(Press-News.org) These proteins are required for melanocyte stem cell self-maintenance and, as such, correct pigmentation throughout the mice's life span. Without these two proteins, the mice's fur turns white.
Their research is published in the review 'Cell Report' and paves the way for serious possibilities in terms of stopping the formation of melanomas, tumours that originate from melanocyte cells.
Melanocytes are cells in the organism used for skin, fur and hair pigment. This pigmentation function provides protection from the sun and lends organisms their colour. Malfunctions in these cells may lead to skin cancer known as melanoma. Melanomas are highly aggressive cancers that become very difficult to treat as they develop and metastases occur.
A few years ago, researchers discovered that, in humans, the B-Raf gene (coding gene for protein of the same name) is mutated in more than 50% of melanoma. Spectacular progress has been made in recent years in the treatment of this cancer, thanks to the development of pharmacological inhibitors that target an enzyme: the B-Raf kinase. However, despite this treatment, cancer returns in several patients, indicating that not all cancerous cells have been eliminated. This led researchers to believe that B-Raf is not the only element driving the cancer process.
In this new research, scientists have tried to understand how melanocytes function normally, to then understand their specific role in cancer. To this end B-Raf protein expression, then, in turn, C-Raf protein expression, were removed from mice with black fur (ideal to clearly see any changes in pigmentation).
No changes in pigmentation were observed for mice that only had their B-Raf or C-Raf expression removed by researchers from the line of cells producing melanocytes.
Mice that had both coding genes for B-Raf and C-Raf removed simultaneously had a normal colour at birth. However, they progressively lost their pigmentation as they grew. They turned grey from black, before becoming increasingly white.
For Alain Eychène, the research team leader, "these observations represent a fault in melanocyte renewal. Since the colour black is present at birth, the pigment cells clearly exist. However, the progressive whitening of the fur, once B-Raf and C-Raf have been removed from the cell line, proves that both these proteins are required for melanocyte renewal".
As is the case for all cells, melanocytes originate from stem cells; the latter are responsible for renewal during moulting. This research shows that it is specifically this population of stem cells alone that disappears progressively in mutant mice.
For Alain Eychène, "This is the first in vivo demonstration of the role of RAF proteins in the self-renewal of stem cells".
The fact that B-Raf and C-Raf are both involved in controlling and renewing pigment stem cells represents another step towards understanding and treating melanoma. By blocking these proteins (using inhibitors) in patients undergoing treatment, it is possible that in time researchers will succeed in eliminating all cancerous stem cells, i.e. the likely cause behind cases of cancer reoccurrence.
###
Sources
B-Raf and C-Raf Are Requiredfor Melanocyte Stem Cell Self-Maintenance
Agathe Valluet,1,2,3,4,6 Sabine Druillennec,1,2,3,4,6 Céline Barbotin,1,2,3,4 Coralie Dorard,1,2,3,4 Anne H. Monsoro-Burq,1,2,3,4Magalie Larcher,1,2,3,4 Celio Pouponnot,1,2,3,4 Manuela Baccarini,5 Lionel Larue,1,2,3,4 and Alain Eychène1,2,3,4,*
1Institut Curie
2INSERM U1021
3CNRS UMR 3347
Centre Universitaire, Orsay F-91405, France
4Universite´ Paris Sud-11, F-91405 Orsay, France
5Center for Molecular Biology, University of Vienna, Max F. Perutz Laboratories, A-1030 Vienna, Austria
6These authors contributed equally to this work
Cell Report http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2012.08.020
A white mouse
2012-10-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mosquito genetics may offer clues to malaria control, Virginia Tech researchers say
2012-10-05
An African mosquito species with a deadly capacity to transmit malaria has a perplexing evolutionary history, according to discovery by researchers at the Fralin Life Science Institute at Virginia Tech.
Closely related African mosquito species originated the ability to transmit human malaria multiple times during their recent evolution, according to a study published this week in PLoS Pathogens by Igor Sharakhov, an associate professor of entomology in the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, and Maryam Kamali of Tehran, Iran, a Ph.D. student in the department of ...
Building 3-D structures from a 2-D template
2012-10-05
This press release is available in German.
Deep below the silicon surface, the SPRIE method produces regular structures in the micrometer range that refract light. (Photo: KIT/CFN)
In modern telecommunications, light carries digital information over kilometers within seconds. Adapted optical materials control the light signals. In the AFM journal, researchers from Berlin, Louvain, and from Karlsruhe Institute of Technology present a method to produce photonic crystals. Their optical properties are adjusted by structures of micrometer size. The method is rapid, cheap, ...
Low incidence of needlestick injuries among staff at national pharmacy chain
2012-10-05
CHICAGO (October 5, 2012) – Vaccinations for flu, tetanus and other common vaccines are increasingly taking place in non-medical settings such as supermarkets and drug stores. This added responsibility for pharmacists increases the risk of needlestick injuries (NSIs), puncture wounds often suffered while preparing or after use of a needle. NSIs can transmit bloodborne pathogens, including hepatitis C and HIV, from an infected patient to the person administering the vaccine.
A new report published in the November issue of Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, the ...
Genotyping helps identify source of clinic infection outbreak
2012-10-05
CHICAGO (October 5, 2012) – Researchers from East Carolina University used a new technique of genotyping to identify the source of a hematology clinic outbreak of Mycobacterium mucogenicum, a gram-positive, acid-fast bacteria found in tap water. This is the first outbreak of M. mucogenicum in an ambulatory care setting; five other outbreaks have been reported in hospital settings since 1995. The study was published in the November issue of Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, the journal of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America.
Using repetitive ...
MIT Research: What number is halfway between 1 and 9? Is it 5 -- or 3?
2012-10-05
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. — Ask adults from the industrialized world what number is halfway between 1 and 9, and most will say 5. But pose the same question to small children, or people living in some traditional societies, and they're likely to answer 3.
Cognitive scientists theorize that that's because it's actually more natural for humans to think logarithmically than linearly: 30 is 1, and 32 is 9, so logarithmically, the number halfway between them is 31, or 3. Neural circuits seem to bear out that theory. For instance, psychological experiments suggest that multiplying the ...
How will smart cars affect the future of driving?
2012-10-05
California, Nevada, and Florida have already made driverless cars street-legal, and continuing advances in the technology have led many to predict that the commercialization of automated vehicles is a real possibility in the not-so-distant future. As driverless vehicles become more commonplace, it is important to understand how humans interact with this new technology. The Human Factors special issue on automation, featuring the latest articles on designing automated vehicles with the driver in mind, is now available online. The October 2012 issue may be found at http://hfs.sagepub.com/content/current. ...
'Disgusted' rats teaching scientists about nausea, work may lead to new cancer treatments
2012-10-05
Nausea is a common and distressing side effect of many drugs and treatments. Unlike vomiting, nausea is not well understood, but new research by University of Guelph scientists may soon change that.
Guelph PhD student Katharine Tuerke, neuroscience researcher Cheryl Limebeer and Prof. Linda Parker in the Department of Psychology believe they've found the mechanism in the brain that is responsible for the sensation of nausea – with the help of some "disgusted" rats.
Their study was published this week in Journal of Neuroscience.
"Although everyone has experienced ...
Tree nut research may unexpectedly lead to medical advances
2012-10-05
This press release is available in Spanish.
Prescription drugs that today help patients fight severe fungal infections might tomorrow be even more effective, thanks to unexpected findings from agriculture-based, food-safety-focused studies by U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientists and their colleagues.
Petri-dish experiments conducted by now-retired USDA Agricultural Research Service (ARS) research leader Bruce C. Campbell, ARS molecular biologist Jong H. Kim, and their co-investigators suggest that pairing conventional antifungal medicines with natural, edible ...
NASA notes Nadine now no more
2012-10-05
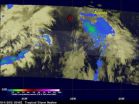
Twenty-three days after Nadine was born, the tropical cyclone's life came to an end in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean. NASA's TRMM satellite caught a look at the fading Nadine one final time on Oct. 3 before it dissipated.
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite passed above long-lasting Nadine for the last time before the tropical storm's dissipation on October 4, 2012 at 0249 UTC (10:49 p.m. EDT October 3, 2012).
TRMM measures rainfall from space and there was very little remaining in Nadine when it passed overhead. Rainfall data from TRMM's Microwave ...
NASA satellites indicate wind shear taking toll on Oscar
2012-10-05
Satellite data is showing that northwesterly wind shear is taking a toll on Tropical Storm Oscar in the central Atlantic and it is expected to dissipate the storm late on Oct. 5, 2012.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Oscar on Oct. 4 at 1335 UTC (9:35 a.m. EDT) and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument captured a true-color image of the storm. The imagery showed bulk of Oscar's clouds and showers were southeast of the center of circulation as a result of wind shear.
On Oct. 5 at 5 a.m. EDT, Oscar's maximum sustained winds ...