(Press-News.org) STANFORD, Calif. — Not everyone is able to be hypnotized, and new research from the Stanford University School of Medicine shows how the brains of such people differ from those who can easily be.
The study, published in the October issue of Archives of General Psychiatry, uses data from functional and structural magnetic resonance imaging to identify how the areas of the brain associated with executive control and attention tend to have less activity in people who cannot be put into a hypnotic trance.
"There's never been a brain signature of being hypnotized, and we're on the verge of identifying one," said David Spiegel, MD, the paper's senior author and a professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences. Such an advance would enable scientists to understand better the mechanisms underlying hypnosis and how it can be used more widely and effectively in clinical settings, added Spiegel, who also directs the Stanford Center for Integrative Medicine.
Spiegel estimates that one-quarter of the patients he sees cannot be hypnotized, though a person's hypnotizability is not linked with any specific personality trait. "There's got to be something going on in the brain," he said.
Hypnosis is described as a trance-like state during which a person has a heightened focus and concentration. It has been shown to help with brain control over sensation and behavior, and has been used clinically to help patients manage pain, control stress and anxiety and combat phobias.
Hypnosis works by modulating activity in brain regions associated with focused attention, and this study offers compelling new details regarding neural capacity for hypnosis.
"Our results provide novel evidence that altered functional connectivity in [the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex] and [the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex] may underlie hypnotizability," the researchers wrote in their paper.
For the study, Spiegel and his Stanford colleagues performed functional and structural MRI scans of the brains of 12 adults with high hypnotizability and 12 adults with low hypnotizability.
The researchers looked at the activity of three different networks in the brain: the default-mode network, used when one's brain is idle; the executive-control network, which is involved in making decisions; and the salience network, which is involved in deciding something is more important than something else.
The findings, Spiegel said, were clear: Both groups had an active default-mode network, but highly hypnotizable participants showed greater co-activation between components of the executive-control network and the salience network. More specifically, in the brains of the highly hypnotizable group the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, an executive-control region of the brain, appeared to be activated in tandem with the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex, which is part of the salience network and plays a role in focusing of attention. By contrast, there was little functional connectivity between these two areas of the brain in those with low hypnotizability.
Spiegel said he was pleased that he and his team found something so clear. "The brain is complicated, people are complicated, and it was surprising we were able to get such a clear signature," he explained.
Spiegel also said the work confirms that hypnotizability is less about personality variables and more about cognitive style. "Here we're seeing a neural trait," he said.
The authors' next step is to further explore how these functional networks change during hypnosis. Spiegel and his team have recruited high- and low-hypnotizable patients for another study during which fMRI assessment will be done during hypnotic states. Funding for that work is being provided by the National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
###
Funding for this study came from the Nissan Research Center, the Randolph H. Chase, MD Fund II, the Jay and Rose Phillips Family Foundation and the National Institutes of Health.
The study's first-author is Fumiko Hoeft, MD, PhD, who was formerly an instructor at Stanford's Center for Interdisciplinary Brain Sciences Research and is now an associate professor of psychiatry at UCSF. Other co-authors are John Gabrieli, PhD, a professor at MIT (then a professor of psychology at Stanford); Susan Whitfield-Gabrieli, a research scientist at MIT (then a science and engineering associate at Stanford); Brian Haas, PhD, an assistant professor at the University of Georgia (then a postdoctoral scholar in the Center for Interdisciplinary Brain Sciences Research at Stanford); Roland Bammer, PhD, associate professor of radiology; and Vinod Menon, PhD, professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences.
Information on the medical school's Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, which also supported this work, is available at http://psychiatry.stanford.edu/.
The Stanford University School of Medicine consistently ranks among the nation's top medical schools, integrating research, medical education, patient care and community service. For more news about the school, please visit http://mednews.stanford.edu. The medical school is part of Stanford Medicine, which includes Stanford Hospital & Clinics and Lucile Packard Children's Hospital. For information about all three, please visit http://stanfordmedicine.org/about/news.html.
PRINT MEDIA CONTACT: Michelle Brandt at (650) 723-0272 (mbrandt@stanford.edu)
BROADCAST MEDIA CONTACT: M.A. Malone at (650) 723-6912 (mamalone@stanford.edu)
END
The fifteenth tropical depression of the Atlantic Ocean hurricane season was born on Oct. 3 an NASA's Terra satellite captured an image of it as it came to be.
NASA's Terra satellite passed over newborn Tropical Depression 15 on Oct. 3 at 8:52 a.m. EDT in the central Atlantic Ocean and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument captured an image of the storm. Shortly after the image was created, forecasters at the National Hurricane Center looking at the MODIS and other satellite data determined that the low pressure area had become a depression.
On ...
NASA's Aqua satellite took an infrared "picture" of Tropical Storm Maliksi in the western North Pacific Ocean and identified the strongest part of the storm being east of its center.
On Oct. 3 at 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT), Tropical storm Maliksi had maximum sustained winds of 45 knots (51.7 mph/83.3 kph). It was located about 470 nautical miles (541 miles/870.4 km) south-southeast of Tokyo, Japan, near 29.4 North and 143.1 East. Maliksi was speeding to the north-northeast at 21 knots (24.1 mph/38.8 kph).
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies ...
VIDEO:
On Oct. 2 at 11:43 p.m. EDT, heavy convective thunderstorms were found in Nadine's northeastern quadrant by NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite. Wind shear had separated the center...
Click here for more information.
NASA satellites continue to gather data from Tropical Storm Nadine on its twenty-second day of life in the eastern Atlantic as it threatens the Azores again. NASA data has shown that wind shear is pushing the bulk of clouds and ...
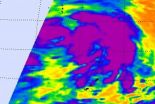
Tropical Storm Gaemi is packing a lot of power around its middle and on one side of the storm, and that was apparent in NASA satellite imagery.
NASA's Terra satellite passed over Tropical Storm Gaemi on Oct. 3 at 0300 UTC (11:00 p.m. EDT, Oct. 2) and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument captured a true-color image of the storm. The image showed a bright white, rounded area around the center that indicated higher, stronger thunderstorms. Higher, stronger thunderstorms also wrapped around the center in a wide band that stretches from north ...
JUPITER, FL, October 3, 2012 – Scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute have developed a novel technology that can identify, in animal models, potential biomarkers of ulcerative colitis, a type of inflammatory bowel disease that affects the lining of the colon.
The study was published October 3, 2012, in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
The new research focuses on the protein arginine deiminases (PAD), which have been implicated in a number of diseases, including cancer, multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis. PADs participate ...
Berkeley — Bisphenol A (BPA), an estrogen-like compound that has drawn increased scrutiny in recent years, has been linked to changes in thyroid hormone levels in pregnant women and newborn boys, according to a new study by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley.
Normal thyroid function is essential to the healthy growth and cognitive development of fetuses and children. Yet, until this study, to be published Thursday, Oct. 4, in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives, little was known about the effects of BPA exposure on thyroid hormones in pregnant ...
A compassion-based meditation program can significantly improve a person's ability to read the facial expressions of others, finds a study published by Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience. This boost in empathic accuracy was detected through both behavioral testing of the study participants and through functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scans of their brain activity.
"It's an intriguing result, suggesting that a behavioral intervention could enhance a key aspect of empathy," says lead author Jennifer Mascaro, a post-doctoral fellow in anthropology at ...
DatingMashup.com is proud to announce its sponsorship of Phoenix Fashion Week. Dale P. Ballard, Founder and CEO of DatingMashup.com explains,
"We'll be providing a special gift that will be found inside various VIP "swag" bags. We think this is a wonderful event not only for DatingMashup.com members, but for anyone who loves fashion and enjoys donating to charitable causes."
This exciting event is taking place at The Talking Stick Resort Casino in Scottsdale, Arizona. The event will house thousands of people over four days and will include a ...
New Harmony Soap Company, a maker of natural, nutrient-rich soaps and skin health products, will introduce a pair of Artisan Wine Soaps this weekend at the 10th Annual Wabash Valley Wine & Art Festival in historic Palestine, Illinois.
As an artisan vendor at the popular Fall festival 45 miles southwest of Terre Haute,Indiana, New Harmony Soap Company will debut a Red Wine Soap and a Honey Wine Soap. The red wine soap is crafted using Reggae Red table wine vinted by Easley Winery of Indianapolis. The honey wine soap uses Camelot Mead Honey Wine vinted by Oliver Winery ...
The boys are, literally, back in town (flying in from Finland, Norway and the US) to appear in a video by renowned film director Tony Klinger (Get Carter, Shout At The Devil, Deep Purple Over Japan, The Kids are Alright - The Who). The A list of rock's greatest are appearing in the promotional video for 'Honest' John Plain's single 'Never Listen To Rumours' are Michael Monroe and Sami Yaffa (Hanoi Rocks/New York Dolls) Martin Chambers (The Pretenders), Glen Matlock (Sex Pistols), Casino Steel (The Boys, Johnny Cash, Carlene Carter), Darrell Bath (The Crybabys and Dogs D'Amour) ...