Northern conifers youngest of the species
2012-10-05
(Press-News.org) New Haven, Conn.—Dramatic shifts in the planet's climate and geography over millions of years changed the course of evolutionary history for conifer trees, according to a Yale paper in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Yale researchers examined the fossil record and genetic makeup of 489 out of more than 600 living conifer species and discovered that while most conifers belong to ancient lineages, most Northern Hemisphere species, including the majority of pines and spruces, appeared within the past 5 million years.
They argue that the migration of tree species and the contraction and expansion of their ranges in response to glacial cycles led to isolated populations and the formation of new species, especially in mountainous environments where conifer diversity is high.
"Extreme climatic shifts through time may have favored the replacement of older lineages with those better adapted to cooler and drier conditions," said Andrew Leslie, the study's co-author and a Yale postdoctoral associate, "resulting in high turnover rates and the disproportionate loss of ancient lineages."
The researchers also found that the lineages of existing conifers in the Southern Hemisphere are millions of years older than their counterparts in the Northern Hemisphere, and believe it is owing to fragmented ranges and mild, wetter habitats that favored their survival.
"The evolutionary history of conifers reflects a complex set of environmental interactions," said Peter Crane, a co-author, professor of botany and dean of the Yale School of Forestry & Environmental Studies. "Nevertheless, we found large-scale and consistent differences between the diversification of southern and northern conifer clades."
The majority of existing conifer species belongs to lineages that diversified during the Cenozoic Era, over 65 million years. Conifers such as firs, hemlocks, larches, pines, spruces (Pinaceae family), junipers and cypresses (Cupressoideae) are found across the Northern Hemisphere, whereas evergreens in the Araucariaceae and Podocarpaceae families and Callitroideae subfamily are found primarily in Argentina, Australia, New Guinea and New Zealand.
Michael Donoghue, a co-author of the study and Sterling Professor of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, said temperate rainforests and broadleaf evergreen forests were common before the Pleistocene Epoch, which spanned 2.5 million years and ended 11,000 years ago, and are still present in New Zealand and in parts of Australia and South America.
"These now-fragmented habitats are among those in which older conifer lineages adapted to warmer or wetter climates and have survived at high diversity," he said. "The evolutionary histories of organisms are shaped by many factors, but this study suggests that global-scale geographic features can leave an unexpected imprint in the way in which groups evolve and diversify."
###
The study, "Hemisphere-scale Differences in Conifer Evolutionary Dynamics," can be viewed at http://www.pnas.org/content/early/2012/09/12/1213621109.full.pdf+html?with-ds=yes.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2012-10-05
Controlling "mixing" between acceptor and donor layers, or domains, in polymer-based solar cells could increase their efficiency, according to a team of researchers that included physicists from North Carolina State University. Their findings shed light on the inner workings of these solar cells, and could lead to further improvements in efficiency.
Polymer-based solar cells consist of two domains, known as the acceptor and the donor layers. Excitons, the energy particles created by solar cells, must be able to travel quickly to the interface of the donor and acceptor ...
2012-10-05
CORVALLIS, Ore. – More than 40 percent of older breast cancer survivors are insufficiently active after leaving a supervised program. But new research shows that those women who developed behavioral skills such as self-confidence and motivation during their program were far more likely to continue exercising on their own.
Regular exercise may reduce the risk of breast cancer recurrence and breast cancer-related mortality, experts say, making it crucial to effectively target breast cancer survivors who do not engage in regular physical activity for interventions.
Researchers ...
2012-10-05
At first blush, many people would probably love to get rid of insects, such as pesky mosquitoes, ants and roaches. But a new study indicates that getting rid of insects could trigger some unwelcome ecological consequences, such as the rapid loss of desired traits in plants, including their good taste and high yields.
Specifically, the study--described in the Oct. 5, 2012 issue of Science and funded by the National Science Foundation showed that evening primroses grown in insecticide-treated plots quickly lost, through evolution, defensive traits that helped protect them ...
2012-10-05
Suicide is the third-leading cause of death for teens, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Now, a University of Missouri public health expert has identified factors that will help parents, medical professionals and educators recognize teens at risk for self injury and suicide.
"For many young people, suicide represents an escape from unbearable situations—problems that seem impossible to solve or negative emotions that feel overwhelming," said Lindsay Taliaferro, an assistant professor of health sciences at MU. "Adults can help these teens dissect ...
2012-10-05
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. – Sandia National Laboratories published the second annual 2012 Wind Plant Reliability Benchmark on Monday, and the results should help the nation's growing wind industry benchmark its performance, understand vulnerabilities and enhance productivity.
Until now, wind farm owners and operators had no way to compare their output with the output of similar operations. To benchmark the reliability of the U.S. wind turbine fleet and identify major causes of failures and downtime, the DOE commissioned Sandia in 2010 to build the Continuous Reliability Enhancement ...
2012-10-05
To believe that technologies once dreamed of in science fiction novels, television shows, and comic strips may one day be a reality, or that real-world technologies might make the fantastic devices of fiction obsolete, you'd need to be either an optimist…or a futurist in the Department of Homeland Security (DHS)'s Science and Technology Directorate (S&T).
To keep dreams grounded, S&T maintains a team of futurists in Arlington, Va., at the Homeland Security Studies & Analysis Institute (HSSAI). There, in the Resilience and Emergency Preparedness / Response Branch, analysts ...
2012-10-05
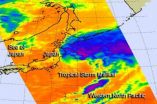
Tropical Storm Maliksi is putting the final touches on Japan, that is, the edge of the storm was seen brushing the country's northern coast as it pulled away on NASA satellite imagery.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Maliksi on Oct. 4 at 0329 UTC (11:29 p.m. EDT, Oct. 3, EDT) and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an infrared image of the storm brushing the Tohoku and Hokkaido prefectures of northern Japan.
On Oct. 4, 2012 at 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT), the Joint Typhoon Warning Center issued their final advisory on Maliksi. At ...
2012-10-05
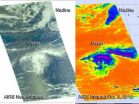
NASA's Aqua satellite provided two different infrared views of the two tropical storms swirling in the Atlantic Ocean. Oscar is battling wind shear that appears destined to tear it apart, while Nadine is merging with a cold front.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over both Tropical Storm Nadine and Tropical Depression 15 (TD15) on Oct. 3 at 1553 UTC (11:53 a.m. EDT), before TD15 became Tropical Storm Oscar. While overhead, the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument aboard Aqua captured two different images of both storms. One image was near infrared and almost visible ...
2012-10-05
Some of the most powerful thunderstorms in a tropical cyclone surround the center of circulation, and NASA's TRMM satellite noticed that rainfall is heaviest in that area of Tropical Storm Gaemi.
When NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite passed over Tropical Storm Gaemi on Oct. 3 at 1241 UTC (8:41 a.m. EDT), the precipitation radar instrument detected light rainfall occurring over most of the storm. Moderate rain was falling at a rate between .78 to 1.57 inches/20 to 40 mm per hour and surrounded a small area of heavy rainfall circling tightly around ...
2012-10-05
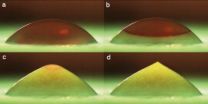
Researchers at the University of Twente, in the Netherlands, placed water droplets on a plate chilled to -20 degrees Celsius and captured images as a freezing front traveled up the droplet. The photos are published in the American Institute of Physics' (AIP) journal Physics of Fluids. The approximately 4-millimeter diameter droplets took about 20 seconds to freeze. During the final stage of freezing, the ice drop developed a pointy tip, as can be seen in Figure 1d. The effect, which is not observed for most other liquids, arises because water expands as it freezes. The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Northern conifers youngest of the species