Oct. 3 at 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT), Tropical storm Maliksi had maximum sustained winds of 45 knots (51.7 mph/83.3 kph). It was located about 470 nautical miles (541 miles/870.4 km) south-southeast of Tokyo, Japan, near 29.4 North and 143.1 East. Maliksi was speeding to the north-northeast at 21 knots (24.1 mph/38.8 kph).
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies ...
VIDEO:
On Oct. 2 at 11:43 p.m. EDT, heavy convective thunderstorms were found in Nadine's northeastern quadrant by NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite. Wind shear had separated the center...
Click here for more information.
NASA satellites continue to gather data from Tropical Storm Nadine on its twenty-second day of life in the eastern Atlantic as it threatens the Azores again. NASA data has shown that wind shear is pushing the bulk of clouds and ...
Tropical Storm Gaemi is packing a lot of power around its middle and on one side of the storm, and that was apparent in NASA satellite imagery.
NASA's Terra satellite passed over Tropical Storm Gaemi on Oct. 3 at 0300 UTC (11:00 p.m. EDT, Oct. 2) and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument captured a true-color image of the storm. The image showed a bright white, rounded area around the center that indicated higher, stronger thunderstorms. Higher, stronger thunderstorms also wrapped around the center in a wide band that stretches from north ...
JUPITER, FL, October 3, 2012 – Scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute have developed a novel technology that can identify, in animal models, potential biomarkers of ulcerative colitis, a type of inflammatory bowel disease that affects the lining of the colon.
The study was published October 3, 2012, in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
The new research focuses on the protein arginine deiminases (PAD), which have been implicated in a number of diseases, including cancer, multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis. PADs participate ...
Berkeley — Bisphenol A (BPA), an estrogen-like compound that has drawn increased scrutiny in recent years, has been linked to changes in thyroid hormone levels in pregnant women and newborn boys, according to a new study by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley.
Normal thyroid function is essential to the healthy growth and cognitive development of fetuses and children. Yet, until this study, to be published Thursday, Oct. 4, in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives, little was known about the effects of BPA exposure on thyroid hormones in pregnant ...
A compassion-based meditation program can significantly improve a person's ability to read the facial expressions of others, finds a study published by Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience. This boost in empathic accuracy was detected through both behavioral testing of the study participants and through functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scans of their brain activity.
"It's an intriguing result, suggesting that a behavioral intervention could enhance a key aspect of empathy," says lead author Jennifer Mascaro, a post-doctoral fellow in anthropology at ...