(Press-News.org) New research from the University of Helsinki, Finland, suggests that a mother's high blood pressure during pregnancy may have an effect on her child's thinking skills all the way into old age. The study is published in the October 3, 2012, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
"High blood pressure and related conditions such as preeclampsia complicate about 10 percent of all pregnancies and can affect a baby's environment in the womb," said study author Katri Räikkönen, PhD. "Our study suggests that even declines in thinking abilities in old age could have originated during the prenatal period when the majority of the development of brain structure and function occurs."
Researchers looked at medical records for the mother's blood pressure in pregnancy for 398 men who were born between 1934 and 1944. The men's thinking abilities were tested at age 20 and then again at an average age of 69. Tests measured language skills, math reasoning and visual and spatial relationships.
The study found that men whose mothers had high blood pressure while pregnant scored 4.36 points lower on thinking ability tests at age 69 compared to men whose mothers did not have high blood pressure. The group also scored lower at the age of 20 and had a greater decline in their scores over the decades than those whose mothers did not have problems with blood pressure. The finding was strongest for math-related reasoning.
The researchers also looked at whether premature birth affected these findings and found no change. Whether the baby's father was a manual laborer or an office worker also did not change the results.
###
For more information, please contact:
Katri Räikkönen, PhD, University of Helsinki
Tel. +358 9 191 29501
Email: katri.raikkonen@helsinki.fi
The study was supported by the Academy of Finland, European Science Foundation, University of Helsinki, the British Heart Foundation, the Finnish Foundation of Cardiovascular Research, the Finnish Diabetes Research Foundation, the Finnish Medical Society, Gulf Läkaresällskapet, the National Doctoral Program of Psychology, the Päivikki and Sakari Sohlberg Foundation, the Juho Vainio Foundation, the Yrjö Jahnsson Foundation, the Signe and Ane Gyllenberg Foundation, the Jalmari and Rauha Ahokas Foundation, the Emil Aaltonen Foundation, the Finnish Ministry of Education and the Finnish Foundation for Pediatric Research.
Mom's high blood pressure in pregnancy could affect child's IQ in old age
2012-10-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Methane emissions can be traced back to Roman times
2012-10-04
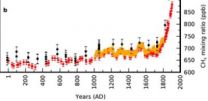
Emissions of the greenhouse gas methane into the atmosphere can be traced back thousands of years in the Greenland ice sheet. Using special analytical methods, researchers from the Niels Bohr Institute, among others, have determined how much methane originates from natural sources and how much is due to human activity. The results go all the way back to Roman times and up to the present, where more than half of the emissions are now man-made. The results are published in the scientific journal, Nature.
Methane is an important greenhouse gas, which today is partly emitted ...
Surprising black-hole discovery changes picture of globular star clusters
2012-10-04
An unexpected discovery by astronomers using the National Science Foundation's Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) is forcing scientists to rethink their understanding of the environment in globular star clusters, tight-knit collections containing hundreds of thousands of stars.
The astronomers used the VLA to study a globular cluster called Messier 22 (M22), a group of stars more than 10,000 light-years from Earth. They hoped to find evidence for a rare type of black hole in the cluster's center. They wanted to find what scientists call an intermediate-mass black hole, ...
50-hour whole genome sequencing provides rapid diagnosis for children with genetic disorders
2012-10-04
KANSAS CITY, Mo. – OCTOBER 3, 2012 – Today investigators at Children's Mercy Hospitals and Clinics in Kansas City reported the first use of whole genome information for diagnosing critically ill infants. As reported in Science Translational Medicine, the team describes STAT-Seq, a whole genome sequencing approach - from blood sample to returning results to a physician - in about 50 hours. Currently, testing even a single gene takes six weeks or more.
Speed of diagnosis is most critical in acute care situations, as in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), where medical ...
Key environmental factors influencing manta ray behavior identified
2012-10-04
Manta rays are more likely to gather together under either a new or a full moon, according to new research published Oct 3 in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Fabrice Jaine and colleagues at the University of Queensland.
The research identifies environmental factors that predict the abundance and behavior of manta rays at Lady Elliott Island in the Great Barrier Reef. The authors comment that knowing these factors is important for conservation efforts, "especially in the context of a changing climate and with targeted fisheries increasingly threatening manta ray populations ...
Oldest evidence of regular meat consumption by early humans found
2012-10-04
A fragment of a child's skull discovered at Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania shows the oldest known evidence of anemia caused by a nutritional deficiency, reports a new paper published Oct. 3 in the open access journal PLOS ONE.
The discovery, made by a global team of researchers led by Manuel Domínguez-Rodrigo from Complutense University, Madrid, suggests that early human ancestors began eating meat much earlier in history than previously believed. The skull fragment identified is thought to belong to a child somewhat younger than two and shows bone lesions that commonly result ...
Novel blood-based protein signature determined for rare, aggressive lung cancer
2012-10-04
Researchers have discovered a panel of 13 blood proteins that may be effective biomarkers to detect malignant mesothelioma, according to a study published Oct. 3 in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Rachel Ostroff from the company SomaLogic, which developed the new test, and colleagues at other institutions.
Malignant mesothelioma is a rare, aggressive form of lung cancer that can develop after prolonged exposure to asbestos. Because early diagnosis is difficult, most patients face a poor prognosis and have few options for treatment. In the study, authors compared proteins ...
Less is more when choosing between groups of assorted items
2012-10-04
When making decisions about the value of an assortment of different objects, people approximate an average overall value, which though frequently useful can lead to apparently irrational decision-making. A new study published Oct 3 in PLOS ONE by Jerald Kralik and colleagues at Dartmouth College shows for the first time that non-human primates also make similar 'irrational' choices based on approximation.
In the study, researchers found that rhesus monkeys preferred a highly-valued food item (a fruit) alone to the identical item paired with a food of positive but lower ...
Mollusc missing link revealed in 3-D
2012-10-04
Scientists have discovered a rare fossil called Kulindroplax, the missing link between two mollusc groups, which is revealed in a 3D computer model, in research published today in the journal Nature.
The researchers have unearthed the worm-like partly shelled Kulindroplax, which they have modelled in a 3D computer animation. Kulindroplax lived in the sea during the Silurian Period, approximately 425 million years ago, when most life lived in the oceans and the first plants were beginning to grow on land. The team found the Kulindroplax fossil, the only one of its kind ...
Blocking tumor-induced inflammation impacts cancer development
2012-10-04
Researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine report the discovery of microbial–dependent mechanisms through which some cancers mount an inflammatory response that fuels their development and growth.
The findings are published in the October 3, 2012 Advanced Online Edition of Nature.
The association between chronic inflammation and tumor development has long been known from the early work of German pathologist Rudolph Virchow. Harvard University pathologist Harold Dvorak later compared tumors with "wounds that never heal," noting the similarities ...
Healthcare professionals as bad as patients at good respiratory inhaler technique
2012-10-04
Healthcare professionals are as bad as patients when it comes to knowing how to use inhalers prescribed for asthma and other respiratory conditions correctly, says an editorial in Drug and Therapeutics Bulletin (DTB).
They therefore can't be relied on to teach patients how to use these devices correctly, says DTB.
But as 45 million prescriptions for respiratory inhalers were dispensed in 2011 in England alone—at a cost of £900 million to the NHS—everyone needs to be more clued up on correct inhaler technique to make sure these drugs work well for patients and offer ...