(Press-News.org) Satellite data is showing that northwesterly wind shear is taking a toll on Tropical Storm Oscar in the central Atlantic and it is expected to dissipate the storm late on Oct. 5, 2012.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Oscar on Oct. 4 at 1335 UTC (9:35 a.m. EDT) and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument captured a true-color image of the storm. The imagery showed bulk of Oscar's clouds and showers were southeast of the center of circulation as a result of wind shear.
On Oct. 5 at 5 a.m. EDT, Oscar's maximum sustained winds were near 50 mph (85 kph), and wind shear is expected to batter Oscar into oblivion over the next day. Oscar was 1,085 miles (1,745 km) west-northwest of the Cape Verde Islands, near latitude 23.0 north and longitude 38.9 west. Oscar is moving toward the northeast near 15 mph (24 kph) and is expected to continue with an increase in forward speed today. The estimated minimum central pressure is 997 millibars.
Oscar's low-level center continued to be exposed on Oct. 5 and is northwest of the bulk of showers and thunderstorms. The National Hurricane Center (NHC) expects Oscar will be absorbed by an approaching cold front later on Oct. 5. NHC noted "strong southerly gale-force winds are expected to continue ahead of the cold front after Oscar dissipates."
INFORMATION:
NASA satellites indicate wind shear taking toll on Oscar
2012-10-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scratching the surface: Stanford engineers examine UV effects on skin mechanics
2012-10-05
Reinhold Dauskardt, PhD, of Stanford's Department of Materials Science and Engineering has been studying skin for years. But when he sent his students to look for data on the mechanical properties of skin, they came back empty-handed. A lot was known about skin structure and disease, but few papers actually talked about its mechanical function – its ability to stretch and resist tension without tearing. "That motivated us to get more interested in the skin itself," said Dauskardt.
He and his team, including Ph.D. student Krysta Biniek and postdoctoral researcher Kemal ...
Using less gas and oil to get where you're going
2012-10-05
An engine without oil will not survive for very long. Pistons need plenty of lubricant in order to be able to move within the cylindrical sleeves in the engine block. Two things are known to raise the resultant level of friction. The first is attributed to distortion of the cylindrical bore hole when the cylinder head is attached, which is known as static distortion. The second occurs when the engine is running and temperatures warp the bore hole. The extent of this thermal distortion depends on prevailing engine temperatures and the specific engine model. In reality, the ...
Origin of ultra-fast manipulation of domain walls discovered
2012-10-05
An international team of researchers has found at the free electron laser FLASH a surprising effect that leads in ferromagnetic materials to a spatially varying magnetization manipulation on an ultrafast timescale. This effect could be the key to further miniaturization and performance increase of magnetic data storage devices. From Mainz, the group of Professor Dr. Mathias Kläui from the Institute of Physics at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz and in particular Felix Büttner, a member of the Graduate School of Excellence "Materials Science in Mainz", were involved. ...
Testing can be useful for students and teachers
2012-10-05
Pop quiz! Tests are good for: (a) Assessing what you've learned; (b) Learning new information; (c) a & b; (d) None of the above.
The correct answer?
According to research from psychological science, it's both (a) and (b) – while testing can be useful as an assessment tool, the actual process of taking a test can also help us to learn and retain new information over the long term and apply it across different contexts.
New research published in journals of the Association for Psychological Science explores the nuanced interactions between testing, memory, and learning ...
Weather-making high-pressure systems predicted to intensify
2012-10-05
DURHAM, N.C. -- High-pressure systems over oceans, which largely determine the tracks of tropical cyclones and hydrological extremes in much of the northern hemisphere, are likely to intensify this century, according to a Duke University-led study.
The study, published online this week in Nature Geoscience, suggests that as summertime near-surface high-pressure systems over the northern Pacific and Atlantic oceans strengthen, they could play an increasingly important role in shaping regional climate, particularly the occurrence of drought and extreme summer rainfall ...
Get with the computer program
2012-10-05
Montreal, October 5, 2012 – From email to Twitter, blogs to word processors, computer programs provide countless communications opportunities. While social applications have dominated the development of the participatory web for users and programmers alike, this era of Web 2.0 is applicable to more than just networking opportunities: it impacts education.
The integration of increasingly sophisticated information and communication tools (ICTs) is sweeping university classrooms. Understanding how learners and instructors perceive the effectiveness of these tools in the ...
There's no place like home -- For dialysis
2012-10-05
Highlights
Home hemodialysis could allow patients to enjoy increased freedom, quality of life, greater ability to travel, and tangible health improvements.
Increased physician and patient education can eliminate barriers to home hemodialysis and increase its use.
Approximately 2 million patients in the world receive some sort of dialysis treatment.
Washington, DC (October 4, 2012) — Most patients with chronic kidney disease who undergo hemodialysis put up with a grueling treatment regimen that involves going into a clinic several days a week and sitting through a ...
Dating encounters between modern humans and Neandertals
2012-10-05
To discover why Neandertals are most closely related to people outside Africa, Harvard and Max Planck Institute scientists have estimated the date when Neandertals and modern Europeans last shared ancestors. The research, published in the journal PLOS Genetics, provides a historical context for the interbreeding. It suggests that it occurred when modern humans carrying Upper Paleolithic technologies encountered Neandertals as they expanded out of Africa.
When the Neandertal genome was sequenced in 2010 it revealed that people outside Africa share slightly more genetic ...
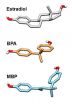
BPA's real threat may be after it has metabolized
2012-10-05
Bisphenol A or BPA is a synthetic chemical widely used in the making of plastic products ranging from bottles and food can linings to toys and water supply lines. When these plastics degrade, BPA is released into the environment and routinely ingested.
New research, however, from the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine suggests it is the metabolic changes that take place once BPA is broken down inside the body that pose the greater health threat.
More than 90 percent of all Americans are believed to carry varying levels of BPA exposure.
In recent ...
Insects shape the genetic landscape through plant defenses
2012-10-05
As restaurant patrons' diverse food preferences give rise to varied menu offerings, so plant-eating insects' preferences play an important role in maintaining and shaping the genetic variation of their host plants in a geographic area, reports an international team of researchers that includes a plant scientist at the University of California, Davis.
The new study, involving aphids and the broccoli-like research plant Arabidopsis thaliana, provides the first measureable evidence that this selective process is driven, in part, by the pressure that multiple natural enemies ...